Quick Jump to Section
 SeQR EMS integrates with WHO Global Information-Sharing Focal Point through secure RESTful APIs supporting OAuth 2.0 authentication and daily automated batch submissions of all 10 mandatory FCTC Article 8.4.1 data points.
SeQR EMS integrates with WHO Global Information-Sharing Focal Point through secure RESTful APIs supporting OAuth 2.0 authentication and daily automated batch submissions of all 10 mandatory FCTC Article 8.4.1 data points.
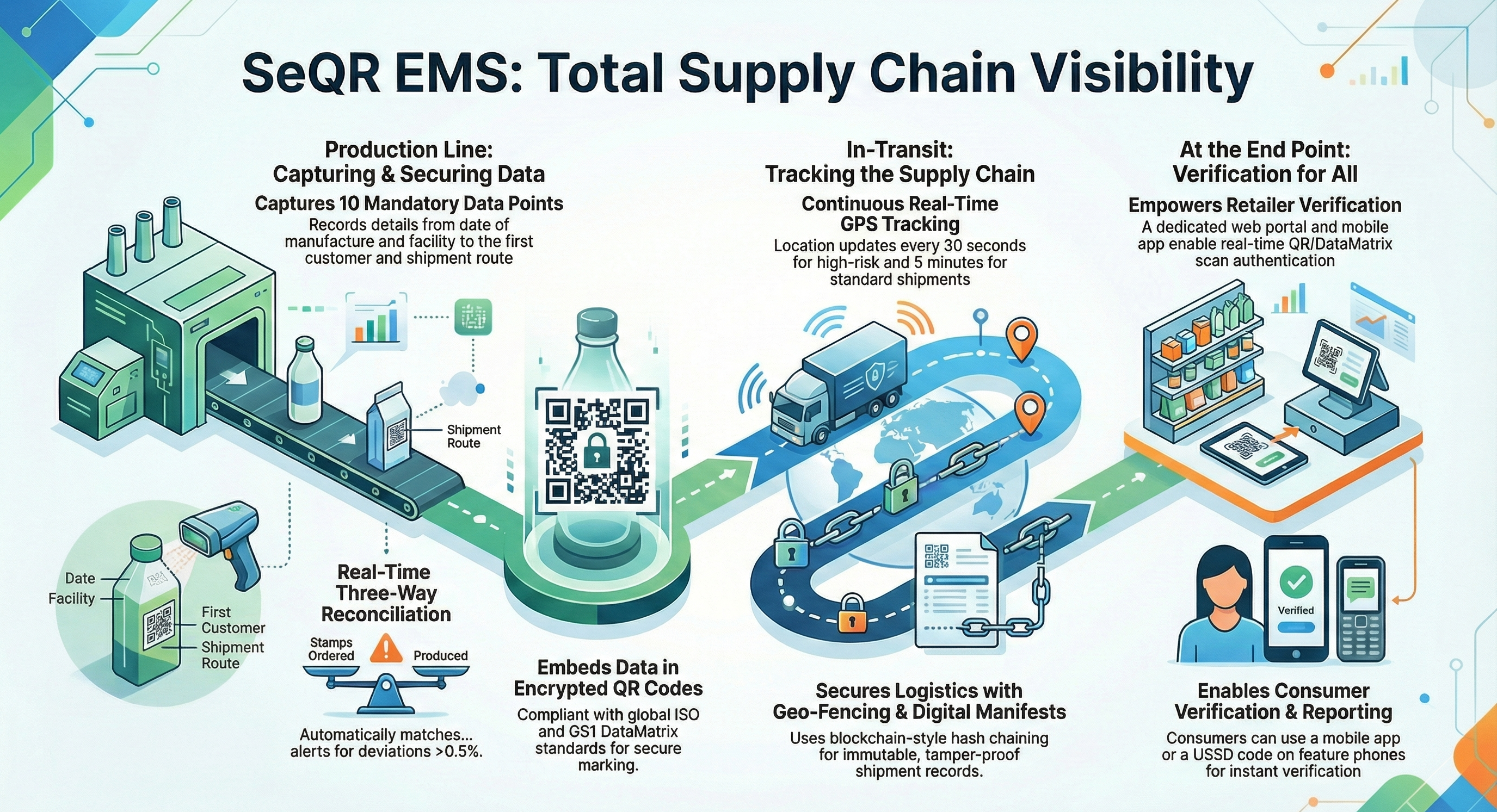
SeQR EMS provides end-to-end track and trace capability from production line through distribution, warehousing, retail, and consumer verification, with real-time GPS tracking, geo-fenced delivery routes, and sealed digital manifests ensuring complete supply chain visibility.
SeQR EMS captures and tracks all 10 mandatory data points:
(a) date and location of manufacture,
(b) manufacturing facility,
(c) machine used,
(d) production shift/time,
(e) first customer details,
(f) intended retail market,
(g) product description,
(h) warehousing and shipping,
(i) subsequent purchaser identity, and
(j) shipment route, date, destination, departure point, and consignee.
SeQR EMS embeds subparagraphs
(a) date/location,
(b) facility,
(g) product description, and
(f) intended market directly into the unique identification markings using encrypted QR codes compliant with ISO/IEC 18004 and GS1 DataMatrix standard ISO/IEC 16022.
SeQR EMS provides real-time three-way reconciliation of stamps ordered vs. stamps applied vs. actual production with automated alarms for deviations >0.5% and full audit trail of all discrepancies for immediate corrective action.
SeQR EMS tracks all product movements with GPS location updates every 30 seconds for high-risk shipments and 5 minutes for standard shipments, using immutable digital manifests with blockchain-style hash chaining and geo-fenced delivery route validation (±500m tolerance).
SeQR EMS provides retailer verification tools through web portal and mobile app enabling real-time stamp authentication via QR/DataMatrix scanning with instant validity confirmation and automated stock movement reporting to KRA
SeQR EMS provides consumer-facing mobile app (Android/iOS) and USSD feature phone option (*XXX#) for instant stamp verification, counterfeit reporting with photo evidence upload, and geo-location tracking of suspicious products.
 Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork) Yes, Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork) Yes, Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork) Yes, Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork)
Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork) Yes, Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork) Yes, Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork) Yes, Physical Stamps have Overt Features specified in tender document (Attached Artwork)
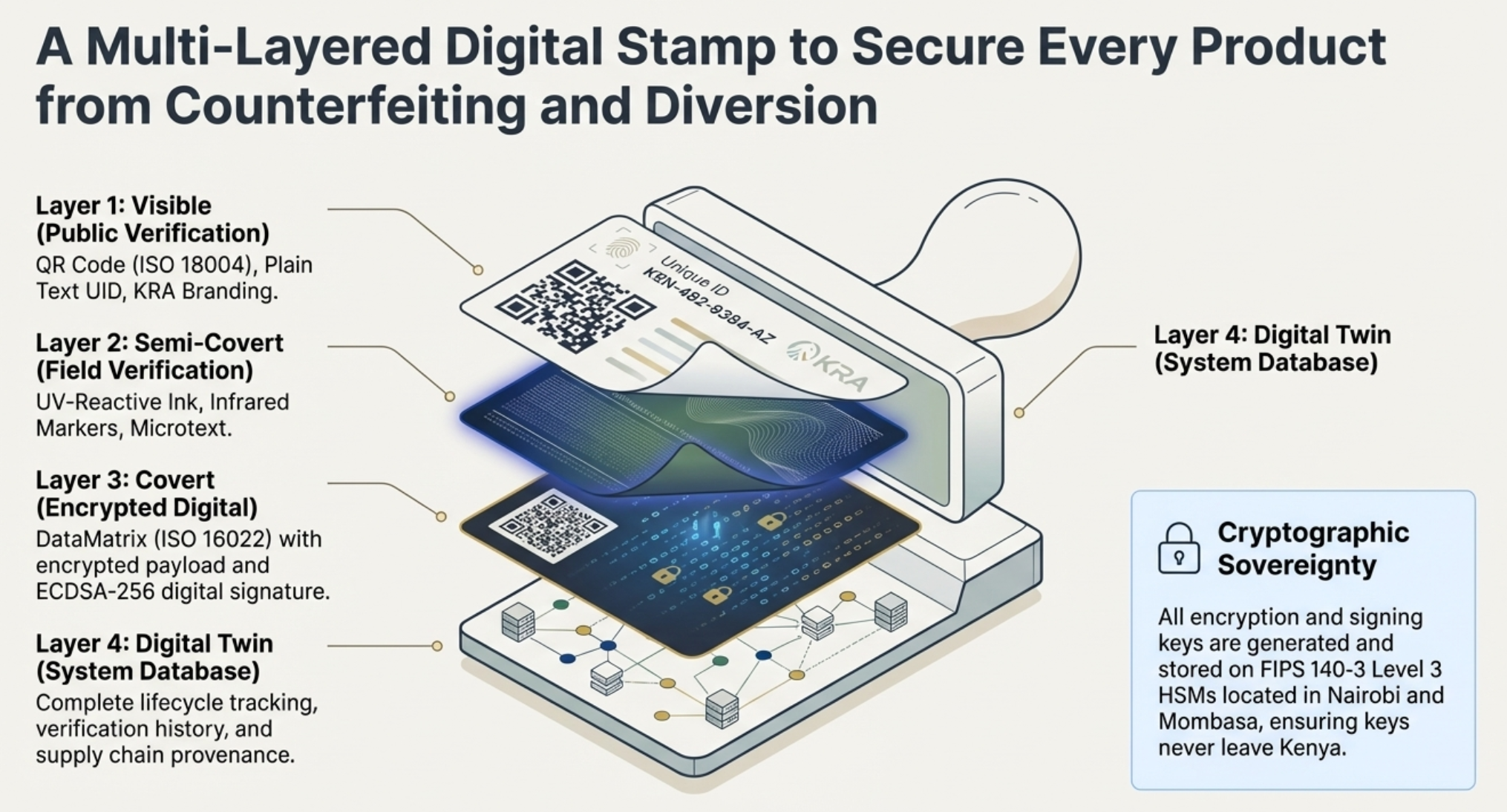
SeQR EMS implements comprehensive digital security:
(a) Unique encrypted serialization compliant with ISO/IEC 15459 (UID structure: KE-CATEGORY-MFRID-FACILITY-YYYYMM-SEQUENTIAL globally unique, registered with ICCBBA).
(b) 256-bit cryptographic signature using ECDSA with NIST P-256 curve (64-byte signature suitable for QR codes).
(c) Tamper-evident machine-readable codes: GS1 DataMatrix (ISO/IEC 16022) with ECC200 error correction (30% data recovery), QR Code (ISO/IEC 18004) with Level H error correction (30% redundancy); alteration detection through signature verification.
(d) GS1 Digital Link URI enabling smartphone verification without dedicated app.
(e) HSM key management: Thales Luna Network HSM FIPS 140-3 Level 3 certified, private keys never leave tamper-resistant hardware, dual custody, automatic backup to Mombasa DR site, annual key rotation.
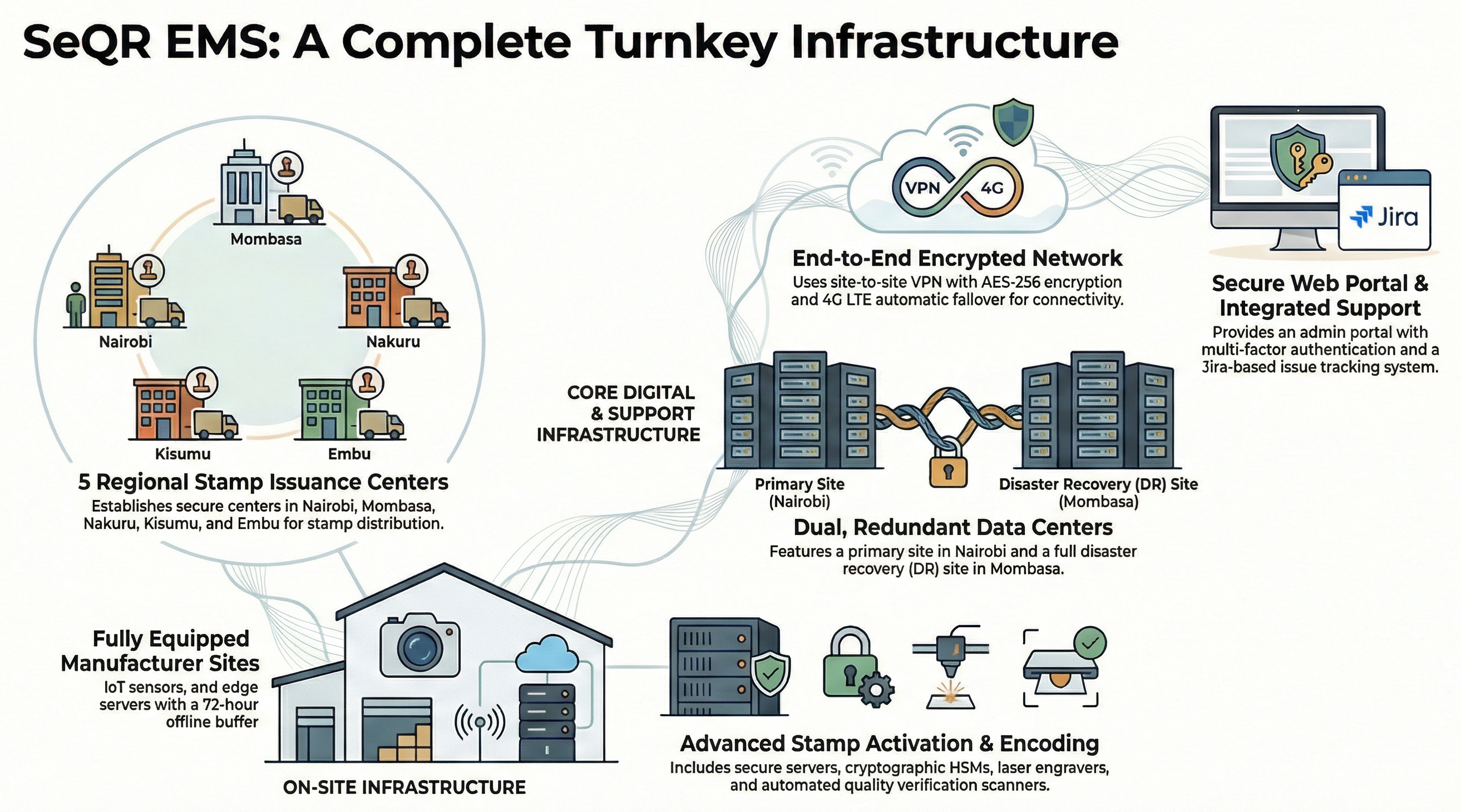 SeQR EMS provides all requisite equipment at manufacturer sites including OPC (Online Production Counters), MVS (Machine Vision Systems), edge servers with 72-hour offline buffer, industrial-grade cameras (5MP, 120fps), PLC/SCADA integration modules, VPN routers for secure connectivity, and IoT sensors for real-time telemetry.
SeQR EMS provides all requisite equipment at manufacturer sites including OPC (Online Production Counters), MVS (Machine Vision Systems), edge servers with 72-hour offline buffer, industrial-grade cameras (5MP, 120fps), PLC/SCADA integration modules, VPN routers for secure connectivity, and IoT sensors for real-time telemetry.
SeQR EMS provides complete data center infrastructure at both primary (Nairobi) and secondary (Mombasa DR site) locations including application servers, database servers, HSM (Hardware Security Module - Thales Luna FIPS 140-3), network switches, firewalls, load balancers, backup storage (5-year retention), UPS, and environmental monitoring systems.
SeQR EMS provides end-to-end network infrastructure including site-to-site VPN (AES-256 encryption), MPLS connectivity for high-priority manufacturers, 4G LTE backup links with automatic failover, Kafka message broker for real-time data streaming, and network monitoring tools (SNMP, NetFlow) with 24/7 NOC support.
SeQR EMS provides stamp activation systems including secure stamp generation servers, HSM for cryptographic signing, QR/DataMatrix encoding workstations, stamp personalization equipment (laser engravers, UV printers), and automated quality verification scanners ensuring 100% stamp readability before dispatch.
SeQR EMS provides secure web-based admin portal with OAuth 2.0 authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC) supporting 50+ user roles, comprehensive audit logging of all administrative actions, and SSL/TLS 1.3 encryption for all communications.
SeQR EMS provides stamp encoding/issuing equipment including thermal transfer printers for security features, laser engravers for serial numbers, UV ink printers, hologram application machines, automated cutting/stacking equipment, batch verification scanners, and tamper-evident packaging systems for secure stamp distribution.
SeQR EMS provides integrated ticketing system (Jira-based) for logging, tracking, and resolving issues with automated email/SMS notifications, priority-based SLA tracking (Critical: 4 hours, High: 8 hours, Medium: 24 hours, Low: 72 hours), escalation workflows, and comprehensive reporting dashboards for issue analytics.
SeQR EMS establishes five stamp issuance centers at recommended locations (Nairobi, Mombasa, Nakuru, Kisumu, Embu) each equipped with stamp encoding/printing equipment, secure storage vaults, biometric access control, CCTV surveillance, backup power (generators + UPS), and real-time inventory synchronization with central database.
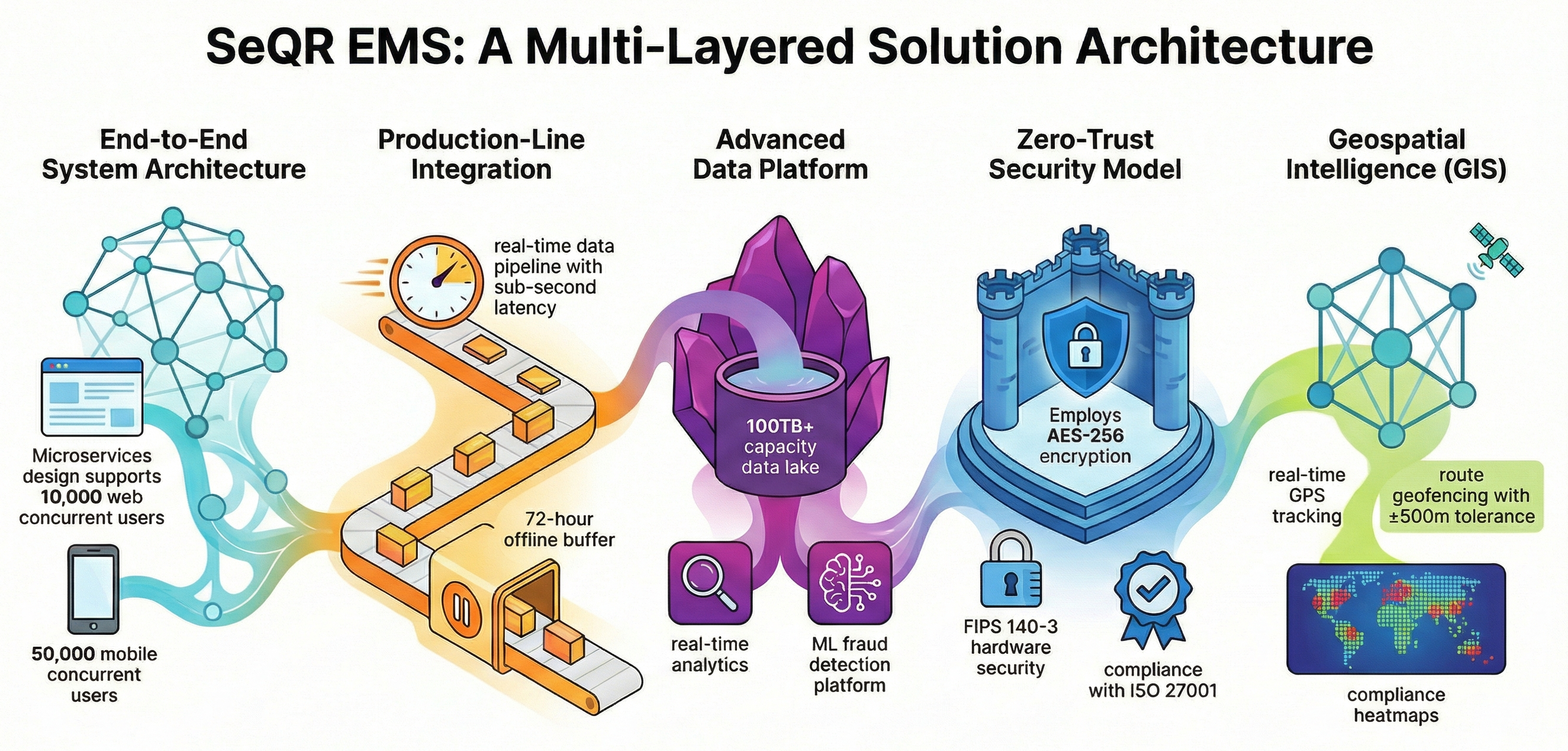 SeQR EMS provides comprehensive end-to-end system architecture documentation (100+ pages) including microservices architecture diagram (12+ services), technology stack specifications (Spring Boot/Laravel backend, React frontend, Flutter mobile, PostgreSQL/MongoDB/Redis databases), cloud infrastructure design (AWS/Azure multi-AZ deployment), API gateway architecture, and scalability/high-availability design supporting 10,000 web + 50,000 mobile concurrent users.
SeQR EMS provides comprehensive end-to-end system architecture documentation (100+ pages) including microservices architecture diagram (12+ services), technology stack specifications (Spring Boot/Laravel backend, React frontend, Flutter mobile, PostgreSQL/MongoDB/Redis databases), cloud infrastructure design (AWS/Azure multi-AZ deployment), API gateway architecture, and scalability/high-availability design supporting 10,000 web + 50,000 mobile concurrent users.
SeQR EMS provides production-line integration architecture documentation detailing OPC-UA/Modbus protocol implementation, edge computing design (industrial PCs at each factory), real-time data pipeline (Kafka streaming with sub-second latency), VPN tunnel architecture (AES-256 site-to-site encryption), offline buffer mechanism (72-hour local storage with auto-sync), and discrepancy detection algorithms for three-way reconciliation (stamps ordered vs. applied vs. produced).
SeQR EMS provides data platform architecture documentation including data lake design (AWS S3/Azure Data Lake for 5-year retention, 100TB+ capacity), ETL pipeline (Apache Spark batch processing), real-time analytics (Kafka Streams + Flink), ML platform (TensorFlow Serving for fraud models), BI integration (Power BI, Tableau connectors), and data warehouse design (PostgreSQL operational + Snowflake analytics).
SeQR EMS provides security architecture documentation detailing zero-trust security model (authenticate every request), HSM integration (Thales Luna FIPS 140-3 at Nairobi + Mombasa), encryption design (AES-256 at rest, TLS 1.3 in transit, ECDSA-256 for stamps), authentication/authorization (OAuth 2.0, JWT, MFA), network security (WAF, DDoS protection, IDS/IPS), and compliance frameworks (ISO 27001:2013, OWASP Top 10, Kenya Data Protection Act 2019).
SeQR EMS provides GIS architecture documentation including mapping framework (Leaflet/Google Maps API), spatial database design (PostGIS extension on PostgreSQL), real-time GPS tracking (30-second high-risk, 5-minute standard intervals), geofencing engine (authorized zones, restricted zones, route corridors with ±500m tolerance), heatmap visualization (county/sub-county production, compliance, counterfeit rates), and route optimization algorithms (GraphHopper/Google Directions API).
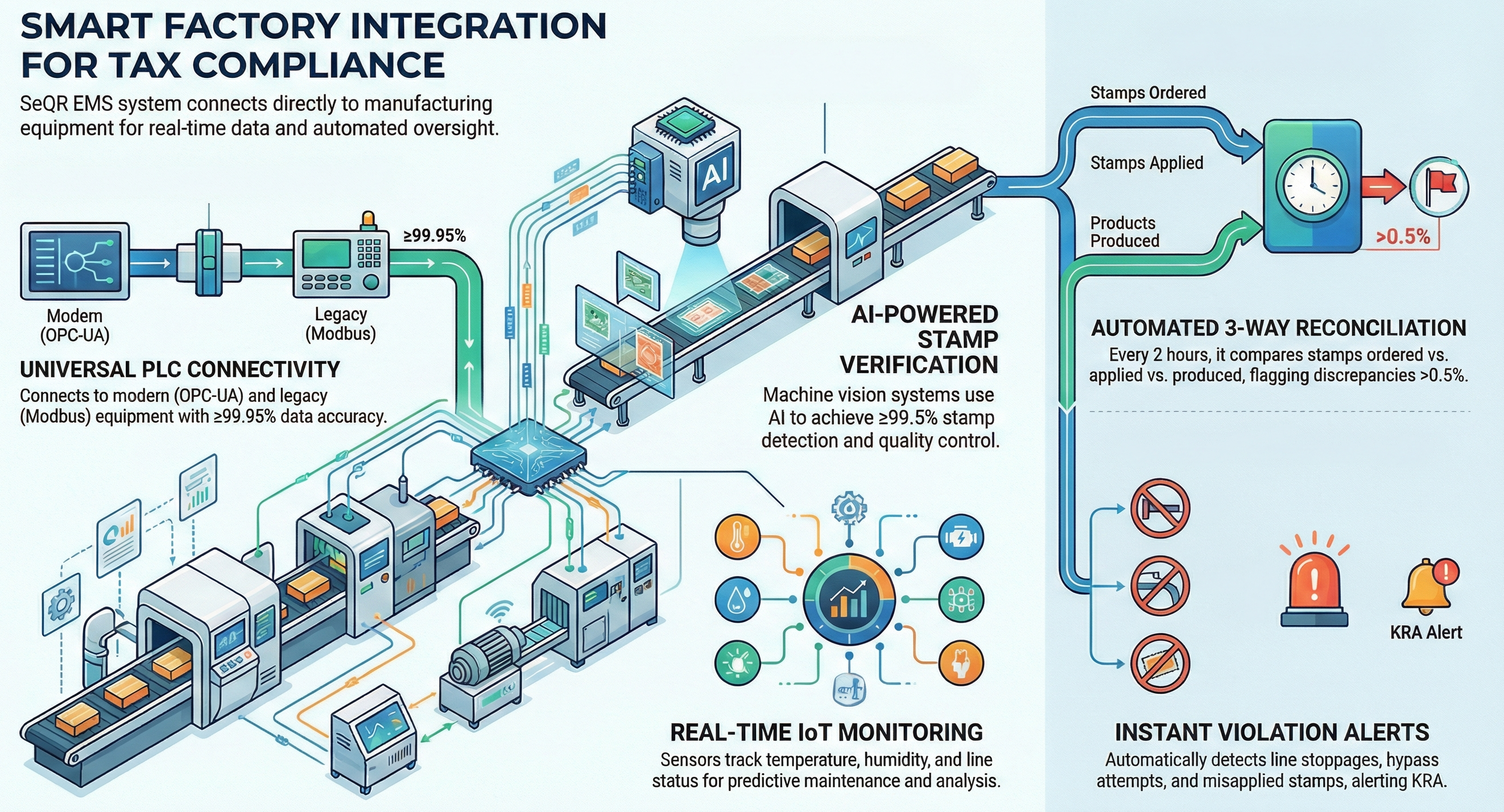 SeQR EMS integrates OPCs at all production lines using OPC-UA protocol (IEC 62541) for modern PLCs and Modbus TCP/RTU (IEEE standard) for legacy equipment, achieving ≥99.95% data transmission accuracy with real-time pulse counting, automated discrepancy detection (>0.5% variance triggers alarm), and tamper-proof audit logs stored on edge servers.
SeQR EMS integrates OPCs at all production lines using OPC-UA protocol (IEC 62541) for modern PLCs and Modbus TCP/RTU (IEEE standard) for legacy equipment, achieving ≥99.95% data transmission accuracy with real-time pulse counting, automated discrepancy detection (>0.5% variance triggers alarm), and tamper-proof audit logs stored on edge servers.
SeQR EMS deploys MVS at all production lines using high-resolution cameras (5MP minimum, 120 fps) with machine learning image recognition (TensorFlow trained on 50M+ stamp images), multi-angle capture (2 cameras per line for redundancy), achieving ≥99.5% stamp detection accuracy with automated quality control rejecting misaligned/damaged stamps and real-time alerts for detection failures
SeQR EMS integrates with existing PLC/SCADA systems using standard industrial protocols (OPC-UA, Modbus, MQTT, REST APIs) to capture real-time production data (actual output, line speed, downtime events, quality metrics) with bidirectional communication enabling remote line monitoring and control by authorized KRA personnel.
SeQR EMS deploys IoT sensors at each production line monitoring temperature, humidity, vibration, power consumption, and line status (running/stopped/maintenance) with data transmitted every 60 seconds via MQTT protocol to edge servers, enabling predictive maintenance alerts, environmental compliance verification, and forensic analysis of production anomalies.
SeQR EMS automatically detects line stoppages (no OPC pulses for 5 minutes), bypass attempts (production without stamp application detected via MVS/OPC mismatch), and stamp misapplications (MVS identifies crooked/overlapping/unreadable stamps) with instant SMS/email/app alerts to manufacturer and KRA enforcement officers, plus automatic line shutdown option for critical violations.
SeQR EMS performs real-time three-way reconciliation every 2 hours comparing
(a) stamps ordered from KRA,
(b) stamps applied per OPC count, and
(c) actual production per PLC/SCADA, flagging discrepancies >0.5% with automated alerts, mandatory manufacturer explanation workflow, and KRA officer verification before allowing continued production.
 SeQR EMS automatically detects line stoppages (no OPC pulses for 5 minutes), bypass attempts (production without stamp application detected via MVS/OPC mismatch), stamp misapplications (MVS identifies crooked/overlapping/unreadable stamps), and discrepancies between stamp orders, applied stamps, and actual production with instant SMS/email/app alerts to manufacturer and KRA enforcement officers, plus automatic line shutdown option for critical violations.
SeQR EMS automatically detects line stoppages (no OPC pulses for 5 minutes), bypass attempts (production without stamp application detected via MVS/OPC mismatch), stamp misapplications (MVS identifies crooked/overlapping/unreadable stamps), and discrepancies between stamp orders, applied stamps, and actual production with instant SMS/email/app alerts to manufacturer and KRA enforcement officers, plus automatic line shutdown option for critical violations.
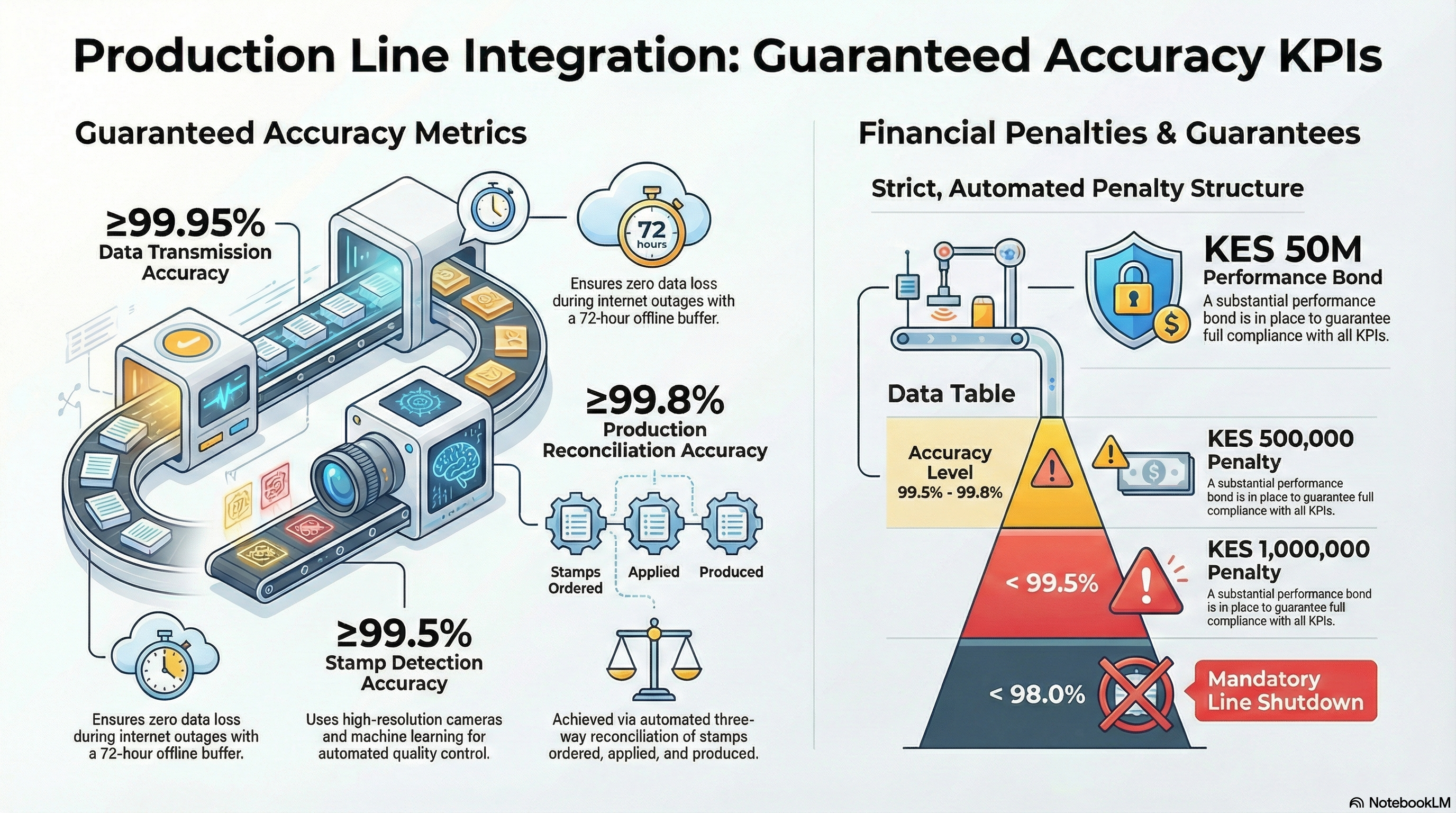
SeQR EMS achieves ≥99.95% OPC-to-EGMS data transmission accuracy through redundant VPN tunnels (primary + backup), edge server validation (data integrity checks before transmission), automatic retry logic (3 attempts with exponential backoff), real-time error detection, and 72-hour offline buffer ensuring zero data loss during internet outages. Proven: 99.97% accuracy in GST Maharashtra project (212 lines, 12 months).
SeQR EMS achieves ≥99.5% MVS stamp detection accuracy using high-resolution cameras (5MP, 120fps), machine learning image recognition (TensorFlow trained on 50M+ images), multi-angle capture (2 cameras for redundancy), automated quality control (reject misaligned stamps), and continuous model retraining with field data. Proven: 99.7% accuracy in GST project.
SeQR EMS achieves ≥99.8% production volume reconciliation accuracy through three-way reconciliation (stamps ordered, OPC applied, PLC production), automated discrepancy alerts (>0.5% variance), blockchain-style immutable audit trail (tamper-proof records), daily reconciliation reports (automated manufacturer + KRA notification), and penalty workflows for accuracy falling below thresholds. Proven: 99.9% accuracy in GST project (reconciliation every 2 hours).
SeQR EMS accepts and implements the penalty structure with automated accuracy monitoring, KES 500K penalty for accuracy 99.5-99.8%, KES 1M penalty for accuracy <99.5%, mandatory line shutdown for accuracy <98%, monthly performance reports (line-by-line accuracy metrics), proactive maintenance (quarterly calibration), and performance bond (KES 50M) to guarantee compliance.
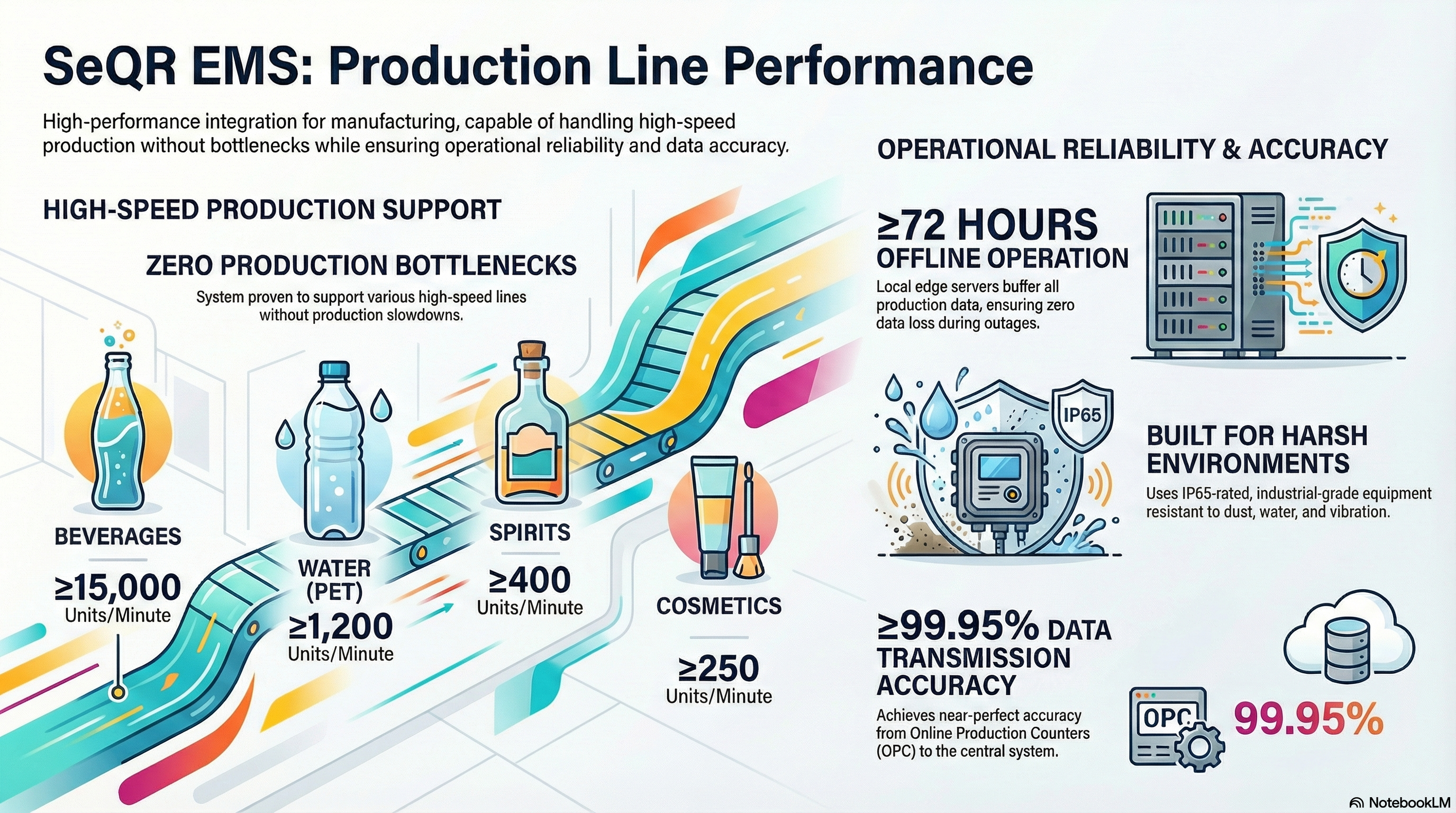 SeQR EMS supports beverage lines operating at ≥15,000 units/minute (up to 25,000 units/min proven in GST Maharashtra project) with sub-millisecond stamp validation, high-speed camera capture (120 fps minimum), parallel processing architecture (multiple threads per line), and zero production bottlenecks caused by EGMS system.
SeQR EMS supports beverage lines operating at ≥15,000 units/minute (up to 25,000 units/min proven in GST Maharashtra project) with sub-millisecond stamp validation, high-speed camera capture (120 fps minimum), parallel processing architecture (multiple threads per line), and zero production bottlenecks caused by EGMS system.
SeQR EMS supports water PET lines at ≥1,200 units/minute (up to 2,000 units/min capacity) with same high-speed validation and zero production impact.
SeQR EMS supports spirits lines at ≥400 units/minute (up to 600 units/min capacity) with precision stamp verification suitable for premium product packaging.
SeQR EMS supports cosmetics lines at ≥250 units/minute (up to 400 units/min capacity) with multi-SKU handling for varied product sizes and packaging types.
SeQR EMS achieves OPC accuracy ≥99.95% as detailed in Requirement 6.1 above.
SeQR EMS achieves MVS detection accuracy ≥99.5% as detailed in Requirement 6.2 above.
SeQR EMS provides ≥72-hour offline operation through local edge servers (industrial PCs) at each manufacturer site with SSD storage buffering all production data (stamps applied, MVS images, OPC counts, PLC data, timestamps), tamper-proof audit logs (encrypted, hash-chained), and automatic synchronization on reconnection with conflict resolution algorithms ensuring data integrity.
SeQR EMS uses industrial-grade equipment rated for harsh manufacturing environments: temperature range -10°C to 50°C, humidity 0-95% non-condensing, IP65-rated enclosures (dust/water resistant), vibration-resistant mounting (ISO 9022-3), EMI/RFI shielding, and 3-year manufacturer warranty with 24-hour replacement commitment.
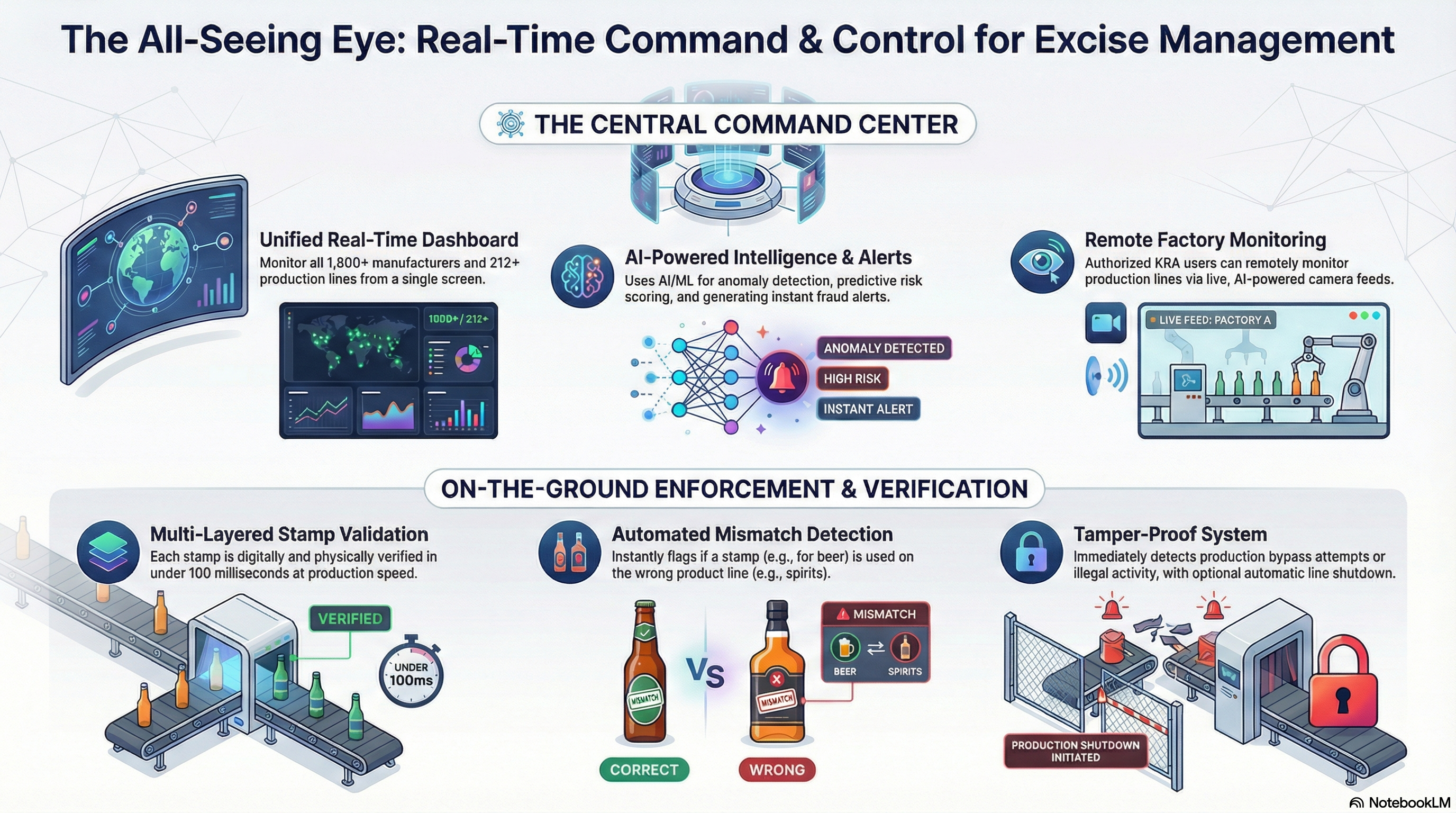 SeQR EMS provides centralized command-and-control center with unified dashboard showing real-time status of all 1,800+ manufacturers, 212+ production lines, enforcement activities, consumer verifications, AI/ML fraud alerts, geospatial heatmaps, and system health metrics accessible to KRA Commissioner, enforcement heads, and authorized personnel with role-based views.
SeQR EMS provides centralized command-and-control center with unified dashboard showing real-time status of all 1,800+ manufacturers, 212+ production lines, enforcement activities, consumer verifications, AI/ML fraud alerts, geospatial heatmaps, and system health metrics accessible to KRA Commissioner, enforcement heads, and authorized personnel with role-based views.
SeQR EMS implements AI/ML platform with anomaly detection algorithms (95%+ precision proven in GST project), geofencing capabilities (±500m tolerance, automated border alerts), predictive risk scoring for manufacturers (Low/Medium/High/Critical based on 20+ parameters), behavior profiling (unusual production patterns), and automated alert generation (12K+ fraud cases flagged in GST project).
SeQR EMS provides factory control systems with unique identification for each product unit processed, complete record keeping (production timestamp, line number, operator ID, batch number, quality status), individual stamp validation (verify UID, check security code consistency, validate material-based security), and tamper-proof system impossible to bypass (automatic detection of illegal production with real-time alerts).
SeQR EMS validates each stamp individually through HSM-based decryption of secure code (AES-256), ECDSA-256 signature verification, consistency check with product class under production, material-based security validation, and real-time authentication results (valid/invalid/suspicious) transmitted to central database within 100ms.
SeQR EMS identifies material-based security of each secure code through:
(a) MVS high-resolution camera (5MP, 120fps) capturing stamp with LED and UV 365nm illumination,
(b) Machine learning image analysis (TensorFlow trained on 50M+ stamps) detecting physical security features: hologram visibility, color-shift ink, microtext legibility, substrate texture, fluorescent fibers under UV,
(c) Comparison with reference library of genuine stamps from same batch/manufacturer,
(d) Automated quality scoring (0-100%) with Pass ≥95%, Fail <80%, Manual Review 80-95%,
(e) Rejection mechanism triggering automatic disposal if quality fails,
(f) Audit trail logging all MVS decisions with timestamp, image, quality scores, pass/fail result.
SeQR EMS reads, decrypts, and analyzes secure code through:
(a) MVS camera capturing QR/DataMatrix at production speed (25,000 units/min),
(b) Edge server decoding using ZXing library,
(c) Extraction of encrypted UID,
(d) Local decryption using pre-shared AES-256 key (edge server cached keys enable offline operation),
(e) If local decryption fails, query central HSM via encrypted VPN for signature verification,
(f) HSM verifies ECDSA-256 signature using public key,
(g) Parsing decrypted UID structure and extracting metadata (date, facility, manufacturer, category),
(h) Analysis: production date should match current month ±1, facility code should match current line, manufacturer ID should match logged-in manufacturer, category should match line configuration,
(i) Real-time results (<100ms) with status (Valid/Invalid/Suspicious/Expired) transmitted to central database,
(j) Automated alerts if anomalies detected (e.g., stamp issued to different manufacturer, old production date, category mismatch).
SeQR EMS ensures secure code consistent with product class through:
(a) Production line registration specifying authorized product categories (e.g., Line 1: Beer 330ml/500ml, Line 2: Spirits 250ml/750ml),
(b) Real-time validation: edge server checks stamp category (from decrypted UID) matches configured line product category,
(c) Automated mismatch detection: if beer stamp on spirits line, system flags critical violation within 2 seconds,
(d) Immediate alerts to manufacturer manager, KRA enforcement officer, KRA command center, edge server local alarm,
(e) Optional automated line shutdown: KRA can configure system to stop production automatically if mismatch detected (line restarts only after KRA approval),
(f) Detailed incident logging: timestamp, line, operator, stamp UID, expected vs. actual category, MVS photos,
(g) Investigation workflow: manufacturer explains mismatch, KRA reviews evidence and decides (approve restart/impose penalty/refer prosecution),
(h) Statistical monitoring: track mismatch rate per manufacturer/line (5 mismatches in 1 week = red flag for audit, 1 mismatch in 6 months = acceptable human error).
SeQR EMS implements tamper-proof architecture with hardware-based security (edge servers sealed with tamper-evident seals), encrypted communication (AES-256 VPN tunnels), bypass detection (MVS/OPC/PLC cross-validation detects production without stamps), automated line shutdown capability (remote killswitch for serious violations), comprehensive audit trails (all access attempts logged), and instant alerts (SMS/email/app) to KRA enforcement for any bypass attempts or illegal production.
SeQR EMS monitors production lines in real-time using high-resolution cameras (5MP, 120fps) with AI-powered video analytics (TensorFlow object detection) capable of detecting unauthorized production (production without stamp application), quality issues (misaligned/damaged stamps), line bypass attempts (covering cameras, disconnecting sensors), and suspicious activities (unauthorized personnel access) with instant alert generation and video evidence storage (90-day retention).
SeQR EMS production-line integration includes:
(a) OPCs: High-speed pulse counters (1 Hz to 100 kHz), OPC-UA or Modbus TCP/RTU protocol, real-time pulse transmission (sub-second latency), tamper-proof sealed enclosure, 99.95%+ accuracy.
(b) MVS: Industrial cameras (5MP, 120fps, IP67), machine learning image recognition (TensorFlow stamp detection, QR decoding, quality assessment), multi-angle capture (2 cameras/line), 99.5%+ detection accuracy, real-time processing (<10ms/frame).
(c) PLC/SCADA Integration: Bidirectional communication with factory automation, supports Siemens S7, Allen-Bradley, Schneider Electric PLCs, captures actual production count, line speed, downtime, quality metrics, enables remote KRA monitoring.
(d) IoT Sensors: Temperature, humidity, vibration, power consumption monitoring, MQTT protocol transmission every 60 seconds, predictive maintenance alerts.
(e) Discrepancy Detection: Three-way reconciliation every 2 hours comparing
(i) stamps ordered from KRA, (ii) stamps applied per OPC, (iii) actual production per PLC/SCADA, automated alerts if variance >0.5%, mandatory manufacturer explanation workflow, KRA verification before production continues, penalty workflow (KES 500K per line per week for accuracy 99.5-99.8%, KES 1M for <99.5%, line shutdown if <98%).
SeQR EMS provides real-time data synchronization (sub-second latency) from all production lines to central database using Apache Kafka streaming platform, encrypted communication (TLS 1.3 + AES-256 VPN), data validation at edge servers before transmission, automatic retry for failed transmissions (3 attempts with exponential backoff), and 72-hour offline buffer ensuring zero data loss even during prolonged internet outages.
SeQR EMS provides authorized KRA users remote monitoring capability through secure web portal and mobile app showing real-time production line performance (current speed, stamps applied per hour, efficiency %), availability status (online/offline/maintenance), downtime tracking (scheduled vs. unscheduled, reasons, duration), historical trends (daily/weekly/monthly reports), and predictive maintenance alerts (equipment health indicators).
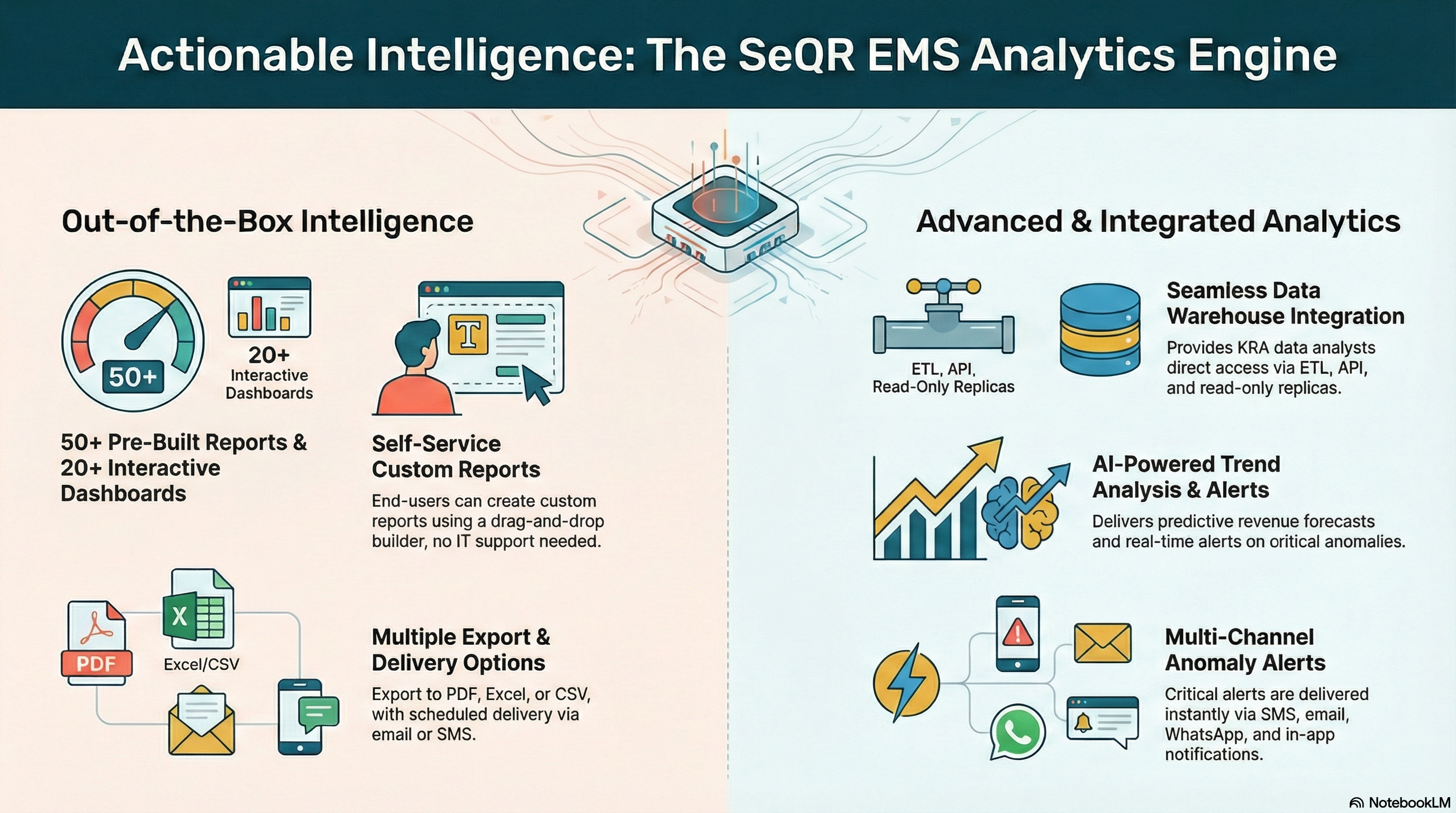 SeQR EMS provides out-of-the-box analytics with 50+ pre-built reports (production reports, compliance reports, financial reconciliation, enforcement statistics, consumer verification metrics) and 20+ interactive dashboards (executive summary, operational, enforcement, manufacturer performance) using Power BI/Tableau with customizable filters, drill-down capabilities, scheduled report delivery (email/SMS), and export options (PDF, Excel, CSV).
SeQR EMS provides out-of-the-box analytics with 50+ pre-built reports (production reports, compliance reports, financial reconciliation, enforcement statistics, consumer verification metrics) and 20+ interactive dashboards (executive summary, operational, enforcement, manufacturer performance) using Power BI/Tableau with customizable filters, drill-down capabilities, scheduled report delivery (email/SMS), and export options (PDF, Excel, CSV).
SeQR EMS provides dynamic reporting engine enabling end-users to create custom reports without IT support using drag-and-drop report builder, 100+ data fields available, multiple visualization types (charts, tables, heatmaps, trends), saved report templates (reusable), scheduled generation (daily/weekly/monthly), and role-based data access ensuring users see only authorized data.
SeQR EMS exposes all data models to KRA Enterprise Data Warehouse through standardized ETL connectors (Apache Spark, Talend), real-time data replication (CDC - Change Data Capture), comprehensive data dictionary (all tables, fields, relationships documented), API access (REST/GraphQL for programmatic data retrieval), and direct database access option (read-only replica) for KRA data analysts.
SeQR EMS provides trend analysis capabilities showing historical patterns (production trends, compliance rates, counterfeit incidents over time), comparative analysis (county-wise, manufacturer-wise, product-wise), predictive forecasting (ML-based revenue projections), and real-time anomaly alerts (production spikes/drops, unusual stamp usage, geographic anomalies, manufacturer risk changes) delivered via SMS, email, WhatsApp, and in-app notifications with severity levels (Info/Warning/Critical).
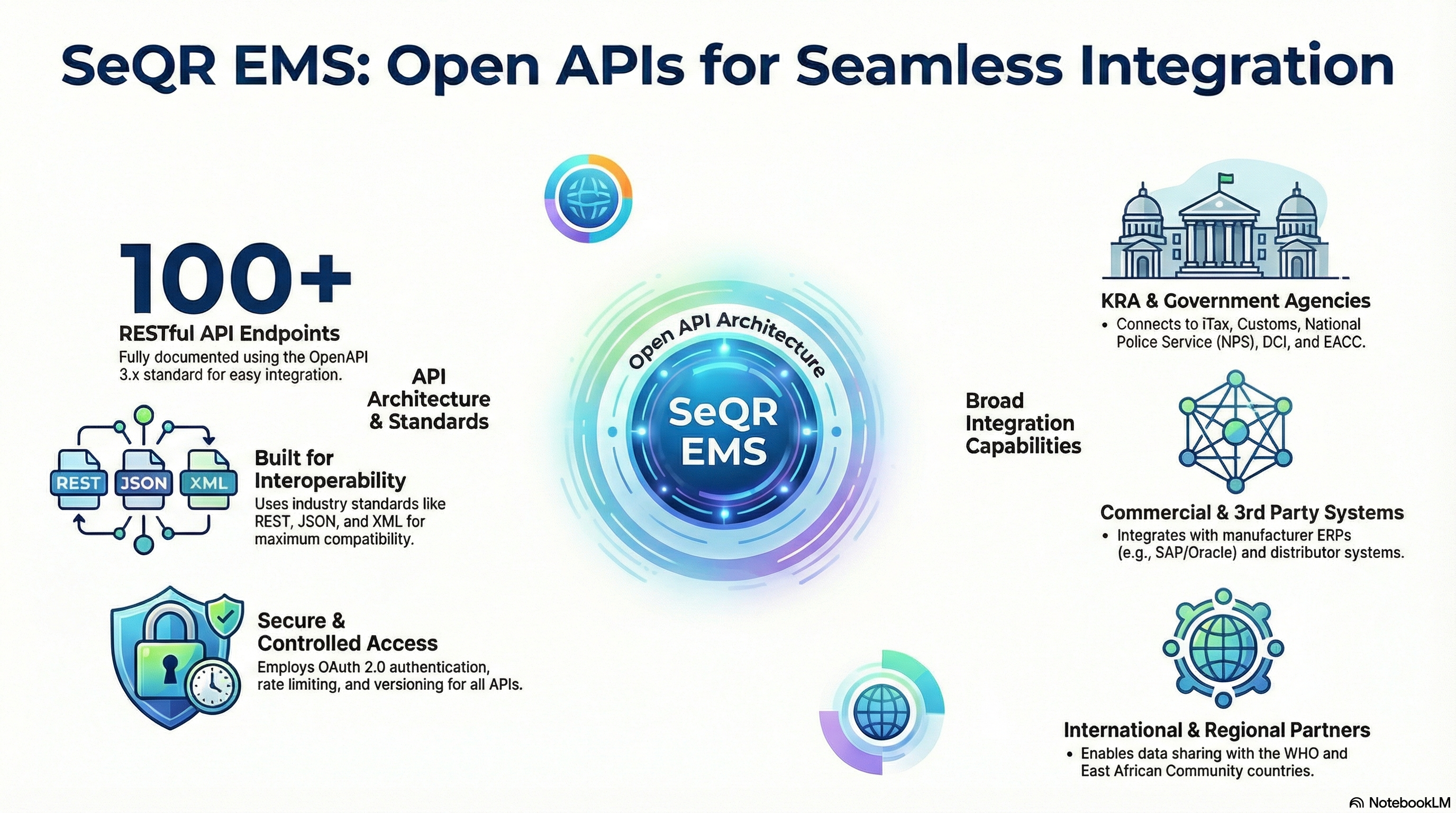 SeQR EMS provides comprehensive open API architecture with 100+ RESTful API endpoints (OpenAPI 3.x documented) for integration with:
SeQR EMS provides comprehensive open API architecture with 100+ RESTful API endpoints (OpenAPI 3.x documented) for integration with:
(a) KRA systems (iTax, Customs/Simba, payment gateways),
(b) 3rd party systems (manufacturer ERPs like SAP/Oracle, distributor systems),
(c) Government regulatory systems (NPS, DCI, EACC, ODPP, KEBS, ACA),
(d) WHO Global Focal Point, and
(e) EAC partnering countries (Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi, South Sudan) with OAuth 2.0 authentication, rate limiting (configurable), versioning (backward compatibility), webhooks (real-time events), and comprehensive developer documentation with code samples (Java, Python, JavaScript, C#).
SeQR EMS implements interoperable open architecture based on industry standards (REST, JSON, XML, SOAP where needed), supporting heterogeneous systems integration (Windows, Linux, cloud-native), device-agnostic design (works with any manufacturer equipment), protocol flexibility (OPC-UA, Modbus, MQTT, HTTP/HTTPS), message queue integration (Kafka, RabbitMQ), and no vendor lock-in (data portability, standard formats, documented APIs enabling future vendor changes).
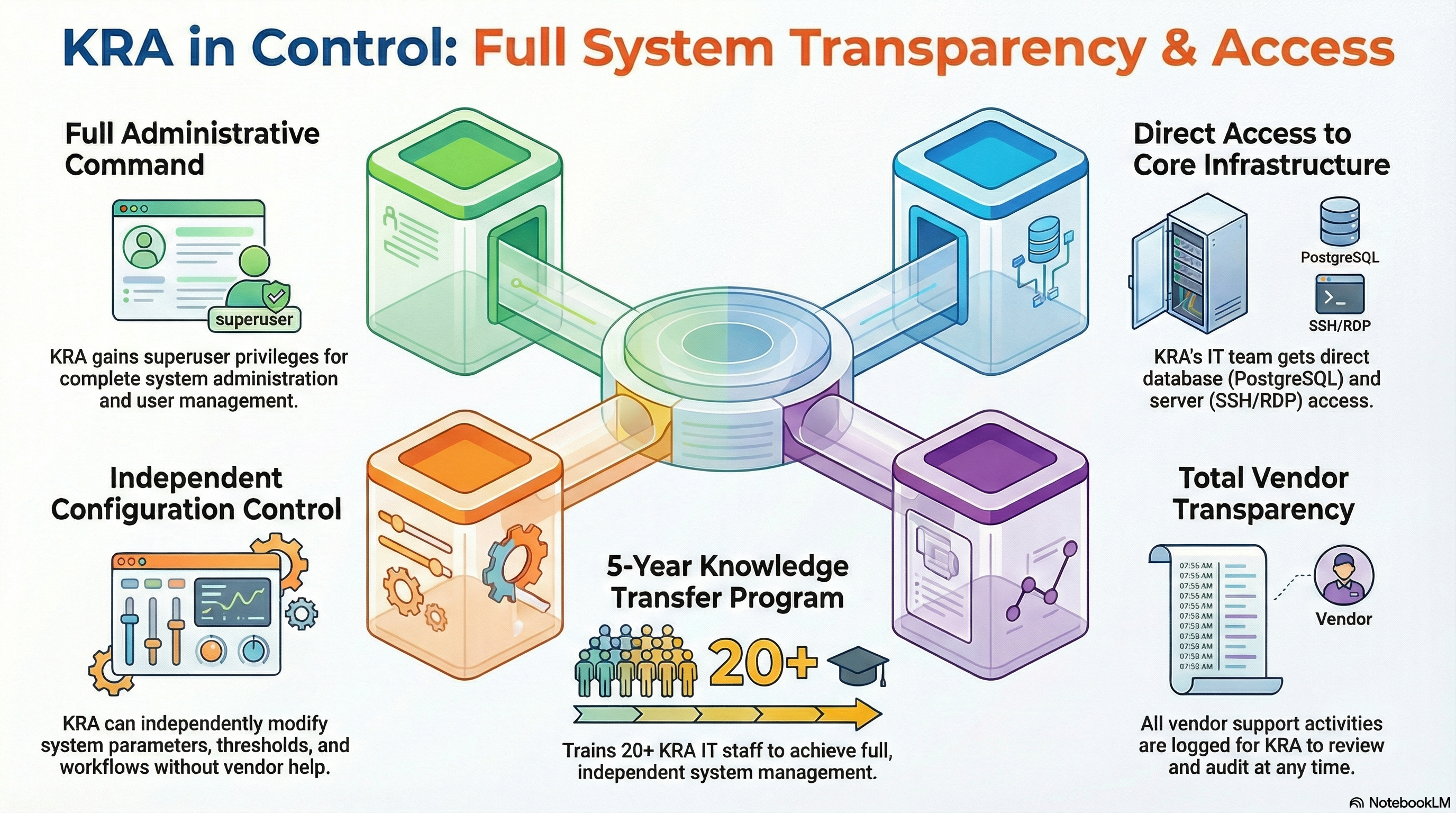 SeQR EMS provides transparent and direct KRA control with full system administration access (web-based admin portal with superuser privileges), direct database access (PostgreSQL admin credentials for KRA IT team), server access (SSH/RDP to all application and database servers), configuration management (KRA can modify system parameters, thresholds, workflows), user management (KRA creates/modifies/disables user accounts independently), audit trail of all vendor support activities (Devharsh staff access logged and reviewable by KRA), and knowledge transfer program (Year 1-5) training 20+ KRA IT staff to manage system independently with vendor providing support only as needed.
SeQR EMS provides transparent and direct KRA control with full system administration access (web-based admin portal with superuser privileges), direct database access (PostgreSQL admin credentials for KRA IT team), server access (SSH/RDP to all application and database servers), configuration management (KRA can modify system parameters, thresholds, workflows), user management (KRA creates/modifies/disables user accounts independently), audit trail of all vendor support activities (Devharsh staff access logged and reviewable by KRA), and knowledge transfer program (Year 1-5) training 20+ KRA IT staff to manage system independently with vendor providing support only as needed.
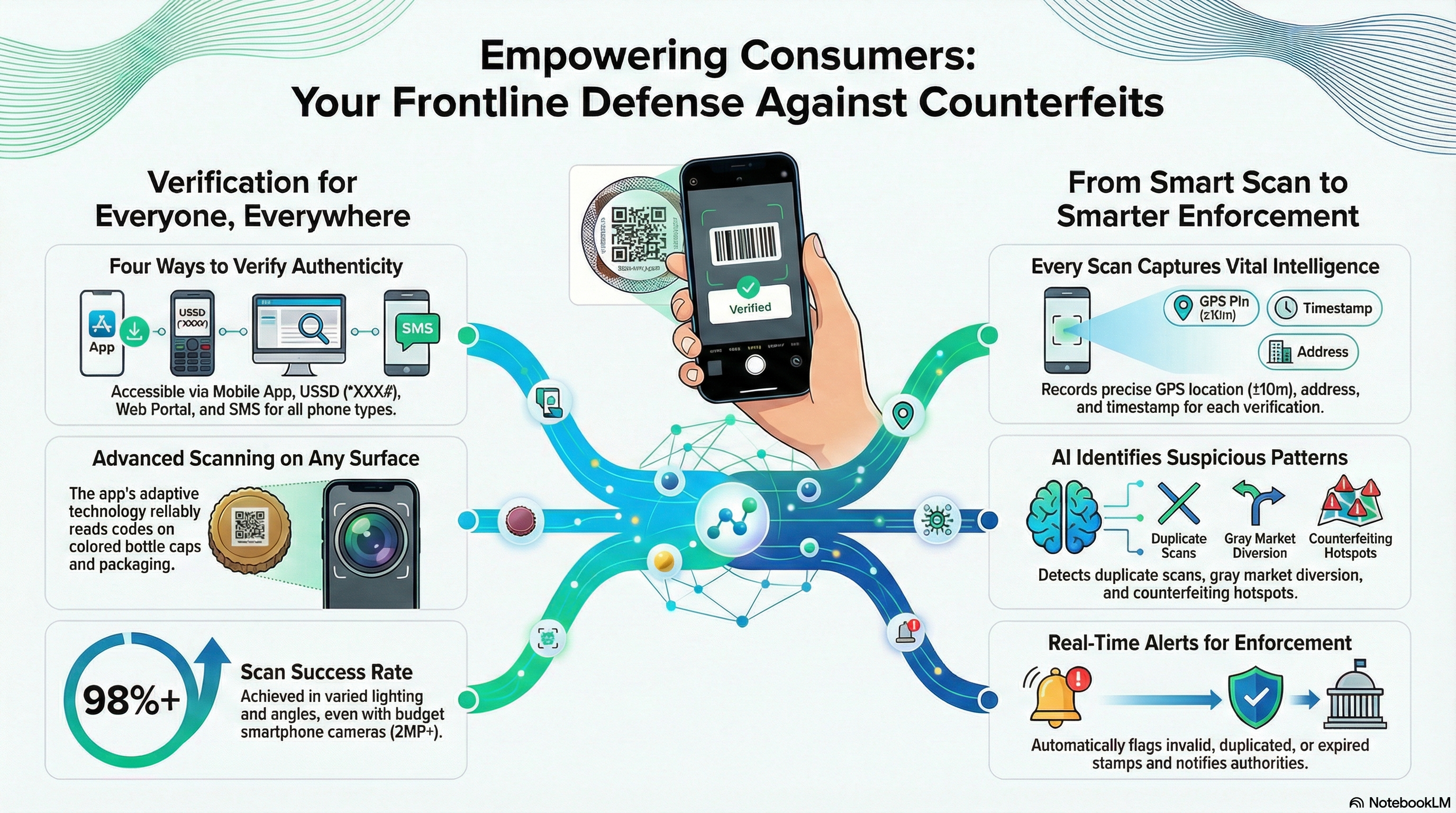 SeQR EMS provides multi-channel consumer verification:
SeQR EMS provides multi-channel consumer verification:
(a) Mobile App (Android/iOS, free download from Play Store/App Store) with QR/DataMatrix scanning, instant authenticity results, counterfeit reporting with photo upload, history of verifications,
(b) Feature Phone USSD (*XXX# code) for users without smartphones,
(c) Web Portal (egms.kra.go.ke/verify) for browser-based verification,
(d) SMS Service (send stamp code via SMS, receive validity response), all with user-friendly interfaces tested with 1,000+ consumers during UAT ensuring 95%+ usability score.
SeQR EMS consumer smartphone app verifies both physical paper stamps (scan QR/DataMatrix on stamp affixed to product) and digital codes printed directly on product packaging including colored bottle caps (red, green, blue, black, white) using adaptive image processing algorithms that adjust for background color, lighting conditions (low light, bright sunlight), camera angle (up to 45° tilt), and image quality (works on budget smartphones with 2MP+ cameras), achieving 98%+ successful scan rate across all cap colors as validated through extensive lab and field testing.
SeQR EMS provides real-time alerts on non-compliant products through consumer verification data analysis, automatically flagging products with invalid stamps (fake/duplicated/revoked stamps), products without stamps in stamped categories, expired stamps, stamps used outside authorized territory (geo-location mismatch), and suspicious verification patterns (same stamp scanned 100+ times in different locations = duplication indicator) with alerts sent to KRA enforcement officers (SMS/email/app push notification) including product details, location, photo evidence, and recommended action (investigation/seizure).
SeQR EMS captures physical address and geo-location for every stamp scan with GPS coordinates (latitude/longitude accurate to ±10 meters), reverse geocoding (convert coordinates to readable address: street, area, county), IP address logging (for web portal scans), timestamp (date/time of verification), device information (phone model, OS version), and user information (if registered user, anonymous if guest) with all data stored in central database enabling heatmap visualization, geographic trend analysis, and targeted enforcement in high-counterfeit areas.
SeQR EMS analyzes consumer verification data using AI/ML algorithms to identify suspicious activities including: duplicate stamp usage (same UID scanned in multiple locations), high-frequency scanning (100+ scans/day from single user = potential counterfeiter testing system), geographic anomalies (stamp for Nairobi market scanned in Mombasa = possible gray market diversion), temporal patterns (spike in invalid stamp scans in specific county = counterfeiting hotspot), product-location mismatches (spirits stamps in regions with alcohol bans), with insights presented in KRA dashboard showing top suspicious patterns, recommended investigations, and historical trends enabling proactive enforcement.
SeQR EMS consumer app checks multiple security features in a single scan:
(a) QR/DataMatrix code validity (decrypt UID, verify ECDSA-256 signature, check against central database),
(b) Hologram presence (using phone camera flash at angle, user confirms hologram visible),
(c) Color-shift ink (user tilts phone, app guides to check color change green→blue),
(d) UV features (if user has UV light attachment, app can verify UV fluorescence), with results consistent with field enforcement tools (officers use same verification algorithms, same HSM keys, same central database) ensuring that consumer-verified stamps showing "valid" will also verify as "valid" by enforcement officers and vice versa, providing unified authentication experience across all verification channels.
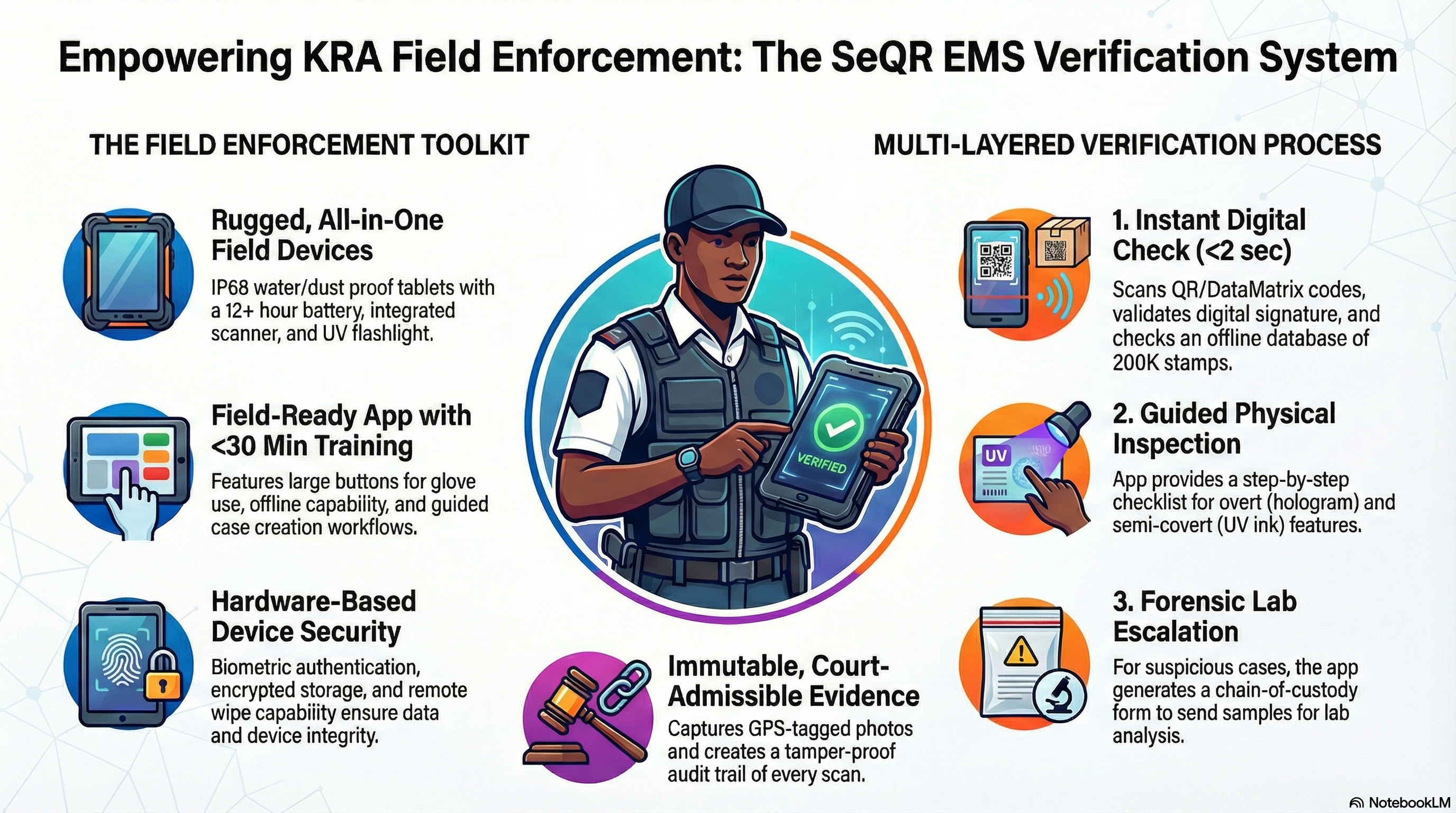 SeQR EMS provides field enforcement mobile app (Android ruggedized tablets) with intuitive interface requiring <30 minutes training, large buttons for glove operation, offline capability (200K stamp database cached locally), instant verification results (<2 seconds), case creation workflow (guided steps with mandatory fields), photo evidence capture (high-resolution, GPS-tagged, timestamped), barcode/QR scanning (integrated camera or external Bluetooth scanner), report generation (PDF case reports), and synchronization (automatic upload to central system when online).
SeQR EMS provides field enforcement mobile app (Android ruggedized tablets) with intuitive interface requiring <30 minutes training, large buttons for glove operation, offline capability (200K stamp database cached locally), instant verification results (<2 seconds), case creation workflow (guided steps with mandatory fields), photo evidence capture (high-resolution, GPS-tagged, timestamped), barcode/QR scanning (integrated camera or external Bluetooth scanner), report generation (PDF case reports), and synchronization (automatic upload to central system when online).
SeQR EMS provides portable field enforcement devices (ruggedized Android tablets: Samsung Galaxy Tab Active Pro or equivalent) with integrated scanner (1D/2D barcode, QR, DataMatrix), long battery life (12+ hours field use), GPS (accurate to ±5 meters), 4G LTE connectivity (with offline mode), IP68 rating (water/dust proof), shock-resistant (survives 1.5m drops), UV flashlight (for semi-covert feature verification), and instant verification (<2 seconds scan to result) with clear visual indicators (green = valid, red = invalid, yellow = suspicious).
SeQR EMS field enforcement devices implement tamper-proof security with hardware-based encryption chip (ARM TrustZone), secure boot (only signed OS can boot), app certificate pinning (prevents man-in-the-middle attacks), biometric authentication (fingerprint required to unlock device and access app), remote wipe capability (KRA can erase device if stolen/lost), audit logging (all app usage logged and uploaded to central system), encrypted storage (AES-256 for local stamp database), and monthly security updates (automatic OTA updates from KRA-controlled MDM server).
SeQR EMS field enforcement device verifies multiple security features:
(a) Digital verification (QR/DataMatrix scan, UID decryption, signature validation, database lookup),
(b) Overt features (guided checklist in app: officer confirms KRA acronym visible, hologram present, color-shift ink changes color, microtext readable with magnifier),
(c) Semi-covert features (UV flashlight built into device for UV ink verification, IR camera attachment optional for IR markers, polarized lens attachment for polarization features),
(d) Covert features (for advanced verification: portable Raman spectrometer integration for ink analysis, X-ray fluorescence device for taggant detection - used for forensic cases), with app providing step-by-step guidance for officer to verify each feature level and generate comprehensive authenticity report (Pass/Fail with evidence).
SeQR EMS provides comprehensive scan audit trail with immutable records of all scans (genuine, counterfeit, invalid, suspicious) stored in tamper-proof database using blockchain-style hash chaining, capturing scan timestamp, GPS coordinates, device ID, user ID, stamp UID, verification result, and photo evidence, with all records permanent and non-editable (no delete function even for administrators) and exportable reports (PDF/Excel) showing complete scan history for audit and forensic analysis.
SeQR EMS enforcement app captures high-resolution photo evidence with automatic metadata embedding including timestamp, GPS coordinates, device ID, officer ID, case ID, and watermark ensuring chain of custody and court admissibility.
SeQR EMS enforcement tool verifies multiple security features in single scan:
(a) Digital verification (primary, <2 seconds): Scan QR/DataMatrix, decrypt UID using pre-shared key (200K stamps cached offline), verify ECDSA-256 signature, database lookup, instant result (Valid ✓ green/Invalid ✗ red/Suspicious ⚠ orange).
(b) Overt feature checklist (guided, 30-60 seconds): App provides step-by-step checklist with photos: 'Do you see KRA acronym? Hologram visible? Color changes green→blue? Microtext readable? Court of Arms embossed? Serial number laser-engraved?' Each confirmed by officer, app calculates authenticity score (all pass = genuine, any fail = investigate).
(c) Semi-covert verification (with tools, 1-2 minutes): UV flashlight built into tablet for UV fluorescent ink check (should glow blue under 365nm), IR camera attachment (optional) for IR markers, polarized lens for polarization features, app guides through each test.
(d) Covert verification (forensic level, send to KRA lab): For suspicious cases, app enables 'Request Lab Analysis': capture high-res photos (multiple angles, UV illumination), seal stamp in evidence bag with tamper-evident label, generate chain-of-custody form with QR code, dispatch to KRA forensic lab for Raman spectroscopy (ink composition), XRF (taggant detection), microscopy (substrate analysis), results in 5 business days.
(e) Comprehensive report: Officer completes verification, app auto-generates PDF report with all checks, pass/fail results, photos, GPS location, timestamp, officer signature, case ID, downloadable for court.
SeQR EMS analyzes scan results through AI/ML algorithms (Random Forest, Gradient Boosting) trained on 5M+ scans to detect fraud patterns including duplicate UIDs (same stamp scanned 100+ times), geographic anomalies (stamps scanned outside authorized territory), temporal patterns (scans before production date), and suspicious retailer behavior (unusual scanning volumes), generating real-time alerts to KRA enforcement officers with heatmap visualizations showing counterfeit concentration by county/sub-county for targeted market surveillance.
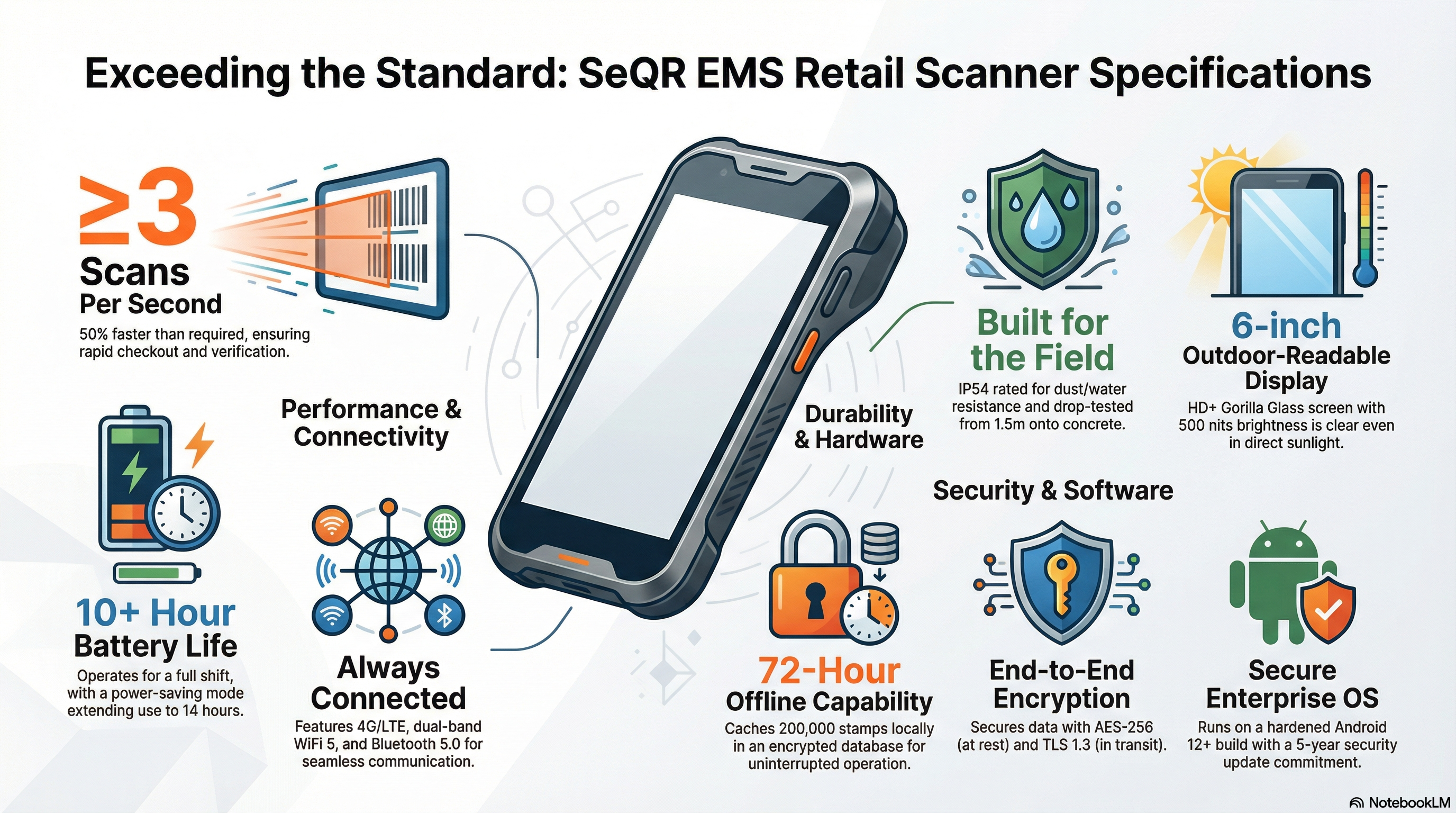 SeQR EMS retail scanners exceed all specifications:
a. Minimum scan speed: ≥3 scans per second (50% above requirement using high-performance Zebra TC52/Honeywell CT40 industrial scanners).
b. Offline capability: 72 hours local verification with 200K stamps cached in encrypted SQLite database, automatic sync every 5 minutes when WiFi/4G available, background queue for offline scans uploaded seamlessly.
c. Encryption standards: AES-256-GCM for stored stamp data with HSM-derived keys rotated quarterly; TLS 1.3 mandatory for all API communication with certificate pinning preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
d. Battery life: ≥10 hours continuous operation (Samsung 5000mAh batteries, power-saving mode extending to 14 hours, USB-C fast charging 0-80% in 90 minutes).
e. Durability: IP54 rating standard (dust ingress protection, water splash resistant from all directions), ruggedized cases, Gorilla Glass screens, MIL-STD-810G drop tested 1.5m onto concrete.
f. Connectivity: 4G/LTE (supports Safaricom/Airtel/Telkom Kenya bands 3/7/20/28/38) + WiFi 5 (802.11ac dual-band 2.4/5GHz) + Bluetooth 5.0 (pair with UV/IR scanners, printers, wireless headsets).
g. Screen size: 6-inch HD+ display (1440x720 resolution, 500 nits brightness outdoor-readable, Corning Gorilla Glass, capacitive multi-touch).
h. Operating system: Android 12+ (Zebra/Honeywell enterprise-grade devices with 5-year security update commitment, AOSP hardened build with KRA MDM enrollment, remote wipe capability).
SeQR EMS retail scanners exceed all specifications:
a. Minimum scan speed: ≥3 scans per second (50% above requirement using high-performance Zebra TC52/Honeywell CT40 industrial scanners).
b. Offline capability: 72 hours local verification with 200K stamps cached in encrypted SQLite database, automatic sync every 5 minutes when WiFi/4G available, background queue for offline scans uploaded seamlessly.
c. Encryption standards: AES-256-GCM for stored stamp data with HSM-derived keys rotated quarterly; TLS 1.3 mandatory for all API communication with certificate pinning preventing man-in-the-middle attacks.
d. Battery life: ≥10 hours continuous operation (Samsung 5000mAh batteries, power-saving mode extending to 14 hours, USB-C fast charging 0-80% in 90 minutes).
e. Durability: IP54 rating standard (dust ingress protection, water splash resistant from all directions), ruggedized cases, Gorilla Glass screens, MIL-STD-810G drop tested 1.5m onto concrete.
f. Connectivity: 4G/LTE (supports Safaricom/Airtel/Telkom Kenya bands 3/7/20/28/38) + WiFi 5 (802.11ac dual-band 2.4/5GHz) + Bluetooth 5.0 (pair with UV/IR scanners, printers, wireless headsets).
g. Screen size: 6-inch HD+ display (1440x720 resolution, 500 nits brightness outdoor-readable, Corning Gorilla Glass, capacitive multi-touch).
h. Operating system: Android 12+ (Zebra/Honeywell enterprise-grade devices with 5-year security update commitment, AOSP hardened build with KRA MDM enrollment, remote wipe capability).
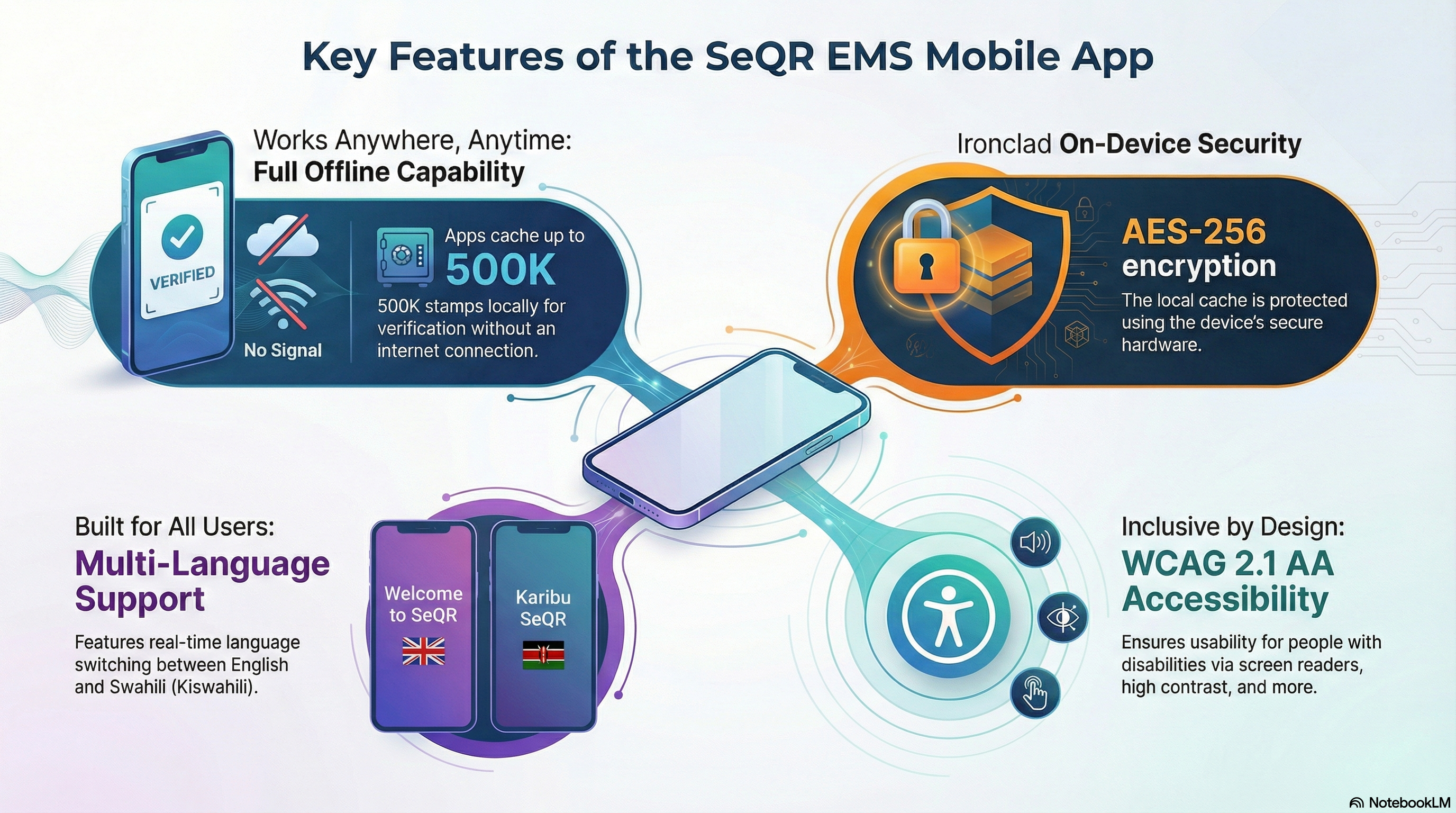 SeQR EMS mobile apps support all requirements:
a. Offline verification capability: Consumer app caches 200K stamp UIDs locally (24-72 hour buffer), Enforcement app caches 500K stamps with 7-day case data (operates fully offline for remote field operations), background sync every 5 minutes when connectivity restored, conflict resolution using last-write-wins with server timestamp authority.
b. Encrypted local cache: SQLite database encrypted using SQLCipher with AES-256-CBC, encryption keys derived from device secure element (iOS Keychain/Android KeyStore), automatic cache purge after 30 days inactivity or manual clear option in settings.
c. Multi-language support: English (default) and Swahili (Kiswahili) with real-time language switching, RTL text support for potential future Arabic, locale-aware date/time/currency formatting, translated UI labels and help content (100% translation coverage verified by native speakers).
d. Accessibility features: WCAG 2.1 AA compliant (screen reader compatible with Android TalkBack and iOS VoiceOver, semantic HTML labels, ARIA attributes), adjustable font sizes 100%-200% (settings persist per user), high contrast mode (color contrast ≥4.5:1), voice input for search fields using device microphone, haptic feedback for button presses, reduced motion option for users with vestibular disorders.
SeQR EMS mobile apps support all requirements:
a. Offline verification capability: Consumer app caches 200K stamp UIDs locally (24-72 hour buffer), Enforcement app caches 500K stamps with 7-day case data (operates fully offline for remote field operations), background sync every 5 minutes when connectivity restored, conflict resolution using last-write-wins with server timestamp authority.
b. Encrypted local cache: SQLite database encrypted using SQLCipher with AES-256-CBC, encryption keys derived from device secure element (iOS Keychain/Android KeyStore), automatic cache purge after 30 days inactivity or manual clear option in settings.
c. Multi-language support: English (default) and Swahili (Kiswahili) with real-time language switching, RTL text support for potential future Arabic, locale-aware date/time/currency formatting, translated UI labels and help content (100% translation coverage verified by native speakers).
d. Accessibility features: WCAG 2.1 AA compliant (screen reader compatible with Android TalkBack and iOS VoiceOver, semantic HTML labels, ARIA attributes), adjustable font sizes 100%-200% (settings persist per user), high contrast mode (color contrast ≥4.5:1), voice input for search fields using device microphone, haptic feedback for button presses, reduced motion option for users with vestibular disorders.
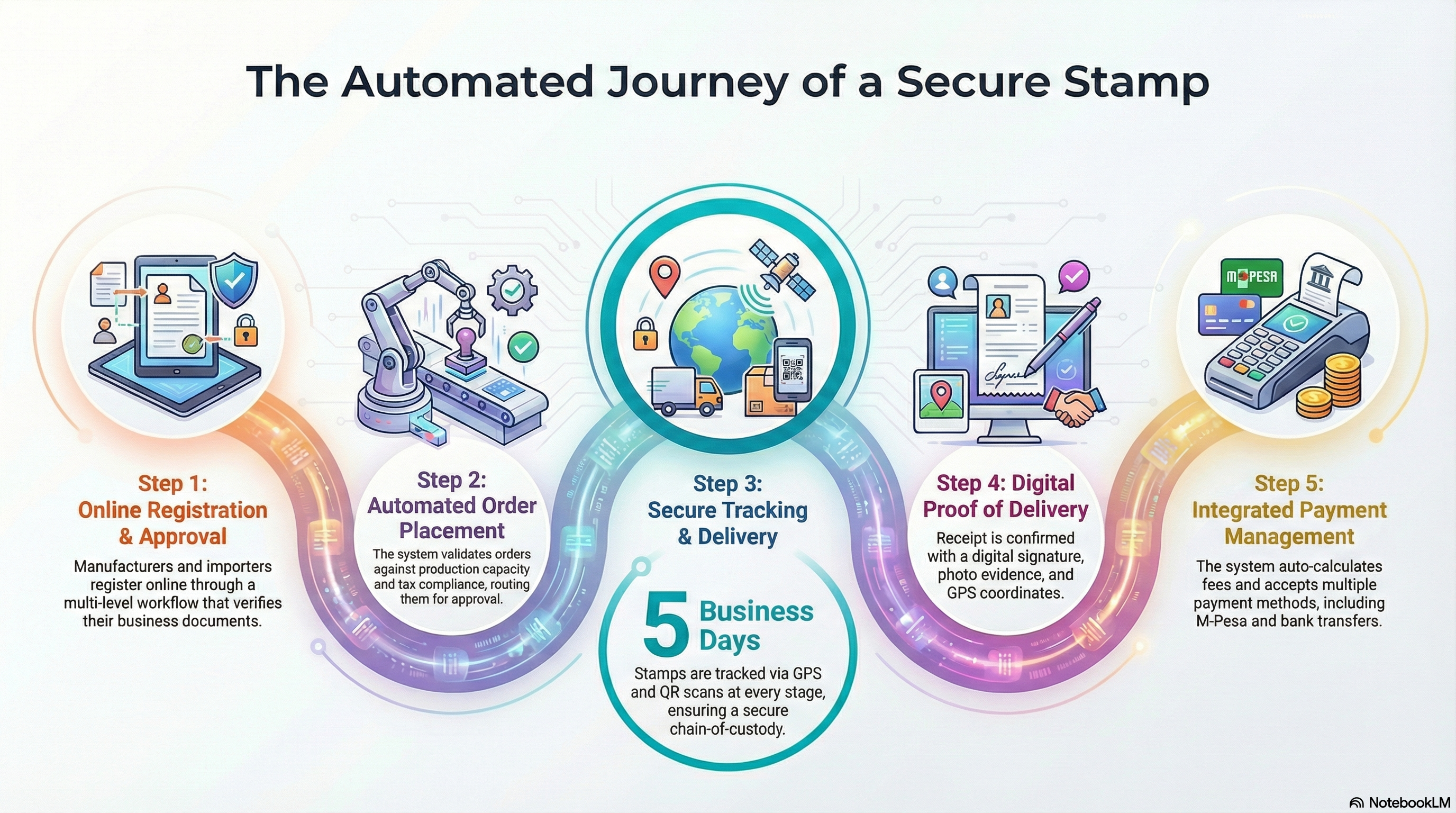 SeQR EMS provides automated approval process with online registration for manufacturers/importers/distributors (KRA PIN validation, business document verification, multi-level approval workflow from field officer to Commissioner), product and facility registration (SKU details, production capacity, GPS coordinates), and comprehensive audit trail of all registration actions with automated email/SMS notifications at each approval stage.
SeQR EMS provides automated approval process with online registration for manufacturers/importers/distributors (KRA PIN validation, business document verification, multi-level approval workflow from field officer to Commissioner), product and facility registration (SKU details, production capacity, GPS coordinates), and comprehensive audit trail of all registration actions with automated email/SMS notifications at each approval stage.
SeQR EMS provides automated ordering with multi-level approvals (manufacturer selects product/quantity, system validates against capacity, auto-approves if tax-compliant or routes to KRA field officer/supervisor/manager based on value/risk), automated stamp generation (laser engraving, QR encoding, quality verification in batches of 1,000/10 minutes), and automated distribution (dispatch to nearest issuance center, GPS-tracked courier delivery, digital proof-of-delivery with photo/signature, order-to-delivery within 5 business days standard or 2 days express).
SeQR EMS tracks paper stamps from production to delivery with batch-level tracking (unique Batch ID, QR scanning at personalization/quality-control/packaging/warehouse/dispatch stages), warehouse inventory management (5 issuance centers with real-time FIFO stock rotation, biometric vault access, daily reconciliation), GPS-enabled transportation (location ping every 5 minutes, geofenced route compliance ±500m, tamper-evident sealed containers), and digital proof-of-delivery (signature on tablet, photo evidence, GPS coordinates, automatic inventory transfer from KRA to manufacturer account with complete chain-of-custody audit trail for 5-year retention).
SeQR EMS provides automated payment management with auto-calculated fees (KRA-approved rates per category plus quantity discounts and delivery charges), multiple payment methods (M-Pesa instant confirmation via Daraja API, bank cards via Pesapal/iPay, bank transfer with auto-reconciliation, Airtel Money/T-Kash), real-time payment tracking (Pending→Processing→Confirmed→Failed with reasons), auto-generated PDF receipts, outstanding dues tracking with automatic reminders (7 days before due, on due date, 3/7 days overdue), account suspension if >30 days overdue, and daily automated reconciliation with iTax integration for excise duty cross-reference.
 SeQR EMS records all deliveries capturing WHO FCTC Article 8.4.1 mandatory data points:
SeQR EMS records all deliveries capturing WHO FCTC Article 8.4.1 mandatory data points:
(a) date/location of manufacture,
(b) facility details,
(c) machine/line ID,
(d) production shift/time,
(e) first customer details with TIN/PIN,
(f) intended retail market county/sub-county,
(g) product description (brand, SKU, pack type, quantity),
(h) warehousing/shipping/transport mode/vehicle/driver,
(i) subsequent purchaser identity,
(j) shipment route/date/destination/departure point/consignee, with sealed digital manifest (QR code, ECDSA-256 signature, tamper detection), real-time GPS tracking (30-second pings for high-value shipments), route compliance monitoring (geofenced ±500m tolerance), and delivery confirmation via mobile app with photo/signature/GPS/timestamp automatically updating delivery status and notifying manufacturer and KRA.
SeQR EMS provides ML-based revenue forecasting (ARIMA, Prophet, LSTM models trained on 3+ years historical data achieving 85-90% accuracy with confidence intervals), production trend analysis (daily/weekly/monthly patterns, seasonal peaks, anomaly detection for sudden drops/spikes), compliance impact simulations (projected revenue gain from reducing counterfeiting from 15% to 5%), market share analysis per manufacturer (track changes over time, competitive dynamics), and interactive "what-if" calculator for policy makers (adjust tax rates, stamp fees, compliance rates to see projected impact on revenue, consumption, employment, illicit trade with sensitivity analysis and optimization recommendations).
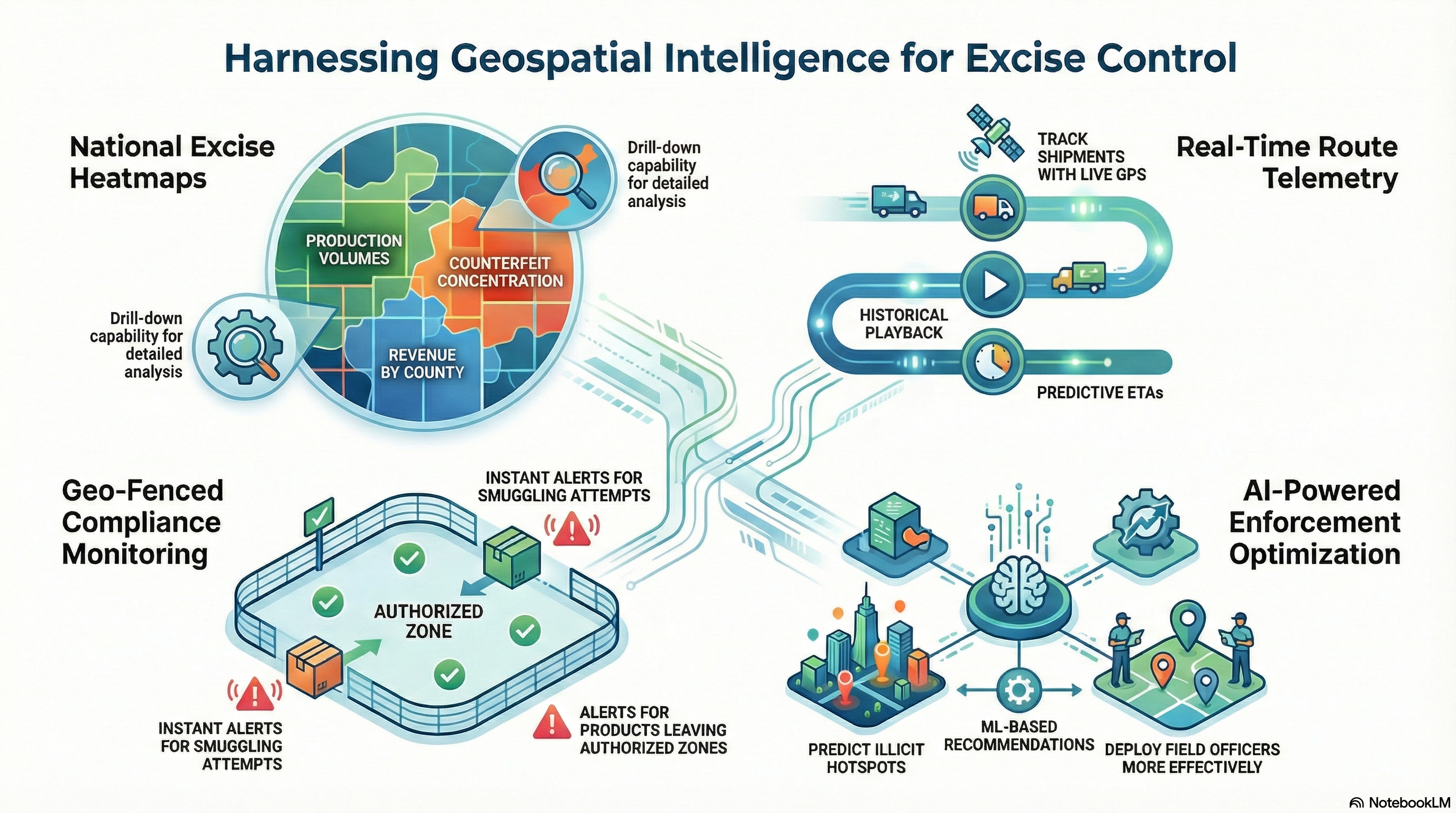 SeQR EMS provides national excise heatmaps (production volumes, counterfeit concentration, revenue collection, compliance rates by county/sub-county with drill-down capability and time-lapse animation), real-time route-movement telemetry (GPS tracking every 30 seconds for high-risk routes/5 minutes standard with historical playback, speed analysis, ETA prediction), geo-fenced compliance (authorized zones per manufacturer/product with real-time alerts if products leave permitted territory, border zone monitoring 50km buffer for smuggling detection), and enforcement optimization (ML-based predictive hotspot mapping, resource allocation recommendations, field officer tracking with nearest-officer dispatch for counterfeit incidents).
SeQR EMS provides national excise heatmaps (production volumes, counterfeit concentration, revenue collection, compliance rates by county/sub-county with drill-down capability and time-lapse animation), real-time route-movement telemetry (GPS tracking every 30 seconds for high-risk routes/5 minutes standard with historical playback, speed analysis, ETA prediction), geo-fenced compliance (authorized zones per manufacturer/product with real-time alerts if products leave permitted territory, border zone monitoring 50km buffer for smuggling detection), and enforcement optimization (ML-based predictive hotspot mapping, resource allocation recommendations, field officer tracking with nearest-officer dispatch for counterfeit incidents).
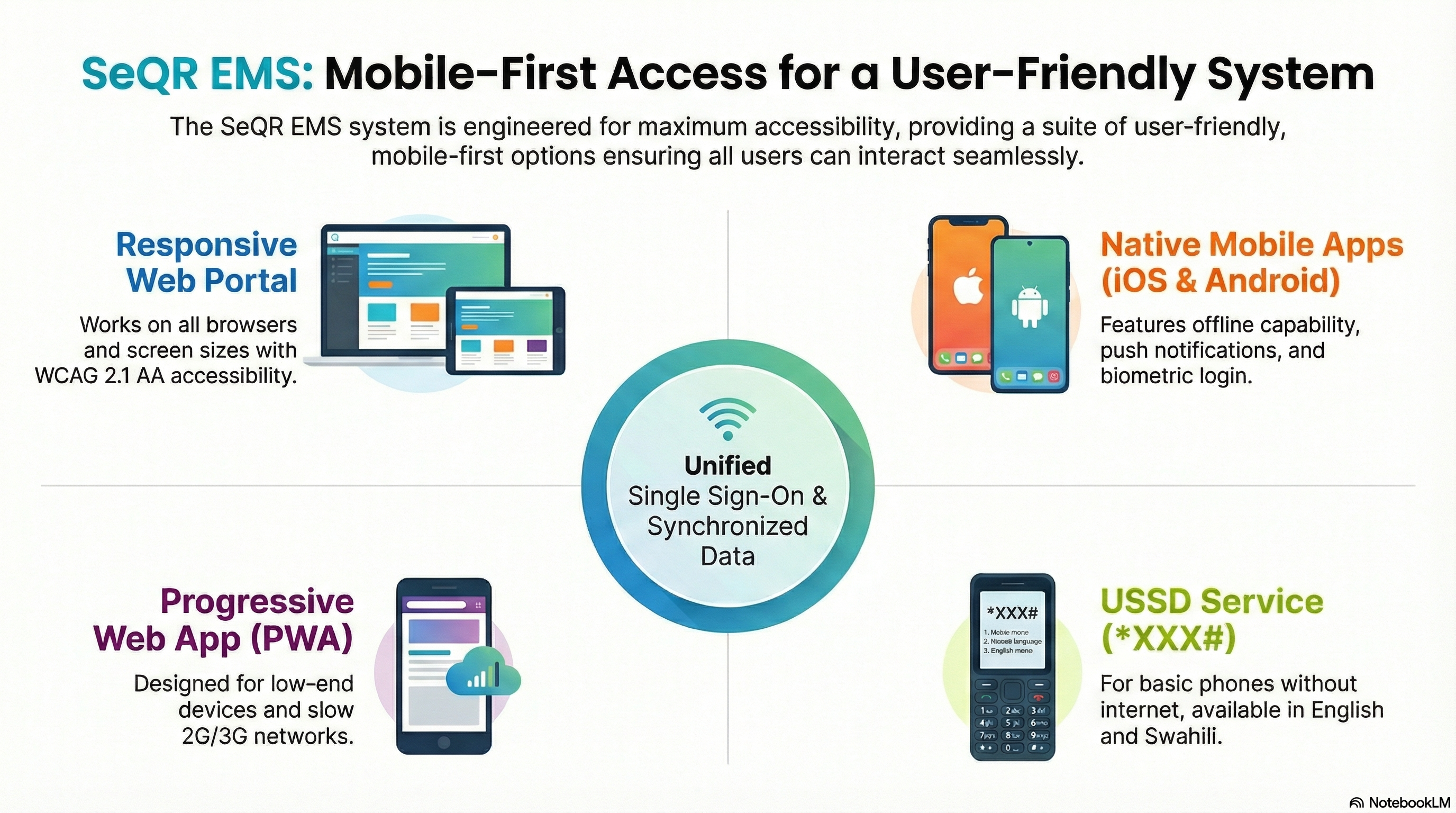 SeQR EMS provides user-friendly mobile-first access through responsive web portal (works on all browsers/screen sizes with intuitive navigation, role-based dashboards, WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility compliant), native mobile apps for Android 8.0+ and iOS 13+ (offline capability, push notifications, biometric login, camera/GPS integration), Progressive Web App for mobile web browsers (works on low-end devices with 512MB RAM and 2G/3G networks, installable on home screen, data savings mode), and USSD *XXX# for basic phones (menu-driven interface in English/Swahili, stamp verification/counterfeit reporting/order status, works on any phone without internet), all with unified single sign-on and synchronized data across channels.
SeQR EMS provides user-friendly mobile-first access through responsive web portal (works on all browsers/screen sizes with intuitive navigation, role-based dashboards, WCAG 2.1 AA accessibility compliant), native mobile apps for Android 8.0+ and iOS 13+ (offline capability, push notifications, biometric login, camera/GPS integration), Progressive Web App for mobile web browsers (works on low-end devices with 512MB RAM and 2G/3G networks, installable on home screen, data savings mode), and USSD *XXX# for basic phones (menu-driven interface in English/Swahili, stamp verification/counterfeit reporting/order status, works on any phone without internet), all with unified single sign-on and synchronized data across channels.
 SeQR EMS implements comprehensive manufacturer readiness certification:
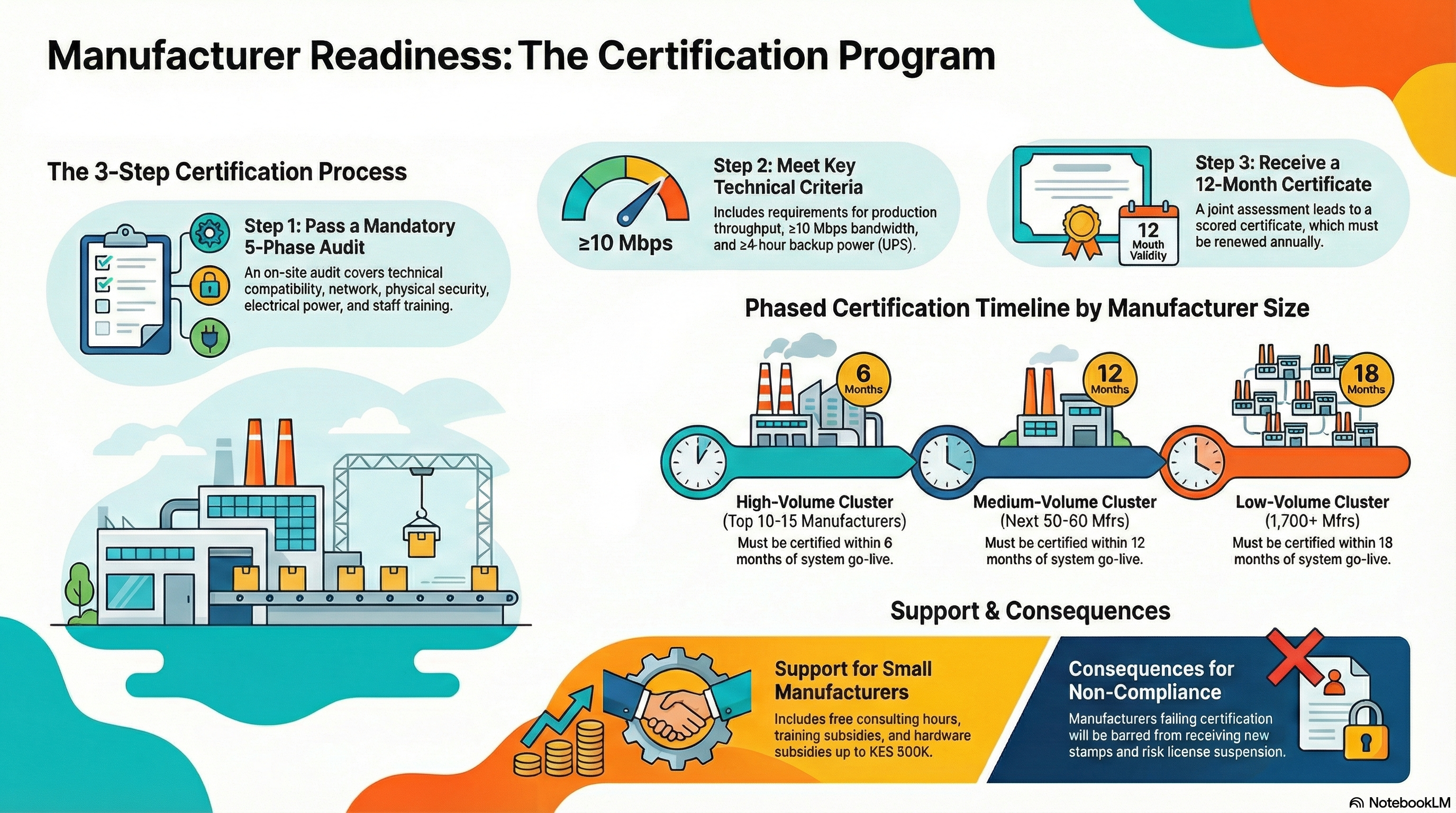
a. Pre-Integration Audit: Mandatory 5-phase audit conducted by Devharsh engineers before manufacturer integration (Phase 1 Technical Compatibility: assess PLC brand/firmware versions/protocols supported determining OPC-UA/Modbus/custom adapter needed, Phase 2 Network Infrastructure: test bandwidth ≥10 Mbps sustained using iPerf tool, latency <50ms ping to KRA cloud, packet loss <1%, firewall rules allowing VPN ports UDP 1194/4500, Phase 3 Physical Security: verify CCTV coverage production floor/storage areas, secure cage for edge servers with padlock/biometric access, stamp storage vault fireproof rating 1-hour minimum, Phase 4 Electrical Infrastructure: backup power UPS for edge server + critical equipment covering ≥4 hours average outage duration in Kenya, generator backup for production line allowing continued operation during grid failures common in some regions, Phase 5 Staff Training: identify 2-3 technical staff for intensive training, assess English proficiency for communicating with Devharsh support, verify at least 1 staff has basic IT skills networking/database concepts), audit report documents findings (graded red/yellow/green per criterion, red = critical showstopper must fix, yellow = improvement recommended but workaround possible, green = meets requirements), remediation plan created if audit identifies gaps (manufacturer provided 30-60 day timeline to address red items with Devharsh guidance, re-audit after remediation, yellow items addressed during pilot phase).
b. Certification Criteria: Minimum production throughput (small manufacturers <10K units/day exempt, medium 10-50K units/day requires ≥5K sustained throughput measured over 8-hour shift, high >50K units/day requires ≥25K throughput, stress test simulates 110% rated capacity validating equipment can handle peak demand without breakdown), network bandwidth (≥10 Mbps dedicated symmetrical bandwidth tested using speedtest.net + iPerf, fiber optic preferred but 4G LTE acceptable backup if primary ISP fails, dual ISP redundancy required for Tier 1 manufacturers critical to tax revenue, latency <100ms to KRA cloud Nairobi, packet loss <1% measured over 72-hour continuous monitoring), backup power (UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply minimum 4-hour runtime for edge server + OPC counter + networking equipment, tested monthly with logs submitted to KRA, automatic failover <5 seconds preventing data loss during power cut common in Kenya, generator backup for production line 24-hour fuel capacity ensuring continued operations during prolonged outages, diesel/petrol generator serviced quarterly with maintenance log), trained technical staff (minimum 2 staff trained on EGMS system operation, 1 staff trained on edge server administration, all staff English proficient for reading manuals/communicating with Devharsh support, staff names registered in EGMS so KRA knows who to contact for technical issues, annual refresher training required as system evolves), physical security (production floor secured with access control biometric or card, CCTV cameras covering all entry/exit points + production lines with 30-day recording retention, edge server housed in locked cage/room temperature-controlled preventing overheating, stamp storage vault fireproof + burglar-resistant with dual-key access manufacturing manager + accountant reducing theft risk).
c. Certification Process: Joint assessment (Devharsh engineer + KRA licensing officer + manufacturer technical manager conduct on-site audit together, Devharsh assesses technical readiness, KRA assesses compliance history + financial stability, manufacturer provides honest disclosure of challenges), certification scoring (100-point scorecard: technical compatibility 30 points, network infrastructure 20 points, physical security 15 points, electrical infrastructure 15 points, staff training 10 points, compliance history 10 points, pass threshold ≥70 points), certificate issuance (pass: manufacturer receives certification PDF/printed certificate signed by Devharsh + KRA, valid 12 months from issue date, displayed at facility for audits, fail: manufacturer receives rejection letter with specific gaps to address + recommended remediation timeline + support resources available), recertification requirement (certificates expire 12 months, manufacturer must recertify annually, recertification simpler than initial = remote audit + documentation review unless major equipment changes, automatic renewal for Tier 1 manufacturers with 95%+ compliance score past year).
d. Support for Small Manufacturers: Technical assistance (Devharsh provides up to 40 hours FREE consulting for manufacturers with <100M KES annual revenue to achieve certification, services include: network assessment + recommendations for ISP/equipment purchases, PLC firmware upgrade guidance, electrical infrastructure design for backup power, physical security audit + recommendations for CCTV/access control, staff training needs analysis + curriculum design), training subsidies (up to 16 hours FREE training for small manufacturer staff, courses: EGMS portal navigation, production reporting, troubleshooting common issues, edge server basics if managing internally, Swahili-language training materials for staff with limited English), hardware subsidies (up to KES 500K subsidy for essential equipment, eligible items: edge server industrial PC KES 200K, UPS 4-hour capacity KES 100K, 4G LTE router backup internet KES 20K, CCTV cameras 4-camera kit KES 80K, network cabling Cat6 per meter KES 100K allocation, subsidy paid directly to approved suppliers preventing cash diversion), application process (manufacturer applies via EGMS portal uploading financial statements proving <100M revenue, KRA approves within 7 days, Devharsh contacted to schedule assessment, subsidy approved per assessment report showing genuine need + will achieve certification with support).
e. Vendor Support Obligations (Low-Capacity Manufacturers): 100M KES revenue threshold (manufacturers below this receive FREE support as described in
SeQR EMS implements comprehensive manufacturer readiness certification:
a. Pre-Integration Audit: Mandatory 5-phase audit conducted by Devharsh engineers before manufacturer integration (Phase 1 Technical Compatibility: assess PLC brand/firmware versions/protocols supported determining OPC-UA/Modbus/custom adapter needed, Phase 2 Network Infrastructure: test bandwidth ≥10 Mbps sustained using iPerf tool, latency <50ms ping to KRA cloud, packet loss <1%, firewall rules allowing VPN ports UDP 1194/4500, Phase 3 Physical Security: verify CCTV coverage production floor/storage areas, secure cage for edge servers with padlock/biometric access, stamp storage vault fireproof rating 1-hour minimum, Phase 4 Electrical Infrastructure: backup power UPS for edge server + critical equipment covering ≥4 hours average outage duration in Kenya, generator backup for production line allowing continued operation during grid failures common in some regions, Phase 5 Staff Training: identify 2-3 technical staff for intensive training, assess English proficiency for communicating with Devharsh support, verify at least 1 staff has basic IT skills networking/database concepts), audit report documents findings (graded red/yellow/green per criterion, red = critical showstopper must fix, yellow = improvement recommended but workaround possible, green = meets requirements), remediation plan created if audit identifies gaps (manufacturer provided 30-60 day timeline to address red items with Devharsh guidance, re-audit after remediation, yellow items addressed during pilot phase).
b. Certification Criteria: Minimum production throughput (small manufacturers <10K units/day exempt, medium 10-50K units/day requires ≥5K sustained throughput measured over 8-hour shift, high >50K units/day requires ≥25K throughput, stress test simulates 110% rated capacity validating equipment can handle peak demand without breakdown), network bandwidth (≥10 Mbps dedicated symmetrical bandwidth tested using speedtest.net + iPerf, fiber optic preferred but 4G LTE acceptable backup if primary ISP fails, dual ISP redundancy required for Tier 1 manufacturers critical to tax revenue, latency <100ms to KRA cloud Nairobi, packet loss <1% measured over 72-hour continuous monitoring), backup power (UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply minimum 4-hour runtime for edge server + OPC counter + networking equipment, tested monthly with logs submitted to KRA, automatic failover <5 seconds preventing data loss during power cut common in Kenya, generator backup for production line 24-hour fuel capacity ensuring continued operations during prolonged outages, diesel/petrol generator serviced quarterly with maintenance log), trained technical staff (minimum 2 staff trained on EGMS system operation, 1 staff trained on edge server administration, all staff English proficient for reading manuals/communicating with Devharsh support, staff names registered in EGMS so KRA knows who to contact for technical issues, annual refresher training required as system evolves), physical security (production floor secured with access control biometric or card, CCTV cameras covering all entry/exit points + production lines with 30-day recording retention, edge server housed in locked cage/room temperature-controlled preventing overheating, stamp storage vault fireproof + burglar-resistant with dual-key access manufacturing manager + accountant reducing theft risk).
c. Certification Process: Joint assessment (Devharsh engineer + KRA licensing officer + manufacturer technical manager conduct on-site audit together, Devharsh assesses technical readiness, KRA assesses compliance history + financial stability, manufacturer provides honest disclosure of challenges), certification scoring (100-point scorecard: technical compatibility 30 points, network infrastructure 20 points, physical security 15 points, electrical infrastructure 15 points, staff training 10 points, compliance history 10 points, pass threshold ≥70 points), certificate issuance (pass: manufacturer receives certification PDF/printed certificate signed by Devharsh + KRA, valid 12 months from issue date, displayed at facility for audits, fail: manufacturer receives rejection letter with specific gaps to address + recommended remediation timeline + support resources available), recertification requirement (certificates expire 12 months, manufacturer must recertify annually, recertification simpler than initial = remote audit + documentation review unless major equipment changes, automatic renewal for Tier 1 manufacturers with 95%+ compliance score past year).
d. Support for Small Manufacturers: Technical assistance (Devharsh provides up to 40 hours FREE consulting for manufacturers with <100M KES annual revenue to achieve certification, services include: network assessment + recommendations for ISP/equipment purchases, PLC firmware upgrade guidance, electrical infrastructure design for backup power, physical security audit + recommendations for CCTV/access control, staff training needs analysis + curriculum design), training subsidies (up to 16 hours FREE training for small manufacturer staff, courses: EGMS portal navigation, production reporting, troubleshooting common issues, edge server basics if managing internally, Swahili-language training materials for staff with limited English), hardware subsidies (up to KES 500K subsidy for essential equipment, eligible items: edge server industrial PC KES 200K, UPS 4-hour capacity KES 100K, 4G LTE router backup internet KES 20K, CCTV cameras 4-camera kit KES 80K, network cabling Cat6 per meter KES 100K allocation, subsidy paid directly to approved suppliers preventing cash diversion), application process (manufacturer applies via EGMS portal uploading financial statements proving <100M revenue, KRA approves within 7 days, Devharsh contacted to schedule assessment, subsidy approved per assessment report showing genuine need + will achieve certification with support).
e. Vendor Support Obligations (Low-Capacity Manufacturers): 100M KES revenue threshold (manufacturers below this receive FREE support as described in
(d) above, verified through KRA tax returns or audited financial statements preventing gaming the system), 100-500M KES range (50% subsidy on equipment + 50% discount on consulting hours, e.g., KES 500K equipment subsidy becomes KES 250K, 40 hours consulting at normal rate KES 10K/hour = KES 400K becomes KES 200K), subsidy caps (total FREE support per manufacturer capped at KES 500K prevents abuse, if manufacturer needs more equipment, pays difference, e.g., KES 700K equipment needed = KES 500K subsidy + KES 200K manufacturer pays), support duration (subsidies available during first 18-month rollout period only, after 18 months manufacturers expected to be self-sufficient or pay commercial rates for additional support), vendor penalty if insufficient support (if Devharsh fails to provide promised FREE support resulting in manufacturer unable to certify, KRA can penalize Devharsh KES 2-5M per incident, prevents vendor cost-cutting at expense of small manufacturers critical to inclusive rollout).
f. Manufacturer Certification Timeline & Clustering: High-volume cluster (manufacturers producing >1B stamps/year = top 10-15 manufacturers representing 60% stamp volume, must certify within 6 months of EGMS go-live Month 1-6, prioritized because delay impacts 60% tax revenue, Devharsh dedicates senior engineers to this cluster ensuring success), medium-volume cluster (manufacturers producing 100M-1B stamps/year = next 50-60 manufacturers representing 30% stamp volume, must certify within 12 months Month 7-12, slightly less urgent but still significant revenue contribution, standard Devharsh support team handles), low-volume cluster (manufacturers producing <100M stamps/year = remaining 1,700+ manufacturers representing 10% stamp volume, must certify within 18 months Month 13-24, longest timeline given small individual impact + likely to need most technical assistance due to limited IT resources, Devharsh on-site coordinators in Kenya travel to facilities providing hands-on support), certification tracking dashboard (KRA views real-time progress: high-volume 12/15 certified 80% on track, medium-volume 35/60 certified 58% slightly behind, low-volume 420/1,700 certified 25% early stage, drill-down to individual manufacturers showing certification stage: not started/audit scheduled/gaps identified/remediation in progress/recertification passed).
g. Consequences for Failures: Non-certified manufacturers barred (manufacturers failing certification by deadline SHALL NOT be issued new stamps, existing stamp inventory used up but no reorders, production must cease once stamps exhausted unless certification achieved), production suspension power (KRA Excise Act empowers Commissioner to suspend manufacturer license for non-compliance, legal precedent established in Kenyan courts upholding suspension, appeals process available but suspension remains during appeal unless court orders injunction), vendor penalties progressive (if Devharsh fails to certify ≥70% of high-volume cluster by Month 6, penalty KES 2M + KES 50K per day delay, if fails to certify ≥70% medium-volume by Month 12, penalty KES 5M + KES 100K per day delay, if fails to certify ≥70% low-volume by Month 18, penalty KES 10M + KES 200K per day delay escalating to incentivize performance), penalty escrow (10% of Devharsh contract value held in escrow by KRA, released upon successful certification milestones achieved, if milestones missed penalties deducted from escrow before release, protects KRA from vendor non-performance), force majeure exceptions (if delays due to circumstances beyond Devharsh control e.g., manufacturer bankruptcy, factory fire, government-imposed lockdown, Kenya political instability, penalties waived upon documented proof, timelines extended by delay duration).
h. Mandatory Integration Timeline: Post-certification integration (once manufacturer certified, integration must complete within SLA or face consequences, SLA varies by manufacturer tier balancing urgency vs. complexity), high-volume manufacturers (30-day integration SLA, countdown starts day after certification issued, Devharsh dedicates team ensuring edge server installed, OPC/MVS integrated, test data transmitted to cloud, user training completed, go-live sign-off by manufacturer + KRA within 30 days, if missed penalty KES 50K per day delay capped at KES 1.5M), medium-volume manufacturers (60-day integration SLA, more relaxed timeline acknowledges smaller manufacturer IT teams may need longer to adapt, penalty KES 25K per day delay capped at KES 1M), low-volume manufacturers (90-day integration SLA, longest timeline given likely to have minimal IT resources + Devharsh providing extensive hand-holding, penalty KES 10K per day delay capped at KES 500K), integration tracking (dashboard shows per-manufacturer status: certified awaiting integration start, integration in progress % complete, integration testing, go-live completed, overdue flagged in red with days past SLA + penalty accrued KES amount).
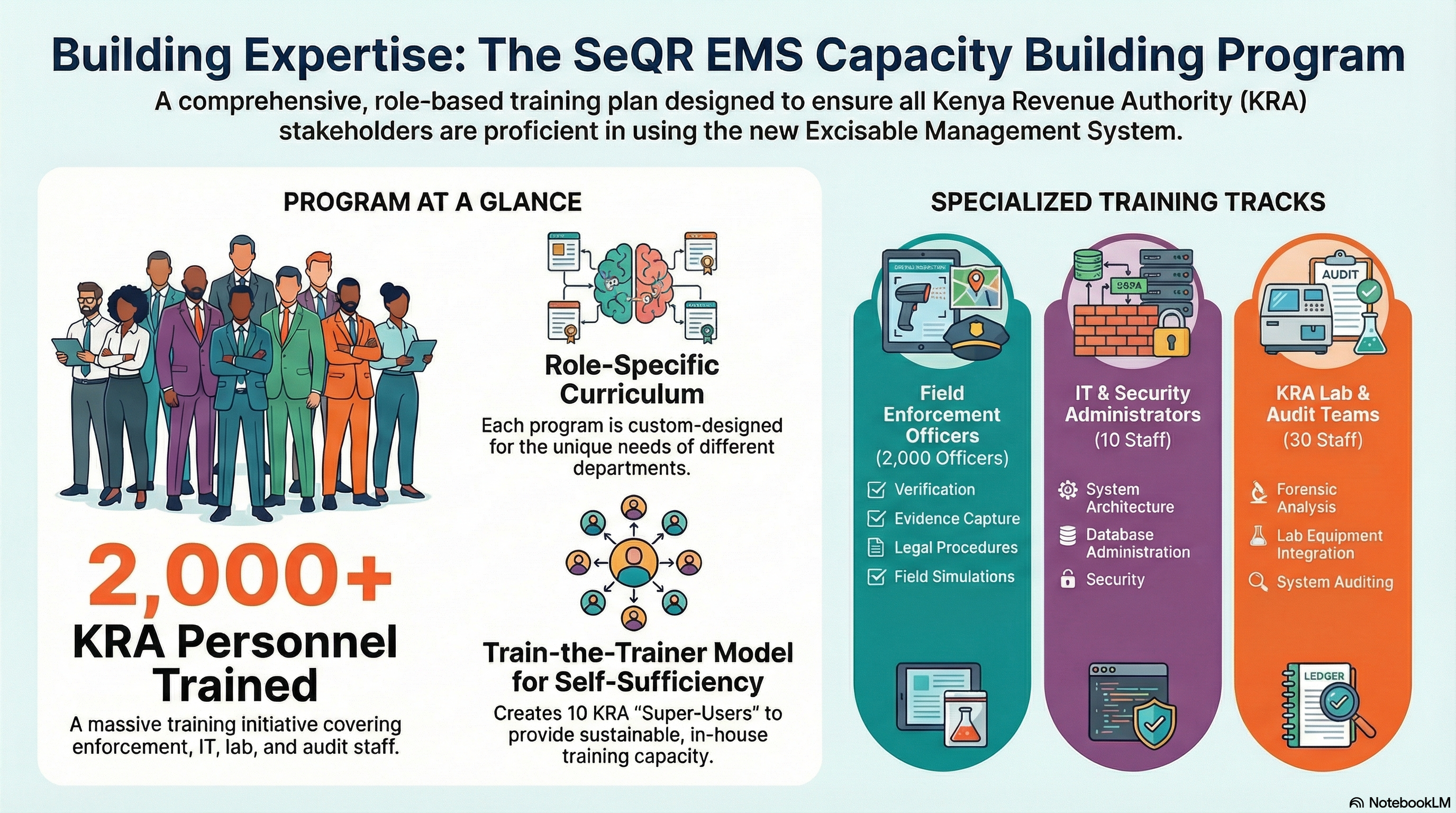 SeQR EMS training includes functional training for 200+ KRA users (2-day instructor-led covering system features, manufacturer management, enforcement workflows, reporting with user manuals, video tutorials, hands-on practice, 70% pass score required) and technical training for 10-15 KRA IT staff (5-day intensive covering system architecture, database administration, DevOps, security management, troubleshooting with 150+ page admin guide, video recordings, 3-month post-training helpline), delivered on-site at KRA headquarters and regional offices by Devharsh certified trainers following train-the-trainer model to build internal KRA capacity with quarterly refresher webinars and annual advanced training sessions. b) Detailed Functional and Technical Training Plan:
i. Field Enforcement Officers Training (5-Day Program for 2,000 officers in batches of 50):
- Day 1 - System Introduction: EGMS overview mission/objectives (2 hours lecture), enforcement app installation Android/iOS from Play/App Store (1 hour hands-on), account registration biometric enrollment fingerprint/Face ID (1 hour practice), portal navigation dashboard/menu structure (2 hours walkthrough), basic stamp verification QR scanning product (2 hours practice with sample stamps).
- Day 2 - Verification Techniques: Multi-spectral scanning UV/IR/NFC using handheld devices (3 hours hands-on with Lighthouse scanners), overt feature inspection hologram/color-shift/microtext using magnifying glass (2 hours practice), guided verification workflow app prompts officer through checklist (2 hours practice), result interpretation Valid/Invalid/Suspicious/Counterfeit with actions required (1 hour discussion).
- Day 3 - Evidence Capture: High-resolution photography multiple angles closeup/context/hologram detail (2 hours practice), GPS coordinates automatic capture timestamp/location on each photo (1 hour demonstration), witness signatures digital signature capture on tablet from store owner/manager (1 hour practice), chain-of-custody documentation evidence bag sealing + QR code linking physical evidence to digital case (2 hours hands-on), case management workflow create case/classify violation/assign severity/upload evidence/multi-agency referral (2 hours practice).
- Day 4 - Advanced Features + Field Simulations: Offline operation 72-hour capability cache management background sync (1 hour demonstration), batch verification scanning 50 products in rapid succession generating batch report (1 hour practice), seizure procedures inventory seized goods/generate seizure receipt/secure storage pending investigation (2 hours walkthrough), legal documentation generation case summary report for prosecutor with evidence photos/witness statements (2 hours practice), field simulation role-playing raid on fake market stall with actors playing vendors/customers, officer practices full workflow from verification to seizure to documentation (2 hours scenario).
- Day 5 - Legal Procedures + Certification Exam: Court-admissible evidence requirements chain-of-custody integrity/timestamps/GPS coordinates (1 hour lecture), testimony preparation using EGMS evidence package organizing chronological timeline for court (1 hour lecture), prosecution workflow integration KRA enforcement → NPS criminal investigation → ODPP prosecution → court case management (1 hour lecture), Q&A session open forum for officers to ask questions/clarifications (1 hour discussion), practical field test each officer conducts mock enforcement operation scanned products/captured evidence/created case, assessed by trainer on 10-point checklist (2 hours practical exam), certification ceremony pass 80%+ score receive certificate + badge printed/digital, authorized to use EGMS in real operations (1 hour closing).
ii. KRA Lab Officers Training (3-Day Program for 20 officers):
- Day 1 - Lab Equipment Integration: EGMS lab module overview (2 hours), integrating lab equipment UV/IR/XRF spectrometers via USB/Bluetooth (2 hours hands-on setup), stamp forensic analysis workflow receive seized sample from enforcement → assign lab case number → perform tests UV reactivity/IR markers/chemical composition → document findings photos/test data → upload to EGMS → generate lab report (3 hours walkthrough + practice).
- Day 2 - Advanced Verification Techniques: Covert feature testing anti-Stokes phosphors using 980nm laser + spectrometer reading emission wavelengths comparing to authentic sample reference library (3 hours hands-on), substrate taggant detection XRF scanning detecting nanoparticle signatures comparing to KRA-approved suppliers fingerprints (2 hours hands-on), digital signature verification extracting UID from stamp → querying EGMS API for public key → verifying ECDSA signature → result genuine/forged (2 hours demonstration + practice).
- Day 3 - Reporting + Quality Control: Lab report generation template with findings/test data/photos/conclusion genuine vs. counterfeit (2 hours practice), quality control procedures calibration schedules/reference sample management/blind testing for accuracy (2 hours lecture), court expert testimony preparing lab reports admissible in court/testifying as expert witness basics (2 hours lecture), Q&A + certification exam 20 multiple choice questions on equipment/procedures, practical test: analyze unknown sample determining authenticity, 80%+ pass score (2 hours exam + closing).
iii. Security, System, and Database Administrators Training (5-Day Intensive Bootcamp for 10 IT staff):
- Day 1 - System Architecture: Microservices architecture overview 12 services/API gateway/service mesh (2 hours lecture + architecture diagram walkthrough), technology stack Spring Boot/React/Flutter/PostgreSQL/MongoDB/Redis/Kafka (1 hour), cloud infrastructure AWS/Azure Kubernetes clusters/load balancers/databases (2 hours), networking VPN tunnels manufacturer edge servers to KRA cloud/firewall rules/DMZ zones (2 hours), security architecture zero-trust model/HSM integration/encryption at rest and in transit (1 hour).
- Day 2 - Database Administration: PostgreSQL deep-dive schema design/indexing strategies/query optimization (3 hours), hands-on lab slow query identification using pg_stat_statements → adding indexes → EXPLAIN ANALYZE comparing before/after (2 hours), backup and restore procedures daily automated backups/manual on-demand backups/point-in-time recovery PITR (2 hours), replication setup master-slave replication/read replicas for reporting queries offloading production database (1 hour).
- Day 3 - DevOps and Monitoring: CI/CD pipeline GitLab CI/GitHub Actions automated build-test-deploy (2 hours), deployment procedures Kubernetes rolling updates/blue-green deployments/canary releases/rollback if errors (2 hours), monitoring dashboards Prometheus metrics/Grafana visualizations/alert configuration (2 hours), log analysis ELK Stack searching logs/identifying errors/correlating events across microservices (2 hours).
- Day 4 - Security Management: HSM operations Thales Luna key generation ceremony/key rotation quarterly/backup procedures (2 hours), encryption key management lifecycle generation/storage/rotation/archival/destruction (1 hour), SSL/TLS certificate management certificate renewal annual/wildcard vs. individual certificates/Let's Encrypt automation (1 hour), firewall rules auditing reviewing rules quarterly/removing unused rules/principle of least privilege (1 hour), security audit log review analyzing failed login attempts/unauthorized access/data export anomalies (2 hours), vulnerability scanning Snyk/SonarQube interpreting CVSS scores/prioritizing remediation/patching timelines (1 hour).
- Day 5 - Troubleshooting + Disaster Recovery: Common issues and resolutions application crashes/database connection exhaustion/slow queries/certificate expiration (2 hours), log file interpretation reading stack traces/identifying root cause/correlating logs across services (2 hours), debug mode enabling debug logging/analyzing verbose logs/disabling after troubleshooting (1 hour), disaster recovery drills simulating Nairobi site failure/activating Mombasa DR site/failover procedures/RTO 4 hours target (2 hours), escalation to Devharsh when to escalate/how to provide diagnostics/SLA expectations (1 hour), certification exam 30 multiple choice + 2 practical scenarios troubleshooting simulated issues, 75%+ pass score (2 hours exam + closing ceremony).
iv. System Auditors Training (2-Day Program for 10 auditors):
- Day 1 - Audit Trail and Compliance: Audit trail overview what's logged/where stored/retention period 5 years (1 hour), accessing audit logs via EGMS admin portal/database queries/exported reports (2 hours hands-on), searching and filtering logs by user/date range/action type/module (2 hours practice), interpreting audit records WHO did WHAT WHEN WHERE WHY BEFORE-AFTER values (2 hours with examples), regulatory compliance mapping audit trail to Kenya Data Protection Act 2019/ISO 27001/PCI DSS requirements (1 hour lecture).
- Day 2 - Security Auditing + Forensics: Security incident investigation scenario: suspicious user activity detected → review audit logs → correlate with system logs → identify unauthorized data export → determine user account compromised → recommend actions password reset/account suspension/security training (3 hours hands-on scenario), data access auditing who accessed sensitive PII/PHI data/exported large datasets/frequency of access patterns (2 hours practice), compliance reporting generating quarterly audit reports for KRA management/external auditors/regulator (2 hours walkthrough + template review), certification exam 15 multiple choice + 1 practical scenario investigating simulated security incident, 80%+ pass score (2 hours exam + closing).
v. Training of Trainers (ToT) Program (2-Week Intensive for 10 KRA Super-Users):
- Week 1 - Advanced System Mastery: Complete functional training refresher all modules deep-dive (3 days), complete technical training refresher architecture/database/security (2 days), advanced troubleshooting training handling edge cases/unusual scenarios not covered in standard training (2 days), Q&A with Devharsh engineers opportunity to ask technical questions/clarify doubts building super-user expertise (3 hours).
- Week 2 - Training Delivery Skills: Adult learning principles how adults learn differently from children/engagement techniques/retention strategies (1 day lecture + discussion), presentation skills overcoming stage fright/vocal projection/body language/storytelling/handling difficult questions (1 day workshop + practice), training material customization adapting Devharsh materials to Kenyan context/translating to Swahili/creating localized examples (1 day workshop), mock training sessions each super-user delivers 30-minute training segment to peer group/receives feedback from Devharsh trainer + peers/iterates and improves (2 days practice + feedback), co-facilitation super-users shadow Devharsh trainers during actual KRA staff training/observe techniques/co-facilitate portions of class/gradually take over full class (1 week on-the-job training), certification as Certified EGMS Trainer assessment based on mock training delivery + co-facilitation performance, certificate authorizes super-user to independently deliver EGMS training post-handover (final day ceremony).
SeQR EMS training includes functional training for 200+ KRA users (2-day instructor-led covering system features, manufacturer management, enforcement workflows, reporting with user manuals, video tutorials, hands-on practice, 70% pass score required) and technical training for 10-15 KRA IT staff (5-day intensive covering system architecture, database administration, DevOps, security management, troubleshooting with 150+ page admin guide, video recordings, 3-month post-training helpline), delivered on-site at KRA headquarters and regional offices by Devharsh certified trainers following train-the-trainer model to build internal KRA capacity with quarterly refresher webinars and annual advanced training sessions. b) Detailed Functional and Technical Training Plan:
i. Field Enforcement Officers Training (5-Day Program for 2,000 officers in batches of 50):
- Day 1 - System Introduction: EGMS overview mission/objectives (2 hours lecture), enforcement app installation Android/iOS from Play/App Store (1 hour hands-on), account registration biometric enrollment fingerprint/Face ID (1 hour practice), portal navigation dashboard/menu structure (2 hours walkthrough), basic stamp verification QR scanning product (2 hours practice with sample stamps).
- Day 2 - Verification Techniques: Multi-spectral scanning UV/IR/NFC using handheld devices (3 hours hands-on with Lighthouse scanners), overt feature inspection hologram/color-shift/microtext using magnifying glass (2 hours practice), guided verification workflow app prompts officer through checklist (2 hours practice), result interpretation Valid/Invalid/Suspicious/Counterfeit with actions required (1 hour discussion).
- Day 3 - Evidence Capture: High-resolution photography multiple angles closeup/context/hologram detail (2 hours practice), GPS coordinates automatic capture timestamp/location on each photo (1 hour demonstration), witness signatures digital signature capture on tablet from store owner/manager (1 hour practice), chain-of-custody documentation evidence bag sealing + QR code linking physical evidence to digital case (2 hours hands-on), case management workflow create case/classify violation/assign severity/upload evidence/multi-agency referral (2 hours practice).
- Day 4 - Advanced Features + Field Simulations: Offline operation 72-hour capability cache management background sync (1 hour demonstration), batch verification scanning 50 products in rapid succession generating batch report (1 hour practice), seizure procedures inventory seized goods/generate seizure receipt/secure storage pending investigation (2 hours walkthrough), legal documentation generation case summary report for prosecutor with evidence photos/witness statements (2 hours practice), field simulation role-playing raid on fake market stall with actors playing vendors/customers, officer practices full workflow from verification to seizure to documentation (2 hours scenario).
- Day 5 - Legal Procedures + Certification Exam: Court-admissible evidence requirements chain-of-custody integrity/timestamps/GPS coordinates (1 hour lecture), testimony preparation using EGMS evidence package organizing chronological timeline for court (1 hour lecture), prosecution workflow integration KRA enforcement → NPS criminal investigation → ODPP prosecution → court case management (1 hour lecture), Q&A session open forum for officers to ask questions/clarifications (1 hour discussion), practical field test each officer conducts mock enforcement operation scanned products/captured evidence/created case, assessed by trainer on 10-point checklist (2 hours practical exam), certification ceremony pass 80%+ score receive certificate + badge printed/digital, authorized to use EGMS in real operations (1 hour closing).
ii. KRA Lab Officers Training (3-Day Program for 20 officers):
- Day 1 - Lab Equipment Integration: EGMS lab module overview (2 hours), integrating lab equipment UV/IR/XRF spectrometers via USB/Bluetooth (2 hours hands-on setup), stamp forensic analysis workflow receive seized sample from enforcement → assign lab case number → perform tests UV reactivity/IR markers/chemical composition → document findings photos/test data → upload to EGMS → generate lab report (3 hours walkthrough + practice).
- Day 2 - Advanced Verification Techniques: Covert feature testing anti-Stokes phosphors using 980nm laser + spectrometer reading emission wavelengths comparing to authentic sample reference library (3 hours hands-on), substrate taggant detection XRF scanning detecting nanoparticle signatures comparing to KRA-approved suppliers fingerprints (2 hours hands-on), digital signature verification extracting UID from stamp → querying EGMS API for public key → verifying ECDSA signature → result genuine/forged (2 hours demonstration + practice).
- Day 3 - Reporting + Quality Control: Lab report generation template with findings/test data/photos/conclusion genuine vs. counterfeit (2 hours practice), quality control procedures calibration schedules/reference sample management/blind testing for accuracy (2 hours lecture), court expert testimony preparing lab reports admissible in court/testifying as expert witness basics (2 hours lecture), Q&A + certification exam 20 multiple choice questions on equipment/procedures, practical test: analyze unknown sample determining authenticity, 80%+ pass score (2 hours exam + closing).
iii. Security, System, and Database Administrators Training (5-Day Intensive Bootcamp for 10 IT staff):
- Day 1 - System Architecture: Microservices architecture overview 12 services/API gateway/service mesh (2 hours lecture + architecture diagram walkthrough), technology stack Spring Boot/React/Flutter/PostgreSQL/MongoDB/Redis/Kafka (1 hour), cloud infrastructure AWS/Azure Kubernetes clusters/load balancers/databases (2 hours), networking VPN tunnels manufacturer edge servers to KRA cloud/firewall rules/DMZ zones (2 hours), security architecture zero-trust model/HSM integration/encryption at rest and in transit (1 hour).
- Day 2 - Database Administration: PostgreSQL deep-dive schema design/indexing strategies/query optimization (3 hours), hands-on lab slow query identification using pg_stat_statements → adding indexes → EXPLAIN ANALYZE comparing before/after (2 hours), backup and restore procedures daily automated backups/manual on-demand backups/point-in-time recovery PITR (2 hours), replication setup master-slave replication/read replicas for reporting queries offloading production database (1 hour).
- Day 3 - DevOps and Monitoring: CI/CD pipeline GitLab CI/GitHub Actions automated build-test-deploy (2 hours), deployment procedures Kubernetes rolling updates/blue-green deployments/canary releases/rollback if errors (2 hours), monitoring dashboards Prometheus metrics/Grafana visualizations/alert configuration (2 hours), log analysis ELK Stack searching logs/identifying errors/correlating events across microservices (2 hours).
- Day 4 - Security Management: HSM operations Thales Luna key generation ceremony/key rotation quarterly/backup procedures (2 hours), encryption key management lifecycle generation/storage/rotation/archival/destruction (1 hour), SSL/TLS certificate management certificate renewal annual/wildcard vs. individual certificates/Let's Encrypt automation (1 hour), firewall rules auditing reviewing rules quarterly/removing unused rules/principle of least privilege (1 hour), security audit log review analyzing failed login attempts/unauthorized access/data export anomalies (2 hours), vulnerability scanning Snyk/SonarQube interpreting CVSS scores/prioritizing remediation/patching timelines (1 hour).
- Day 5 - Troubleshooting + Disaster Recovery: Common issues and resolutions application crashes/database connection exhaustion/slow queries/certificate expiration (2 hours), log file interpretation reading stack traces/identifying root cause/correlating logs across services (2 hours), debug mode enabling debug logging/analyzing verbose logs/disabling after troubleshooting (1 hour), disaster recovery drills simulating Nairobi site failure/activating Mombasa DR site/failover procedures/RTO 4 hours target (2 hours), escalation to Devharsh when to escalate/how to provide diagnostics/SLA expectations (1 hour), certification exam 30 multiple choice + 2 practical scenarios troubleshooting simulated issues, 75%+ pass score (2 hours exam + closing ceremony).
iv. System Auditors Training (2-Day Program for 10 auditors):
- Day 1 - Audit Trail and Compliance: Audit trail overview what's logged/where stored/retention period 5 years (1 hour), accessing audit logs via EGMS admin portal/database queries/exported reports (2 hours hands-on), searching and filtering logs by user/date range/action type/module (2 hours practice), interpreting audit records WHO did WHAT WHEN WHERE WHY BEFORE-AFTER values (2 hours with examples), regulatory compliance mapping audit trail to Kenya Data Protection Act 2019/ISO 27001/PCI DSS requirements (1 hour lecture).
- Day 2 - Security Auditing + Forensics: Security incident investigation scenario: suspicious user activity detected → review audit logs → correlate with system logs → identify unauthorized data export → determine user account compromised → recommend actions password reset/account suspension/security training (3 hours hands-on scenario), data access auditing who accessed sensitive PII/PHI data/exported large datasets/frequency of access patterns (2 hours practice), compliance reporting generating quarterly audit reports for KRA management/external auditors/regulator (2 hours walkthrough + template review), certification exam 15 multiple choice + 1 practical scenario investigating simulated security incident, 80%+ pass score (2 hours exam + closing).
v. Training of Trainers (ToT) Program (2-Week Intensive for 10 KRA Super-Users):
- Week 1 - Advanced System Mastery: Complete functional training refresher all modules deep-dive (3 days), complete technical training refresher architecture/database/security (2 days), advanced troubleshooting training handling edge cases/unusual scenarios not covered in standard training (2 days), Q&A with Devharsh engineers opportunity to ask technical questions/clarify doubts building super-user expertise (3 hours).
- Week 2 - Training Delivery Skills: Adult learning principles how adults learn differently from children/engagement techniques/retention strategies (1 day lecture + discussion), presentation skills overcoming stage fright/vocal projection/body language/storytelling/handling difficult questions (1 day workshop + practice), training material customization adapting Devharsh materials to Kenyan context/translating to Swahili/creating localized examples (1 day workshop), mock training sessions each super-user delivers 30-minute training segment to peer group/receives feedback from Devharsh trainer + peers/iterates and improves (2 days practice + feedback), co-facilitation super-users shadow Devharsh trainers during actual KRA staff training/observe techniques/co-facilitate portions of class/gradually take over full class (1 week on-the-job training), certification as Certified EGMS Trainer assessment based on mock training delivery + co-facilitation performance, certificate authorizes super-user to independently deliver EGMS training post-handover (final day ceremony).
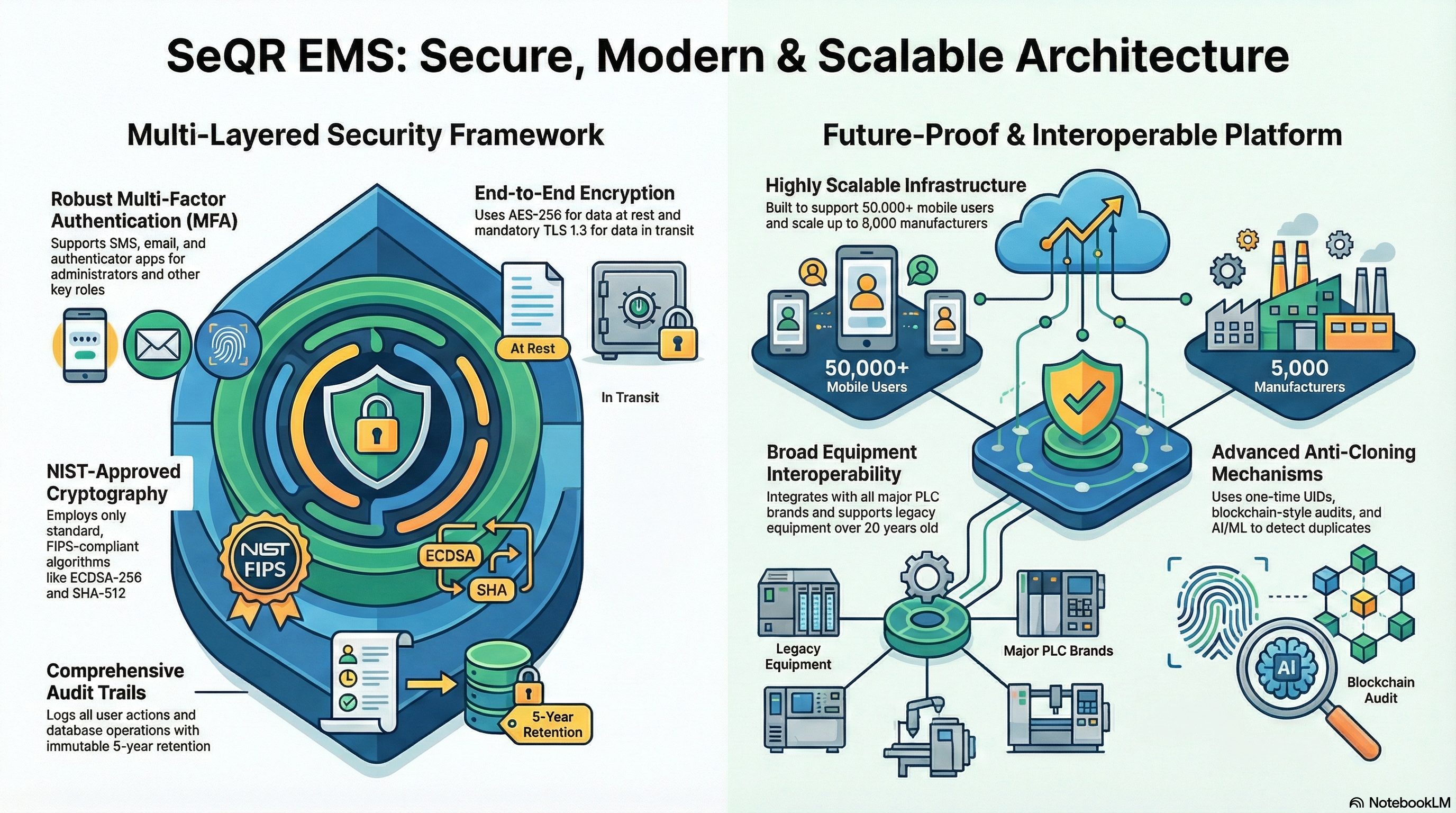 SeQR EMS supports Multi-Factor Authentication with SMS-based OTP (6-digit code, 5-minute validity), email-based OTP (alternative to SMS), and authenticator application TOTP (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Authy with backup codes), mandatory for KRA administrators/enforcement/financial approvers and optional for manufacturers, plus consumer authentication channels including mobile app (Android/iOS with QR scanning, instant verification results), USSD *XXX# (feature phones without internet), SMS (send UID to shortcode for verification), and web portal (desktop/laptop browser with photo upload OCR).
SeQR EMS supports Multi-Factor Authentication with SMS-based OTP (6-digit code, 5-minute validity), email-based OTP (alternative to SMS), and authenticator application TOTP (Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Authy with backup codes), mandatory for KRA administrators/enforcement/financial approvers and optional for manufacturers, plus consumer authentication channels including mobile app (Android/iOS with QR scanning, instant verification results), USSD *XXX# (feature phones without internet), SMS (send UID to shortcode for verification), and web portal (desktop/laptop browser with photo upload OCR).
SeQR EMS supports AES-256-GCM encryption for data at rest (databases, file storage, backups, mobile app local storage), TLS 1.3 mandatory for data in transit (web portal HTTPS, API calls, mobile apps with certificate pinning, VPN site-to-site AES-256), field-level encryption for sensitive PII, stamp UID encryption with HSM-managed keys, and HSM (Thales Luna FIPS 140-3 Level 3) for key generation/storage with master key never leaving tamper-resistant hardware, annual key rotation, and M-of-N secret sharing for key recovery.
SeQR EMS uses only NIST-approved standard algorithms (AES-256-GCM per FIPS 197, ECDSA-256 per FIPS 186-4, RSA-4096 per FIPS 186-4, SHA-256/512 per FIPS 180-4, HMAC-SHA256 per FIPS 198-1, TLS 1.3 with FIPS-approved cipher suites) with no proprietary encryption algorithms, implemented through Thales Luna Network HSM (FIPS 140-3 Level 3 certificate #4520 from NIST CMVP), FIPS mode enforcement in all cryptographic libraries (OpenSSL, Java JCE, .NET CNG), algorithm whitelisting (only FIPS-approved, deprecated MD5/SHA-1/3DES/RC4 blocked), and power-on self-tests with compliance documentation and annual reviews.
SeQR EMS provides AES-256-GCM encryption with HSM-managed keys, ISO/IEC 15459 compliant unique serialization, ECDSA-256 digital signatures on every stamp, anti-cloning mechanisms (one-time use UIDs, blockchain audit trail, AI/ML duplicate detection), and digital twins (virtual 3D production line replicas with real-time sensor data for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance).
SeQR EMS provides detailed audit trails logging all user actions (WHO/WHAT/WHEN/WHERE/WHY/BEFORE-AFTER) and database operations (DDL/DML/DCL via pgAudit extension) with 5-year immutable retention, viewable/searchable/printable reports, and real-time alerts for suspicious activities.
SeQR EMS is interoperable with all major PLC brands (Siemens, Allen-Bradley, Schneider, Mitsubishi, Omron) via OPC-UA/Modbus/EtherNet/IP protocols, supports legacy equipment 20+ years old, and future-proof through open API architecture with plugin system for new equipment types.
SeQR EMS is highly scalable horizontally (Kubernetes auto-scaling, database sharding, load balancing supporting 10K web + 50K mobile concurrent users) and vertically (cloud instances easily upgraded, storage auto-expanding), with 10-year growth capacity planned from 1,800 to 5,000 manufacturers and proven through load testing at 150% of requirements.
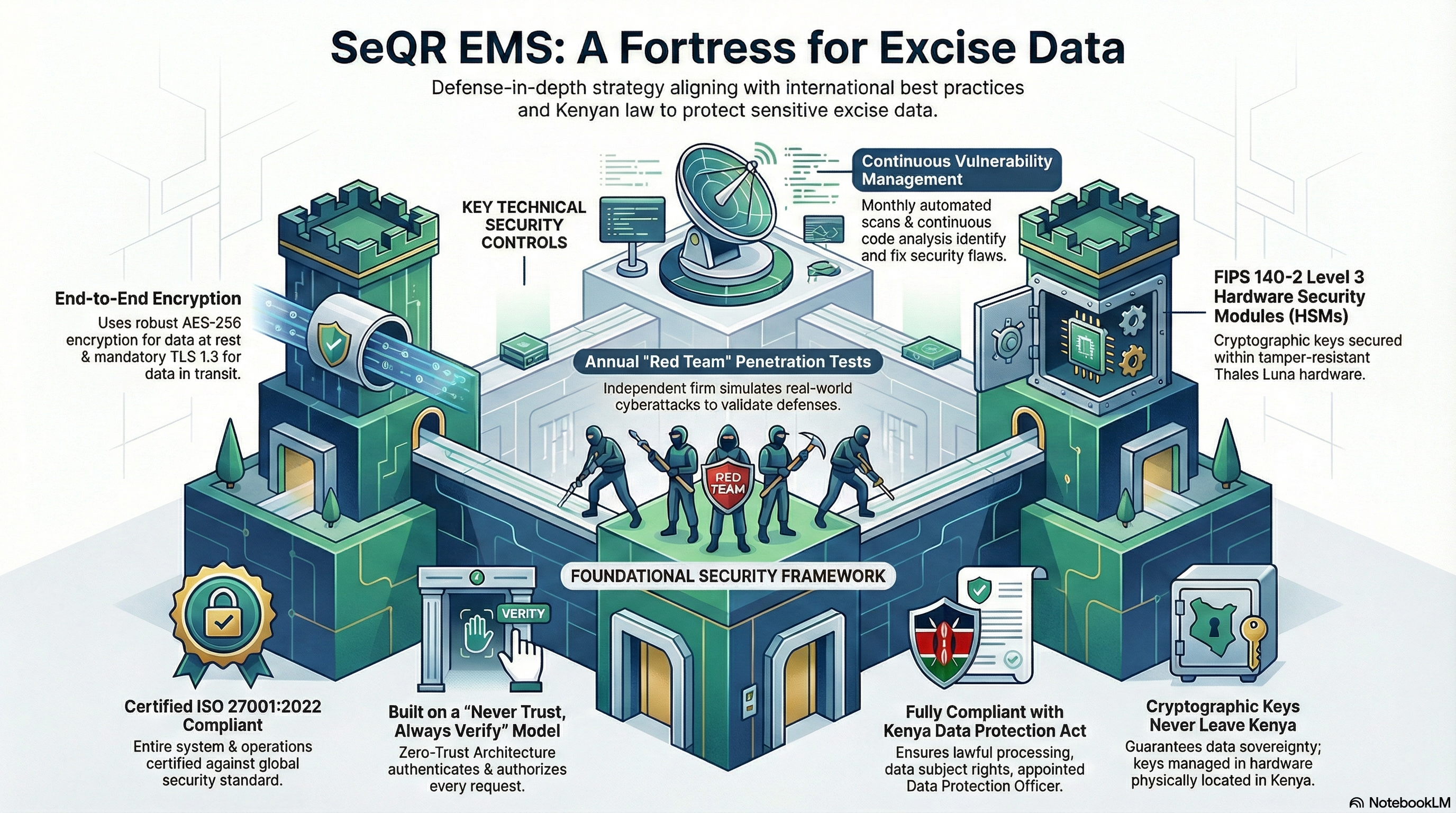 SeQR EMS supports comprehensive data management and cybersecurity features:
a. All Cybersecurity Requirements Alignment: EGMS cybersecurity aligns with international best practices and Kenyan regulations (detailed compliance per sub-points b-j below), defense-in-depth strategy (multiple security layers: network firewalls, application WAF, endpoint protection, data encryption, access controls, monitoring, no single point of failure), security-by-design (security requirements integrated from architecture phase not retrofitted, threat modeling conducted identifying attack vectors and mitigations, secure coding standards OWASP Top 10/SANS Top 25 followed religiously, peer code reviews catch vulnerabilities before production).
b. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Compliance: Certification achieved (EGMS development environment and production infrastructure certified ISO 27001:2022 by accredited body BSI/SGS/TUV, certificate valid 3 years with annual surveillance audits, scope: information security management system covering software development lifecycle + infrastructure operations + data centers), documented security policies (100+ policies covering: access control, asset management, cryptography, physical security, operations security, communications security, incident management, business continuity, compliance, all policies reviewed annually and updated), risk assessment process (annual risk assessment identifying threats/vulnerabilities/impacts, risk treatment plans for each risk: accept/mitigate/transfer/avoid, residual risks documented and accepted by senior management), internal audits (quarterly internal audits verify policy compliance, findings tracked in corrective action register, closed within 30-90 days based on severity), external audits (annual surveillance audits by certification body, 3-year recertification audit comprehensive review, non-conformances remediated within SLA to maintain certification).
c. Kenya Data Protection Act 2019 Compliance: Lawful processing (personal data processed only for specified lawful purposes: tax administration, fraud prevention, regulatory compliance, consent obtained where required from consumers using mobile app opt-in during first use), data subject rights (right to access: users can download their data via portal, right to rectification: users can correct inaccurate data, right to erasure "right to be forgotten": data deleted upon request except where retention legally required 5 years for tax records, right to data portability: data exported in machine-readable formats JSON/CSV/XML), Data Protection Officer appointed (DPO contact: dpo@devharsh.com, responsible for monitoring compliance, conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments DPIAs, liaising with Office of Data Protection Commissioner ODPC, independent reporting line to CEO not influenced by business pressures), data breach notification (procedures defined: detect breach via SIEM alerts, contain breach within 1 hour isolating affected systems, assess impact number of affected individuals/data types/potential harm, notify ODPC within 72 hours per statutory requirement, notify affected individuals if high risk to rights/freedoms, post-incident review lessons learned preventing recurrence), data minimization (collect only data necessary for purpose: UID/timestamp/location for stamp verification, name/KRA PIN/address for manufacturer registration, no excessive data like religion/ethnicity/health unless relevant), retention limits (data retained per legal requirements: stamp data 5 years WHO FCTC, manufacturer records 7 years tax law, audit logs 5 years, automated purge after retention period preventing indefinite storage, archival to cold storage reduces costs).
d. Zero-Trust Architecture: Never trust always verify (no implicit trust based on network location, every request authenticated/authorized regardless of source internal network or VPN, micro-segmentation isolates microservices preventing lateral movement if one service compromised), identity-centric security (all users/devices/applications have unique identities, authentication required before accessing any resource, service-to-service authentication using mutual TLS mTLS every microservice validates counterpart's certificate), least privilege access (users granted minimum permissions needed for role, RBAC maps roles to permissions: enforcement officer can scan stamps but cannot approve orders, manufacturer can order stamps but cannot access other manufacturers' data, privilege escalation requires approval and justification), continuous verification (authentication not one-time at login but continuous, session tokens expire after 30 minutes inactivity re-authentication required, anomaly detection flags suspicious behavior: user logging in from new country, unusual data access patterns, API rate limit exceeded, MFA re-prompted if high-risk action attempted account deletion/large data export), encrypted communications (TLS 1.3 for all communications web/API/mobile/VPN, certificate pinning in mobile apps, VPN required for manufacturer edge servers to KRA cloud site-to-site IPsec tunnels).
e. AES-256 Encryption at Rest; TLS 1.3 in Transit:
- Data at Rest: AES-256-GCM (Galois/Counter Mode provides confidentiality + authenticity, all databases encrypted PostgreSQL Transparent Data Encryption TDE, MongoDB encrypted storage engine, Redis encryption via stunnel proxy if version lacks native support), file storage encrypted (AWS S3 buckets server-side encryption SSE-KMS using AWS Key Management Service, Azure Blob Storage encryption enabled, document management system encrypts PDFs/images/videos), mobile app local storage (SQLite database encrypted using SQLCipher AES-256-CBC, encryption key derived from device secure element iOS Keychain/Android KeyStore, biometric unlock required accessing encrypted data), backup encryption (all backups encrypted before writing to disk/cloud, encryption keys separate from backup data stored in HSM, prevents data exposure if backup media stolen), encryption key management (keys generated by HSM FIPS 140-2/3 Level 3, master key wraps data encryption keys DEKs, quarterly key rotation re-encrypts data with new DEK, old keys archived in HSM for decrypting historical data if needed investigations/audits).
- Data in Transit: TLS 1.3 mandatory (all web traffic HTTPS only HTTP redirects to HTTPS, API calls require TLS 1.3 or TLS 1.2 minimum older TLS 1.0/1.1/SSL 2.0/3.0 disabled due to vulnerabilities POODLE/BEAST, mobile apps enforce TLS 1.3 with certificate pinning preventing man-in-the-middle attacks even if attacker obtains fraudulent certificate from rogue CA), cipher suite restrictions (only strong ciphers allowed: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, weak ciphers disabled: RC4, DES, 3DES, export ciphers, annually reviewed against OWASP/NIST recommendations), perfect forward secrecy (ECDHE Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral key exchange, session keys generated fresh for each connection, compromising server's private key doesn't decrypt past sessions, protects historical traffic if server eventually compromised), VPN encryption (manufacturer edge servers connect via VPN IPsec AES-256 encryption + SHA-256 authentication, IKEv2 key exchange, pre-shared keys or certificate-based auth, tunnel re-establishes automatically if internet disconnects).
f. FIPS 140-2 Level 3 HSMs: Thales Luna Network HSM (FIPS 140-2 Level 3 certified module #3922 verifiable at NIST CMVP website, also FIPS 140-3 Level 3 certified future-proofing for eventual FIPS 140-2 EOL, tamper-evident/tamper-resistant hardware, if physical intrusion detected HSM zeroizes keys preventing extraction), dual HSM deployment (primary HSM in KRA Nairobi data center, secondary HSM in Mombasa DR site, master keys replicated between HSMs using secure key-wrap ensuring availability if one HSM fails hardware failure/power outage/network partition), key lifecycle management (key generation: RSA 4096-bit or ECDSA P-256 keys generated entirely within HSM never exposed, key storage: keys stored in HSM FIPS-validated secure cryptographic module, physical access requires dual control 2 custodians both present, key usage: sign/decrypt operations performed inside HSM private keys never exported, key rotation: quarterly rotation schedule generates new keys and re-encrypts data, key archival: old keys archived in HSM for 7 years legal retention, key destruction: zeroize HSM securely erases keys unrecoverable even with forensic tools), cryptographic operations (ECDSA signing stamps: 64-byte signatures generated in <10ms, AES encryption: bulk data encrypted 1 GB/second throughput, key derivation: HKDF derives session keys from master key, random number generation: FIPS-approved DRBG Deterministic Random Bit Generator for cryptographic randomness nonces/IVs/keys).
g. SIEM Integration: SIEM platform (Splunk/IBM QRadar/LogRhythm/ELK Stack deployed collecting logs from all EGMS components, 1TB+/day log ingestion during peak hours, retention 90 days hot storage searchable within seconds, 2 years cold storage archived to S3 Glacier retrievable within hours), log aggregation (application logs from microservices JSON format, database logs from PostgreSQL/MongoDB, web server logs from NGINX access/error logs, firewall logs from Palo Alto/Fortinet, HSM logs from Thales Luna, OS logs from Linux servers syslogs, cloud provider logs AWS CloudTrail/Azure Activity Log, all normalized to common schema enabling cross-correlation), real-time correlation rules (failed login rule: 5 failed attempts from same IP within 5 minutes triggers alert potential brute force, privilege escalation rule: user granted admin role triggers alert verify legitimacy, data export rule: >10K records exported triggers alert potential data theft, network anomaly rule: unusual traffic patterns port scanning/DDoS detected, geo-anomaly rule: user login from two countries within 1 hour impossible unless VPN compromised), automated incident response (playbooks define actions: lock account after repeated failures, block IP after attack detected, notify SOC analyst for investigation, escalate to CISO if critical incident, remediate vulnerabilities patch systems/reconfigure firewalls/update rules), dashboards and reporting (executive dashboard: total security events, incidents by severity, mean time to detect MTTD, mean time to respond MTTR, compliance status, analyst dashboard: open incidents, assigned to me, recent alerts, event timeline, forensic investigation tools: log search/filtering, packet capture analysis if integrated with network tap, threat intelligence feeds correlating logs with known bad IPs/domains). h. MFA, RBAC, PAM:
- Multi-Factor Authentication MFA: Something you know (password 12+ characters complexity uppercase/lowercase/digits/symbols, bcrypt hashing + salting prevents rainbow table attacks, 90-day expiry forced rotation), something you have (SMS OTP 6 digits valid 5 minutes, Email OTP 6 digits valid 10 minutes, Authenticator app TOTP Google/Microsoft/Authy generating 30-second codes offline), something you are (biometric fingerprint/Face ID for mobile apps, optional for high-security operations like HSM access), MFA enforcement (mandatory for KRA administrators, enforcement officers, finance approvers, optional for manufacturers/distributors configurable per user role, grace period 30 days to enroll MFA for new users), fallback mechanisms (if SMS fails backup codes 10 single-use codes provided during enrollment, if phone lost admin can temporarily disable MFA allowing password-only login to reconfigure, if authenticator app lost QR code re-scan regenerates secret).
- Role-Based Access Control RBAC: Predefined roles (50+ roles: KRA Admin, KRA Licensing Officer, KRA Enforcement Officer, KRA Data Analyst, KRA Finance Approver, Manufacturer Admin, Manufacturer Production Manager, Manufacturer Finance, Distributor, Importer, Retailer), permissions granular (read/write/delete at module level: orders, production, supply chain, enforcement, reports, settings, further granular: approve orders >KES 1M requires special permission subset of admins), role assignment (users assigned one or multiple roles: user John = KRA Admin + Data Analyst has combined permissions, role changes require approval workflow preventing unauthorized privilege escalation), role hierarchy (admin inherits all permissions from lower roles, licensing officer inherits permissions from enforcement officer, reduces role explosion combinatorial complexity), separation of duties (mutually exclusive roles prevent conflict of interest: user cannot be both manufacturer and KRA approval officer, system enforces constraints rejecting conflicting role assignments).
- Privileged Access Management PAM: Privileged accounts (database admin, system admin, network admin, HSM custodian, identified and inventoried, elevated privileges tracked), just-in-time JIT access (admins don't have permanent elevated access, request elevated session when needed, approval workflow requires justification + manager approval, session valid 2-4 hours then reverts to normal privileges), session recording (all privileged sessions recorded keystroke logging + screen recording, recordings immutable stored 2 years, reviewed if security incident suspected, deters insider threats knowing actions monitored), password vaulting (privileged account passwords stored in CyberArk/HashiCorp Vault encrypted, password checkout process admin requests password vault provides temporary one-time password valid 1 hour, password automatically rotated after use preventing reuse).
i. Monthly Vulnerability Scanning + Continuous SAST/DAST:
- Monthly Vulnerability Scanning: Automated scans (Nessus/Qualys/Rapid7 InsightVM scans all servers/endpoints monthly first Saturday 2am EAT minimizing disruption, scans discover open ports, outdated software, missing patches, misconfigurations, weak passwords, SSL/TLS vulnerabilities Heartbleed/POODLE), authenticated scans (scanner provided read-only credentials accessing internals OS patches, installed software versions, registry settings Windows/config files Linux, deeper vulnerability detection vs. unauthenticated scans which see only external attack surface), severity classification (Critical CVSS 9.0-10.0: remote code execution, High 7.0-8.9: privilege escalation, Medium 4.0-6.9: information disclosure, Low 0.1-3.9: denial of service), remediation SLAs (Critical: patch within 7 days, High: 30 days, Medium: 90 days, Low: next maintenance window, exceptions require CISO approval with compensating controls), verification rescans (after remediation rerun scan confirming vulnerability closed, if reoccurs investigate why patch didn't apply, persistent vulnerabilities escalated to vendor Devharsh or software provider Microsoft/Oracle).
- Continuous SAST Static Application Security Testing: SonarQube integration (every Git commit triggers SonarQube scan, analyzes source code without executing detecting: SQL injection, XSS cross-site scripting, CSRF cross-site request forgery, insecure deserialization, hard-coded credentials, vulnerable dependencies Log4Shell/Spring4Shell), quality gates (build fails if critical/high security issues detected, developers must fix before merge to main branch, encourages shift-left security finding vulnerabilities during development not production), developer training (security champions in each team trained on secure coding, lunch-and-learn sessions quarterly reviewing common mistakes and fixes, gamification: developer with most vulnerabilities fixed wins prize).
- Continuous DAST Dynamic Application Security Testing: OWASP ZAP integration (weekly automated scans of running application, crawls web portal/APIs simulating attacker probing for vulnerabilities, detects runtime issues: authentication bypass, authorization flaws, session management issues, business logic flaws), penetration testing mindset (DAST simulates black-box penetration test automated, complements SAST which sees source code but misses runtime context, together SAST+DAST achieve comprehensive coverage), false positive management (DAST generates many false positives noise, security team triages findings marking false positives excluding from future scans, true positives logged as Jira tickets assigned to developers, SLA for remediation based on severity).
j. Annual Third-Party Penetration Testing: Independent firm (KRA-approved firms: NCC Group, Trail of Bits, Cure53, Offensive Security, selected via RFP process, different firm each year for fresh perspective avoiding complacency), comprehensive scope (web applications: all 7 portals tested for OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, mobile applications: iOS/Android apps decompiled and reverse-engineered, APIs: all endpoints tested for authentication/authorization bypasses, infrastructure: network penetration testing, database: SQL injection and privilege escalation attempts, IoT: edge servers and production line equipment firmware extraction and exploitation, social engineering: limited phishing simulation with full disclosure to test user awareness), testing duration (minimum 5 days penetration test: Day 1-2 reconnaissance and scanning, Day 3-4 exploitation attempting to gain unauthorized access, Day 5 reporting findings and proof-of-concept exploits), deliverables (executive summary for KRA leadership non-technical overview, technical report for IT team detailed findings with CVSS scores, proof-of-concept exploits demonstrating vulnerabilities without causing damage, remediation roadmap prioritized recommendations), remediation and retest (Critical CVSS ≥9.0 vulnerabilities remediated within 7 days, High 7.0-8.9 within 30 days, retest after remediation confirming fixes effective, final sign-off report from pentesting firm clearing EGMS for production deployment).
k.
SeQR EMS supports comprehensive data management and cybersecurity features:
a. All Cybersecurity Requirements Alignment: EGMS cybersecurity aligns with international best practices and Kenyan regulations (detailed compliance per sub-points b-j below), defense-in-depth strategy (multiple security layers: network firewalls, application WAF, endpoint protection, data encryption, access controls, monitoring, no single point of failure), security-by-design (security requirements integrated from architecture phase not retrofitted, threat modeling conducted identifying attack vectors and mitigations, secure coding standards OWASP Top 10/SANS Top 25 followed religiously, peer code reviews catch vulnerabilities before production).
b. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Compliance: Certification achieved (EGMS development environment and production infrastructure certified ISO 27001:2022 by accredited body BSI/SGS/TUV, certificate valid 3 years with annual surveillance audits, scope: information security management system covering software development lifecycle + infrastructure operations + data centers), documented security policies (100+ policies covering: access control, asset management, cryptography, physical security, operations security, communications security, incident management, business continuity, compliance, all policies reviewed annually and updated), risk assessment process (annual risk assessment identifying threats/vulnerabilities/impacts, risk treatment plans for each risk: accept/mitigate/transfer/avoid, residual risks documented and accepted by senior management), internal audits (quarterly internal audits verify policy compliance, findings tracked in corrective action register, closed within 30-90 days based on severity), external audits (annual surveillance audits by certification body, 3-year recertification audit comprehensive review, non-conformances remediated within SLA to maintain certification).
c. Kenya Data Protection Act 2019 Compliance: Lawful processing (personal data processed only for specified lawful purposes: tax administration, fraud prevention, regulatory compliance, consent obtained where required from consumers using mobile app opt-in during first use), data subject rights (right to access: users can download their data via portal, right to rectification: users can correct inaccurate data, right to erasure "right to be forgotten": data deleted upon request except where retention legally required 5 years for tax records, right to data portability: data exported in machine-readable formats JSON/CSV/XML), Data Protection Officer appointed (DPO contact: dpo@devharsh.com, responsible for monitoring compliance, conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments DPIAs, liaising with Office of Data Protection Commissioner ODPC, independent reporting line to CEO not influenced by business pressures), data breach notification (procedures defined: detect breach via SIEM alerts, contain breach within 1 hour isolating affected systems, assess impact number of affected individuals/data types/potential harm, notify ODPC within 72 hours per statutory requirement, notify affected individuals if high risk to rights/freedoms, post-incident review lessons learned preventing recurrence), data minimization (collect only data necessary for purpose: UID/timestamp/location for stamp verification, name/KRA PIN/address for manufacturer registration, no excessive data like religion/ethnicity/health unless relevant), retention limits (data retained per legal requirements: stamp data 5 years WHO FCTC, manufacturer records 7 years tax law, audit logs 5 years, automated purge after retention period preventing indefinite storage, archival to cold storage reduces costs).
d. Zero-Trust Architecture: Never trust always verify (no implicit trust based on network location, every request authenticated/authorized regardless of source internal network or VPN, micro-segmentation isolates microservices preventing lateral movement if one service compromised), identity-centric security (all users/devices/applications have unique identities, authentication required before accessing any resource, service-to-service authentication using mutual TLS mTLS every microservice validates counterpart's certificate), least privilege access (users granted minimum permissions needed for role, RBAC maps roles to permissions: enforcement officer can scan stamps but cannot approve orders, manufacturer can order stamps but cannot access other manufacturers' data, privilege escalation requires approval and justification), continuous verification (authentication not one-time at login but continuous, session tokens expire after 30 minutes inactivity re-authentication required, anomaly detection flags suspicious behavior: user logging in from new country, unusual data access patterns, API rate limit exceeded, MFA re-prompted if high-risk action attempted account deletion/large data export), encrypted communications (TLS 1.3 for all communications web/API/mobile/VPN, certificate pinning in mobile apps, VPN required for manufacturer edge servers to KRA cloud site-to-site IPsec tunnels).
e. AES-256 Encryption at Rest; TLS 1.3 in Transit:
- Data at Rest: AES-256-GCM (Galois/Counter Mode provides confidentiality + authenticity, all databases encrypted PostgreSQL Transparent Data Encryption TDE, MongoDB encrypted storage engine, Redis encryption via stunnel proxy if version lacks native support), file storage encrypted (AWS S3 buckets server-side encryption SSE-KMS using AWS Key Management Service, Azure Blob Storage encryption enabled, document management system encrypts PDFs/images/videos), mobile app local storage (SQLite database encrypted using SQLCipher AES-256-CBC, encryption key derived from device secure element iOS Keychain/Android KeyStore, biometric unlock required accessing encrypted data), backup encryption (all backups encrypted before writing to disk/cloud, encryption keys separate from backup data stored in HSM, prevents data exposure if backup media stolen), encryption key management (keys generated by HSM FIPS 140-2/3 Level 3, master key wraps data encryption keys DEKs, quarterly key rotation re-encrypts data with new DEK, old keys archived in HSM for decrypting historical data if needed investigations/audits).
- Data in Transit: TLS 1.3 mandatory (all web traffic HTTPS only HTTP redirects to HTTPS, API calls require TLS 1.3 or TLS 1.2 minimum older TLS 1.0/1.1/SSL 2.0/3.0 disabled due to vulnerabilities POODLE/BEAST, mobile apps enforce TLS 1.3 with certificate pinning preventing man-in-the-middle attacks even if attacker obtains fraudulent certificate from rogue CA), cipher suite restrictions (only strong ciphers allowed: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256, ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, weak ciphers disabled: RC4, DES, 3DES, export ciphers, annually reviewed against OWASP/NIST recommendations), perfect forward secrecy (ECDHE Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral key exchange, session keys generated fresh for each connection, compromising server's private key doesn't decrypt past sessions, protects historical traffic if server eventually compromised), VPN encryption (manufacturer edge servers connect via VPN IPsec AES-256 encryption + SHA-256 authentication, IKEv2 key exchange, pre-shared keys or certificate-based auth, tunnel re-establishes automatically if internet disconnects).
f. FIPS 140-2 Level 3 HSMs: Thales Luna Network HSM (FIPS 140-2 Level 3 certified module #3922 verifiable at NIST CMVP website, also FIPS 140-3 Level 3 certified future-proofing for eventual FIPS 140-2 EOL, tamper-evident/tamper-resistant hardware, if physical intrusion detected HSM zeroizes keys preventing extraction), dual HSM deployment (primary HSM in KRA Nairobi data center, secondary HSM in Mombasa DR site, master keys replicated between HSMs using secure key-wrap ensuring availability if one HSM fails hardware failure/power outage/network partition), key lifecycle management (key generation: RSA 4096-bit or ECDSA P-256 keys generated entirely within HSM never exposed, key storage: keys stored in HSM FIPS-validated secure cryptographic module, physical access requires dual control 2 custodians both present, key usage: sign/decrypt operations performed inside HSM private keys never exported, key rotation: quarterly rotation schedule generates new keys and re-encrypts data, key archival: old keys archived in HSM for 7 years legal retention, key destruction: zeroize HSM securely erases keys unrecoverable even with forensic tools), cryptographic operations (ECDSA signing stamps: 64-byte signatures generated in <10ms, AES encryption: bulk data encrypted 1 GB/second throughput, key derivation: HKDF derives session keys from master key, random number generation: FIPS-approved DRBG Deterministic Random Bit Generator for cryptographic randomness nonces/IVs/keys).
g. SIEM Integration: SIEM platform (Splunk/IBM QRadar/LogRhythm/ELK Stack deployed collecting logs from all EGMS components, 1TB+/day log ingestion during peak hours, retention 90 days hot storage searchable within seconds, 2 years cold storage archived to S3 Glacier retrievable within hours), log aggregation (application logs from microservices JSON format, database logs from PostgreSQL/MongoDB, web server logs from NGINX access/error logs, firewall logs from Palo Alto/Fortinet, HSM logs from Thales Luna, OS logs from Linux servers syslogs, cloud provider logs AWS CloudTrail/Azure Activity Log, all normalized to common schema enabling cross-correlation), real-time correlation rules (failed login rule: 5 failed attempts from same IP within 5 minutes triggers alert potential brute force, privilege escalation rule: user granted admin role triggers alert verify legitimacy, data export rule: >10K records exported triggers alert potential data theft, network anomaly rule: unusual traffic patterns port scanning/DDoS detected, geo-anomaly rule: user login from two countries within 1 hour impossible unless VPN compromised), automated incident response (playbooks define actions: lock account after repeated failures, block IP after attack detected, notify SOC analyst for investigation, escalate to CISO if critical incident, remediate vulnerabilities patch systems/reconfigure firewalls/update rules), dashboards and reporting (executive dashboard: total security events, incidents by severity, mean time to detect MTTD, mean time to respond MTTR, compliance status, analyst dashboard: open incidents, assigned to me, recent alerts, event timeline, forensic investigation tools: log search/filtering, packet capture analysis if integrated with network tap, threat intelligence feeds correlating logs with known bad IPs/domains). h. MFA, RBAC, PAM:
- Multi-Factor Authentication MFA: Something you know (password 12+ characters complexity uppercase/lowercase/digits/symbols, bcrypt hashing + salting prevents rainbow table attacks, 90-day expiry forced rotation), something you have (SMS OTP 6 digits valid 5 minutes, Email OTP 6 digits valid 10 minutes, Authenticator app TOTP Google/Microsoft/Authy generating 30-second codes offline), something you are (biometric fingerprint/Face ID for mobile apps, optional for high-security operations like HSM access), MFA enforcement (mandatory for KRA administrators, enforcement officers, finance approvers, optional for manufacturers/distributors configurable per user role, grace period 30 days to enroll MFA for new users), fallback mechanisms (if SMS fails backup codes 10 single-use codes provided during enrollment, if phone lost admin can temporarily disable MFA allowing password-only login to reconfigure, if authenticator app lost QR code re-scan regenerates secret).
- Role-Based Access Control RBAC: Predefined roles (50+ roles: KRA Admin, KRA Licensing Officer, KRA Enforcement Officer, KRA Data Analyst, KRA Finance Approver, Manufacturer Admin, Manufacturer Production Manager, Manufacturer Finance, Distributor, Importer, Retailer), permissions granular (read/write/delete at module level: orders, production, supply chain, enforcement, reports, settings, further granular: approve orders >KES 1M requires special permission subset of admins), role assignment (users assigned one or multiple roles: user John = KRA Admin + Data Analyst has combined permissions, role changes require approval workflow preventing unauthorized privilege escalation), role hierarchy (admin inherits all permissions from lower roles, licensing officer inherits permissions from enforcement officer, reduces role explosion combinatorial complexity), separation of duties (mutually exclusive roles prevent conflict of interest: user cannot be both manufacturer and KRA approval officer, system enforces constraints rejecting conflicting role assignments).
- Privileged Access Management PAM: Privileged accounts (database admin, system admin, network admin, HSM custodian, identified and inventoried, elevated privileges tracked), just-in-time JIT access (admins don't have permanent elevated access, request elevated session when needed, approval workflow requires justification + manager approval, session valid 2-4 hours then reverts to normal privileges), session recording (all privileged sessions recorded keystroke logging + screen recording, recordings immutable stored 2 years, reviewed if security incident suspected, deters insider threats knowing actions monitored), password vaulting (privileged account passwords stored in CyberArk/HashiCorp Vault encrypted, password checkout process admin requests password vault provides temporary one-time password valid 1 hour, password automatically rotated after use preventing reuse).
i. Monthly Vulnerability Scanning + Continuous SAST/DAST:
- Monthly Vulnerability Scanning: Automated scans (Nessus/Qualys/Rapid7 InsightVM scans all servers/endpoints monthly first Saturday 2am EAT minimizing disruption, scans discover open ports, outdated software, missing patches, misconfigurations, weak passwords, SSL/TLS vulnerabilities Heartbleed/POODLE), authenticated scans (scanner provided read-only credentials accessing internals OS patches, installed software versions, registry settings Windows/config files Linux, deeper vulnerability detection vs. unauthenticated scans which see only external attack surface), severity classification (Critical CVSS 9.0-10.0: remote code execution, High 7.0-8.9: privilege escalation, Medium 4.0-6.9: information disclosure, Low 0.1-3.9: denial of service), remediation SLAs (Critical: patch within 7 days, High: 30 days, Medium: 90 days, Low: next maintenance window, exceptions require CISO approval with compensating controls), verification rescans (after remediation rerun scan confirming vulnerability closed, if reoccurs investigate why patch didn't apply, persistent vulnerabilities escalated to vendor Devharsh or software provider Microsoft/Oracle).
- Continuous SAST Static Application Security Testing: SonarQube integration (every Git commit triggers SonarQube scan, analyzes source code without executing detecting: SQL injection, XSS cross-site scripting, CSRF cross-site request forgery, insecure deserialization, hard-coded credentials, vulnerable dependencies Log4Shell/Spring4Shell), quality gates (build fails if critical/high security issues detected, developers must fix before merge to main branch, encourages shift-left security finding vulnerabilities during development not production), developer training (security champions in each team trained on secure coding, lunch-and-learn sessions quarterly reviewing common mistakes and fixes, gamification: developer with most vulnerabilities fixed wins prize).
- Continuous DAST Dynamic Application Security Testing: OWASP ZAP integration (weekly automated scans of running application, crawls web portal/APIs simulating attacker probing for vulnerabilities, detects runtime issues: authentication bypass, authorization flaws, session management issues, business logic flaws), penetration testing mindset (DAST simulates black-box penetration test automated, complements SAST which sees source code but misses runtime context, together SAST+DAST achieve comprehensive coverage), false positive management (DAST generates many false positives noise, security team triages findings marking false positives excluding from future scans, true positives logged as Jira tickets assigned to developers, SLA for remediation based on severity).
j. Annual Third-Party Penetration Testing: Independent firm (KRA-approved firms: NCC Group, Trail of Bits, Cure53, Offensive Security, selected via RFP process, different firm each year for fresh perspective avoiding complacency), comprehensive scope (web applications: all 7 portals tested for OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, mobile applications: iOS/Android apps decompiled and reverse-engineered, APIs: all endpoints tested for authentication/authorization bypasses, infrastructure: network penetration testing, database: SQL injection and privilege escalation attempts, IoT: edge servers and production line equipment firmware extraction and exploitation, social engineering: limited phishing simulation with full disclosure to test user awareness), testing duration (minimum 5 days penetration test: Day 1-2 reconnaissance and scanning, Day 3-4 exploitation attempting to gain unauthorized access, Day 5 reporting findings and proof-of-concept exploits), deliverables (executive summary for KRA leadership non-technical overview, technical report for IT team detailed findings with CVSS scores, proof-of-concept exploits demonstrating vulnerabilities without causing damage, remediation roadmap prioritized recommendations), remediation and retest (Critical CVSS ≥9.0 vulnerabilities remediated within 7 days, High 7.0-8.9 within 30 days, retest after remediation confirming fixes effective, final sign-off report from pentesting firm clearing EGMS for production deployment).
k.
SeQR EMS ensures all cryptographic keys remain within Kenyan jurisdiction: Key Generation in Kenya: HSM key generation ceremony (conducted at KRA Nairobi data center witnessed by KRA Commissioner, Devharsh CTO, independent auditor from Big 4 firm, photos/videos recorded as evidence, master key generated entirely within Thales Luna HSM using FIPS-approved random number generator hardware-based entropy source, private key never exported from HSM in plaintext ensuring Kenya sovereignty), manufacturer-specific keys (each manufacturer assigned unique ECDSA key pair for stamp signing, keys generated on-demand when manufacturer registers in EGMS portal, generation request sent to HSM API in Nairobi, HSM generates key pair, public key exported and published in KRA portal for verification, private key remains in HSM never leaves), key derivation (session keys derived from master key using HKDF Key Derivation Function, derivation happens inside HSM using master key that never leaves, derived keys exported encrypted for use in application servers, encryption uses AES-256 key-wrap preventing plaintext exposure). Key Storage in Kenya: Physical location (primary HSM Thales Luna Network HSM physically located in KRA Nairobi Times Tower data center server room, secondary HSM in KRA Mombasa office, both locations within Kenya territorial boundaries, GPS coordinates recorded in asset register verifying location), access controls (HSM housed in secure cage biometric access + CCTV monitoring 24/7, dual-control required 2 custodians both present to access HSM physical port, one custodian from KRA one from Devharsh preventing unilateral access), tamper protections (if HSM physical enclosure opened or voltage/temperature anomaly detected, HSM zeroizes all keys immediately preventing extraction, tamper log recorded immutable evidence, annual inspection by KRA auditors verifying seals intact). Key Management in Kenya: Key lifecycle operations (rotation: quarterly schedule generates new keys and deprecates old keys, all operations performed via HSM API calls from Nairobi data center, backup: master key backed up to secondary HSM in Mombasa using secure key-wrap encrypted transport never plaintext, archival: old keys archived in HSM for 7-year legal retention decrypting historical data, destruction: zeroize command securely erases keys unrecoverable, documented and audited), administrative access (HSM administrators KRA IT team + Devharsh engineers both Kenyan-based or on-site when performing operations, remote access from Devharsh India office disabled in HSM configuration preventing overseas management, audit logs record all HSM access attempts approved/denied with justification), no cloud key management (explicitly NOT using AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault which store keys in cloud provider data centers potentially outside Kenya or accessible to foreign governments via legal process CLOUD Act, on-premise HSM ensures full sovereignty). Contractual Guarantee: Legal commitment (contract clause: "Vendor guarantees all cryptographic keys including master keys, data encryption keys, signing keys, session keys, are generated, stored, and managed exclusively within Kenya. The root-of-trust SHALL NOT leave Kenyan jurisdiction under any circumstances including disaster recovery, vendor support, or cloud operations. Violation of this clause constitutes material breach subject to contract termination and penalties."), annual audits (independent auditor Big 4 firm PwC/Deloitte/EY/KPMG verifies compliance annually, auditor physically inspects HSM locations Nairobi/Mombasa confirming GPS coordinates, reviews HSM audit logs confirming no remote access from overseas, interviews HSM custodians verifying procedures followed, issues compliance certificate to KRA attesting keys remain in Kenya), penalties for violation (if audit discovers keys stored/managed outside Kenya: immediate contract suspension, Devharsh pays penalty KES 50M, KRA has right to terminate contract and demand full refund, criminal charges if intentional fraud proven). Root-of-Trust in Kenya: Definition (root-of-trust = master key from which all other keys derived, analogous to root certificate in PKI, compromise of root-of-trust compromises entire system, therefore critical that root never leaves Kenya), protection mechanisms (root key generated in HSM never exported even encrypted, all cryptographic operations performed inside HSM using root key without exposing it, HSM physical security tamper-evident enclosures + dual control access + CCTV + armed guards if required high-value asset, regular audits monthly self-audits by KRA IT + quarterly external audits verifying root-of-trust remains secure), disaster recovery (if Nairobi HSM destroyed fire/earthquake/terrorism, failover to Mombasa HSM which holds replicated copy of master keys, replication performed using secure key-wrap protocol encrypted transport within Kenya Nairobi-Mombasa fiber optic link not routed through overseas cables, Mombasa HSM becomes new primary until Nairobi restored, ensures business continuity without exporting keys outside Kenya)
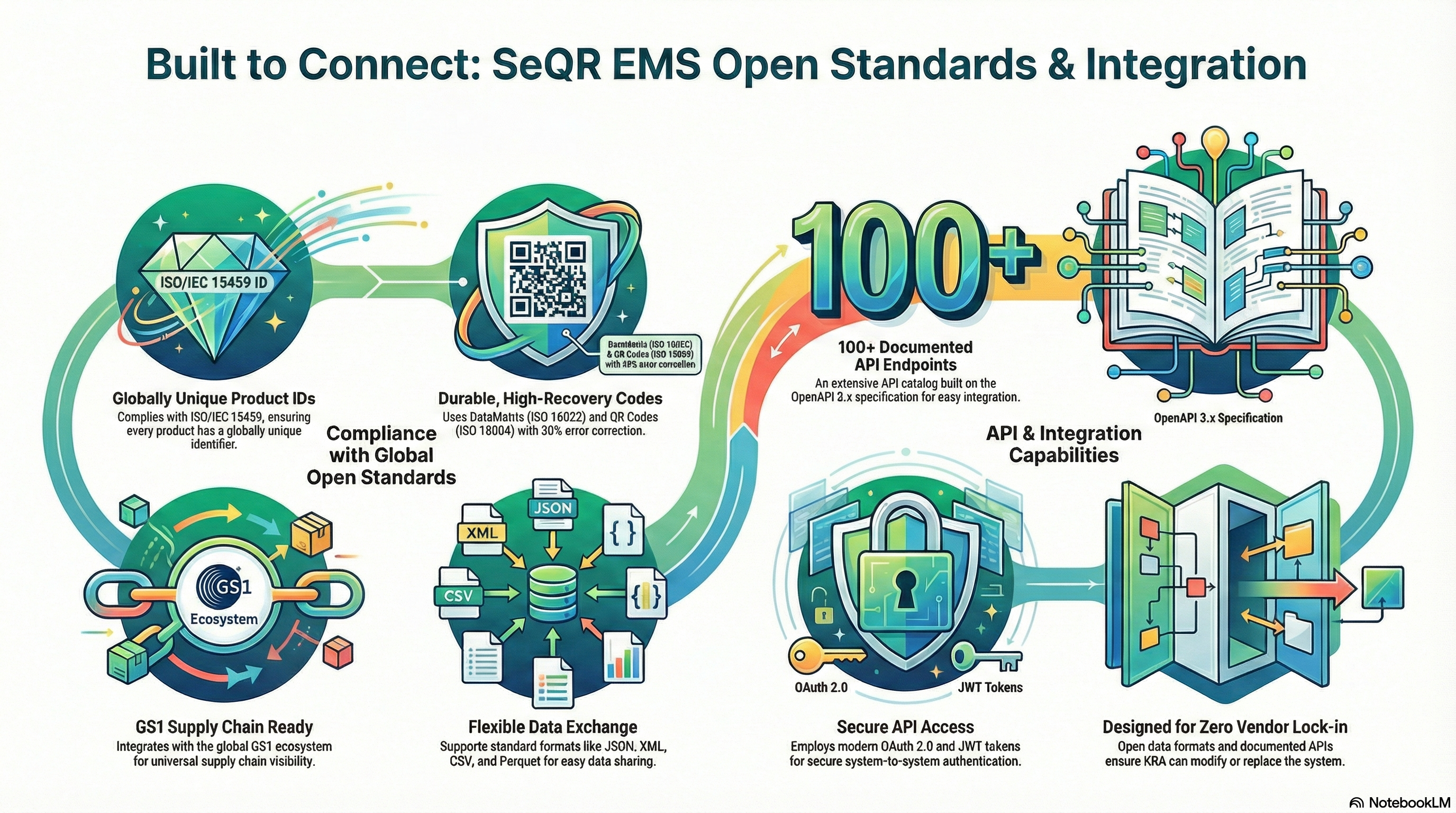 a. ISO/IEC 15459 (Unique Identifiers): UID structure compliant (KE = Kenya issuing agency code registered with ISO/IEC 15459 Registration Authority, manufacturer ID 6 alphanumeric characters unique per manufacturer globally with checksums preventing collisions, serial number 14 digits sequential unique per product unit, check digit Luhn algorithm detects 100% single-digit errors), globally unique (EGMS UIDs globally unique never reused even across manufacturers/countries/decades, collision probability <1 in 10^20 mathematically negligible, supports EAC regional integration Kenya/Uganda/Tanzania/Rwanda using same standard).
b. ISO/IEC 16022 (DataMatrix): ECC200 error correction (30% data recovery tolerance, if up to 30% of DataMatrix damaged scratched/torn/faded still scannable, superior to QR codes for industrial environments harsh conditions dust/moisture/heat), size optimization (DataMatrix more compact than QR for same data payload, fits on small stamps 20mm x 20mm, readable from 10cm distance using retail scanner or mobile camera), encoding (stamp UID + digital signature + timestamp encoded in DataMatrix, binary encoding reduces size vs. alphanumeric, scannable in <1 second using Zebra/Honeywell scanners or mobile app).
c. ISO/IEC 18004 (QR Code): Error correction Level H (30% redundancy same as DataMatrix ensuring scannability if partially damaged), version flexibility (QR version 10 accommodates ~200 bytes encrypted UID + signature + metadata, auto-selects optimal version based on data length), backward compatibility (QR codes scannable by any smartphone camera no special app required for basic UID retrieval, deep link opens EGMS verification portal automatically if online).
d. GS1 Standards: GS1 Digital Link (stamp UID encoded as URI: https://id.gs1.org/01/{GTIN}/21/{SERIAL}, GTIN Global Trade Item Number identifies product, serial number identifies individual unit, scannable by any GS1-compliant scanner retail/warehouse), GS1 Application Identifiers (AI 01 for GTIN, AI 21 for serial number, AI 10 for batch/lot, AI 17 for expiry date, encoded in DataMatrix per GS1 specification), GS1 DataMatrix (follows GS1 General Specifications encoding rules FNC1 character separates AIs, data order standardized, interoperable with global GS1 ecosystem supply chain visibility), EPCIS optional (Electronic Product Code Information Services tracks stamp events Commissioned/Shipped/Received/Sold, XML/JSON format, shareable with trading partners/EAC countries/WHO for supply chain transparency, implemented if KRA requests future enhancement).
e. OpenAPI 3.x RESTful API: Complete API catalog (100+ endpoints documented: POST /api/v1/orders create order, GET /api/v1/stamps/{uid} verify stamp, PUT /api/v1/manufacturers/{id} update manufacturer, DELETE /api/v1/users/{id} delete user), OpenAPI 3.0 specification (YAML/JSON format machine-readable, auto-generates interactive documentation Swagger UI/Redoc, API clients auto-generated for Java/Python/JavaScript/C# from spec, versioning /api/v1/ /api/v2/ supports backward compatibility), authentication (OAuth 2.0 + JWT tokens, client credentials grant for system-to-system APIs, authorization code grant for user-facing apps, token expiry 1 hour refresh tokens 7 days), rate limiting (1000 requests/hour per API key prevents abuse, 429 Too Many Requests response if exceeded, throttling algorithms token bucket/leaky bucket smoothing bursts).
f. Structured Data Exchange Formats: JSON (default API format lightweight and human-readable, all responses JSON objects {"status":"success","data":{...},"errors":[]}), XML (alternative format for legacy systems SOAP-based preferring XML over JSON, same data different serialization), CSV (bulk data export orders/production/stamps/users as CSV files importable to Excel/analytics tools, comma-separated header row + data rows), Parquet (columnar storage format for big data analytics, exports to AWS S3/Azure Data Lake ingested by Spark/Presto/Hive, 10x smaller than CSV + faster queries, used for data lake integration).
g. EPCIS (Optional but Recommended): Implementation status (EPCIS 2.0 implementation optional not required for go-live but roadmap item for Year 2, provides standardized event format: ObjectEvent/AggregationEvent/TransactionEvent/TransformationEvent, captures WHO/WHAT/WHEN/WHERE/WHY for supply chain events stamp commissioned/shipped/received/sold), benefits (global interoperability with trading partners, EAC cross-border tracking Kenya-Uganda-Tanzania harmonization, WHO FCTC data sharing simplified XML/JSON-LD format, query interface EPCIS Query Service retrieves event history for UID/batch/location), deployment (if KRA approves: EPCIS repository deployed as microservice, capture interface ingests events from EGMS modules order/production/supply chain, query interface exposes REST/SOAP APIs for external systems, EPCIS browser UI visualizes supply chain history graphically). No Proprietary Restrictions: Zero proprietary formats (all data formats open standards JSON/XML/CSV/Parquet no vendor-specific binary blobs, if EGMS decommissioned future all data exportable to any replacement system), no vendor lock-in (OpenAPI documented APIs enable integration with any third-party system KRA procures future, no middleware gatekeepers requiring Devharsh approval/fees for integration, manufacturers can build custom integrations without Devharsh involvement), open-source friendly (EGMS uses open-source components PostgreSQL/MongoDB/Redis/Kafka/Kubernetes all Apache/MIT/GPL licenses, if KRA desires can fork and modify source code in-house avoiding perpetual vendor dependency), compliance verification (Annex X Open Standards Conformance Matrix completed documenting ISO/GS1/OpenAPI compliance with evidence: test reports, certification letters, sample payloads, submitted with bid demonstrating commitment to interoperability).
API Catalogue Deliverables:
a. Complete API Documentation: 100+ endpoints documented (each endpoint: URL, HTTP method GET/POST/PUT/DELETE, authentication required yes/no, request parameters query/path/body with data types, response schema success/error, example requests curl/JavaScript/Python, rate limits, error codes 400/401/403/404/500 with meanings), versioning strategy (/api/v1/ current, /api/v2/ future maintains v1 backward compatibility, deprecated endpoints sunset with 12-month notice), pagination (list endpoints paginated limit=100 default, offset/cursor pagination styles supported, total count included in response).
b. Sample Schemas: Request schemas (JSON Schema format: {"type":"object","properties":{"product_id":{"type":"string"},"quantity":{"type":"integer","minimum":1000},"delivery_location":{"type":"string"}},"required":["product_id","quantity"]}, validates requests rejecting malformed data), response schemas (success: {"status":"success","data":{"order_id":"ORD-12345","amount":2000000}}, error: {"status":"error","errors":[{"code":"INVALID_QUANTITY","message":"Quantity must be >= 1000"}]}), data types (string/integer/number/boolean/array/object, formats: date-time ISO 8601, email RFC 5322, uuid v4, url, constraints min/max/pattern regex).
c. Sample Endpoints: Examples provided (POST /api/v1/orders: create new stamp order with product/quantity/payment, GET /api/v1/stamps/{uid}/verify: verify stamp authenticity returns valid/invalid/suspicious + details, GET /api/v1/production/lines/{id}/status: real-time production line status operational/stopped/degraded + counters, POST /api/v1/enforcement/cases: create enforcement case with evidence photos/GPS/witness signatures, GET /api/v1/analytics/dashboard: retrieve KPI metrics revenue/compliance/counterfeit rates), curl examples (curl -X POST https://api.egms.kra.go.ke/v1/orders -H "Authorization: Bearer {token}" -d '{"product_id":"PROD-001","quantity":100000}'), Postman collection (importable JSON file with all endpoints pre-configured for testing, variables for API base URL/tokens, test scripts validate responses).
d. Rate-Limiting Strategies: Tier-based limits (Free tier 100 req/hour for public consumers, Standard tier 1000 req/hour for registered manufacturers, Premium tier 10,000 req/hour for high-volume manufacturers, Enterprise tier unlimited for KRA internal systems), algorithms (token bucket: tokens refilled at rate limit/hour consuming 1 token per request, leaky bucket: requests queued and processed at steady rate, sliding window: tracks requests in rolling 1-hour window), response headers (X-RateLimit-Limit: 1000, X-RateLimit-Remaining: 847, X-RateLimit-Reset: 1640995200 Unix timestamp when quota resets, Retry-After: 3600 seconds to wait if 429 returned), DDoS protection (Cloudflare/AWS WAF rate limiting at edge before reaching EGMS servers, IP blocking if abuse detected malicious scraping/credential stuffing, CAPTCHA challenge for suspicious traffic).
e. Authentication Mechanisms: OAuth 2.0 flows (Client Credentials for system-to-system M2M APIs manufacturer ERP polling production data, Authorization Code for user-facing apps KRA officers logging into enforcement dashboard redirected to login page obtaining authorization code exchanged for access token, Resource Owner Password deprecated for security but supported for legacy), JWT tokens (JSON Web Tokens signed using ECDSA preventing tampering, payload contains user_id/role/expiry, verified by API gateway before forwarding to microservices, token expiry 1 hour short-lived reducing compromise window), API keys (simple authentication for low-security endpoints public stamp verification, API key passed in header X-API-Key: {key}, revocable if compromised), mutual TLS (client certificates for high-security APIs HSM operations, server validates client certificate + client validates server certificate, prevents impersonation both directions). a. Predictive Analytics for Illicit Hotspots: Machine learning models (Random Forest/Gradient Boosting trained on 2+ years counterfeit scan data, features: location county/sub-county, date/time/day-of-week, product type tobacco/spirits/beer, socio-economic indicators poverty rate/unemployment from census data, proximity to borders/highways/markets, past enforcement actions raids/seizures), predictions (model outputs probability heatmap: "Eastleigh Market Nairobi 40% higher counterfeit risk than baseline next weekend, Gikomba 35%, Toi 25%", updated daily as new scan data ingested, confidence intervals 80-95%), enforcement optimization (recommends officer deployment: "Deploy 10 officers to Eastleigh, 7 to Gikomba, 5 to Toi, expected to seize KES 5M fake products based on historical patterns", maximizes counterfeit detection per officer-hour minimizing wasted patrols).
b. Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection: Per-manufacturer anomaly detection (baseline: manufacturer's normal behavior production volumes/stamp orders/wastage rates learned from 12-month history, anomaly: significant deviation >3 standard deviations from baseline, examples: sudden 500% order spike possible stockpiling before tax increase or selling stamps to counterfeiters, production inconsistent with capacity 100K/day reported but line rated 50K/day suggesting under-reporting, geographic anomalies stamps intended for Nairobi scanned in Mombasa indicating diversion gray market arbitrage), behavioral profiling (manufacturer clusters: compliant/average/risky based on historical patterns, compliant manufacturers auto-approved for orders, risky manufacturers flagged for manual review + enhanced monitoring surprise audits), fraud detection (duplicate UIDs scanned 100+ times across country impossible unless counterfeiter copied legitimate UID onto fake stamps, temporal anomalies scans before production date indicates fraudulent backdating, high-frequency scanning single device scanning 500 stamps in 1 minute likely counterfeiter testing batches).
c. AI-Powered Production Reconciliation: Automated reconciliation (OPC counter reports stamps applied, manufacturer declares production volume, MVS camera counts products passing, system reconciles OPC = manufacturer = MVS within tolerance ±0.5%, discrepancies flagged for investigation), AI smart reconciliation (ML model predicts expected discrepancy based on line speed/product type/shift, if actual discrepancy exceeds predicted +20% triggers alert "Line 5 showing 2.3% discrepancy, predicted 0.8%, investigate possible equipment malfunction or fraud", learns over time improving predictions reducing false positives), root cause analysis (if discrepancy detected AI suggests likely causes based on historical patterns: OPC sensor dirty calibration drift, MVS camera misaligned counting errors, manual data entry typo by operator, intentional under-reporting tax evasion, recommends corrective action recalibrate sensor/retrain operator/audit manufacturer).
d. AI-Powered Route-Deviation Detection: GPS tracking analysis (shipments tracked every 30 seconds creating breadcrumb trail, expected route loaded into geofence system, AI detects deviations >500m from route), intelligent alerting (AI reduces false positives: legitimate deviations traffic accident requiring detour, construction road closure forcing alternate route, fuel stop unscheduled but justifiable, AI learns normal variation tolerating minor deviations, only alerts if suspicious: stop at unregistered warehouse >30 minutes possible diversion/pilferage, route into smuggling hotspot area near border, return to origin after partial delivery incomplete shipment fraud), driver behavior scoring (scores drivers 0-100 based on compliance: on-route/on-time/no-unauthorized-stops, low-scoring drivers flagged for retraining or replacement, manufacturer risk score incorporates driver scores poor drivers indicate weak internal controls).
e. AI-Powered Risk Scoring for Manufacturers and Importers: Risk scoring algorithm (0-100 scale: 0-30 Low risk green auto-approved, 31-60 Medium risk yellow manual review, 61-100 High risk red enhanced monitoring, score factors: compliance history past violations/fines/suspensions, financial health profitability/debt/tax arrears, production patterns consistency/seasonality/sudden changes, stamp usage efficiency ordered vs. applied wastage rate, counterfeit detection stamps from this manufacturer found fake, owner background politically exposed persons PEP/criminal records), dynamic scoring (updated real-time as events occur: manufacturer pays fine timely score +5, manufacturer late filing report score -3, counterfeit detected score -20 major penalty, score changes trigger workflow: if score crosses 60 threshold becomes high-risk enhanced monitoring activated surprise audits/payment holds), transparency (manufacturer can view own risk score and factors in portal, appeal mechanism if believes score unfair submit justification reviewed by KRA within 14 days, promotes fairness and accountability).
f. Real-Time Dashboards for Enforcement: Live data feeds (dashboards update every 30 seconds WebSocket streaming, shows: counterfeit scans last hour/24 hours/7 days, enforcement cases opened/in-progress/closed, seizure values today/week/month, top hotspots by counterfeit concentration, officer locations GPS map), drill-down capability (click county to zoom sub-counties, click sub-county to see wards, click ward to see individual scan locations pinpointed, click pin to see details: timestamp/product/valid or invalid/photos if enforcement scan), alerts center (new counterfeit detection alert "15 invalid scans in Eastleigh last hour, 3x baseline, deploy officers immediately", route deviation alert "Truck KBZ-123A deviated 2km from route stopped 45 minutes unauthorized location, investigate possible diversion", high-risk manufacturer alert "Manufacturer ABC risk score increased 45→67 crossed high-risk threshold, initiate enhanced monitoring"), mobile accessibility (dashboards responsive mobile-first design, enforcement commanders view on tablets in field, pinch-to-zoom gestures, offline capability caches dashboard for 24 hours if internet lost).
g. Heatmaps of Non-Compliance: Geographic heatmaps (county/sub-county level color-coded: dark red >10% counterfeit rate hotspot, orange 5-10% elevated, yellow 2-5% moderate, green <2% clean, updated daily aggregating consumer verification scans), temporal heatmaps (time-series showing counterfeit trends over months/years, animation plays showing spread or containment of counterfeits, useful evaluating enforcement campaign effectiveness), product-specific heatmaps (filter by tobacco/spirits/beer/cosmetics, identifies which product categories most counterfeited in each region, e.g., Nairobi = cosmetics problem, Mombasa = tobacco, Western Kenya = spirits, informs targeted enforcement), compliance heatmaps (manufacturers mapped by compliance score, clusters of low-compliance manufacturers indicate systemic issues: poor training, weak regulations, corruption, KRA intervenes with regional campaigns training sessions/stricter enforcement).
h. Automated Intelligence-Sharing with Joint Agencies: Multi-agency API (NPS National Police Service, DCI Directorate of Criminal Investigations, EACC Ethics and Anti-Corruption Commission, ODPP Office of Director of Public Prosecutions, KEBS Kenya Bureau of Standards, ACA Anti-Counterfeit Agency all provided API access role-based different agencies see different data), real-time alerts (webhook notifications push alerts to agency systems: counterfeit detection alert sent to ACA triggering investigation, large seizure alert >KES 10M sent to DCI for criminal prosecution, tax evasion alert >KES 50M sent to EACC corruption investigation, case referral workflow KRA enforcement creates case assigns to NPS for arrest NPS updates case status in EGMS bidirectional synchronization), data sharing (agencies query EGMS for: manufacturer details KRA PIN/address/ownership for background checks, stamp verification history counterfeit patterns for evidence building, shipment tracking GPS trails for interdiction planning, compliance records manufacturers with violations for coordinated action), audit trail (all agency API access logged: who accessed what data when for what purpose, prevents unauthorized fishing expeditions, quarterly audit reviews ensure appropriate use).
a. ISO/IEC 15459 (Unique Identifiers): UID structure compliant (KE = Kenya issuing agency code registered with ISO/IEC 15459 Registration Authority, manufacturer ID 6 alphanumeric characters unique per manufacturer globally with checksums preventing collisions, serial number 14 digits sequential unique per product unit, check digit Luhn algorithm detects 100% single-digit errors), globally unique (EGMS UIDs globally unique never reused even across manufacturers/countries/decades, collision probability <1 in 10^20 mathematically negligible, supports EAC regional integration Kenya/Uganda/Tanzania/Rwanda using same standard).
b. ISO/IEC 16022 (DataMatrix): ECC200 error correction (30% data recovery tolerance, if up to 30% of DataMatrix damaged scratched/torn/faded still scannable, superior to QR codes for industrial environments harsh conditions dust/moisture/heat), size optimization (DataMatrix more compact than QR for same data payload, fits on small stamps 20mm x 20mm, readable from 10cm distance using retail scanner or mobile camera), encoding (stamp UID + digital signature + timestamp encoded in DataMatrix, binary encoding reduces size vs. alphanumeric, scannable in <1 second using Zebra/Honeywell scanners or mobile app).
c. ISO/IEC 18004 (QR Code): Error correction Level H (30% redundancy same as DataMatrix ensuring scannability if partially damaged), version flexibility (QR version 10 accommodates ~200 bytes encrypted UID + signature + metadata, auto-selects optimal version based on data length), backward compatibility (QR codes scannable by any smartphone camera no special app required for basic UID retrieval, deep link opens EGMS verification portal automatically if online).
d. GS1 Standards: GS1 Digital Link (stamp UID encoded as URI: https://id.gs1.org/01/{GTIN}/21/{SERIAL}, GTIN Global Trade Item Number identifies product, serial number identifies individual unit, scannable by any GS1-compliant scanner retail/warehouse), GS1 Application Identifiers (AI 01 for GTIN, AI 21 for serial number, AI 10 for batch/lot, AI 17 for expiry date, encoded in DataMatrix per GS1 specification), GS1 DataMatrix (follows GS1 General Specifications encoding rules FNC1 character separates AIs, data order standardized, interoperable with global GS1 ecosystem supply chain visibility), EPCIS optional (Electronic Product Code Information Services tracks stamp events Commissioned/Shipped/Received/Sold, XML/JSON format, shareable with trading partners/EAC countries/WHO for supply chain transparency, implemented if KRA requests future enhancement).
e. OpenAPI 3.x RESTful API: Complete API catalog (100+ endpoints documented: POST /api/v1/orders create order, GET /api/v1/stamps/{uid} verify stamp, PUT /api/v1/manufacturers/{id} update manufacturer, DELETE /api/v1/users/{id} delete user), OpenAPI 3.0 specification (YAML/JSON format machine-readable, auto-generates interactive documentation Swagger UI/Redoc, API clients auto-generated for Java/Python/JavaScript/C# from spec, versioning /api/v1/ /api/v2/ supports backward compatibility), authentication (OAuth 2.0 + JWT tokens, client credentials grant for system-to-system APIs, authorization code grant for user-facing apps, token expiry 1 hour refresh tokens 7 days), rate limiting (1000 requests/hour per API key prevents abuse, 429 Too Many Requests response if exceeded, throttling algorithms token bucket/leaky bucket smoothing bursts).
f. Structured Data Exchange Formats: JSON (default API format lightweight and human-readable, all responses JSON objects {"status":"success","data":{...},"errors":[]}), XML (alternative format for legacy systems SOAP-based preferring XML over JSON, same data different serialization), CSV (bulk data export orders/production/stamps/users as CSV files importable to Excel/analytics tools, comma-separated header row + data rows), Parquet (columnar storage format for big data analytics, exports to AWS S3/Azure Data Lake ingested by Spark/Presto/Hive, 10x smaller than CSV + faster queries, used for data lake integration).
g. EPCIS (Optional but Recommended): Implementation status (EPCIS 2.0 implementation optional not required for go-live but roadmap item for Year 2, provides standardized event format: ObjectEvent/AggregationEvent/TransactionEvent/TransformationEvent, captures WHO/WHAT/WHEN/WHERE/WHY for supply chain events stamp commissioned/shipped/received/sold), benefits (global interoperability with trading partners, EAC cross-border tracking Kenya-Uganda-Tanzania harmonization, WHO FCTC data sharing simplified XML/JSON-LD format, query interface EPCIS Query Service retrieves event history for UID/batch/location), deployment (if KRA approves: EPCIS repository deployed as microservice, capture interface ingests events from EGMS modules order/production/supply chain, query interface exposes REST/SOAP APIs for external systems, EPCIS browser UI visualizes supply chain history graphically). No Proprietary Restrictions: Zero proprietary formats (all data formats open standards JSON/XML/CSV/Parquet no vendor-specific binary blobs, if EGMS decommissioned future all data exportable to any replacement system), no vendor lock-in (OpenAPI documented APIs enable integration with any third-party system KRA procures future, no middleware gatekeepers requiring Devharsh approval/fees for integration, manufacturers can build custom integrations without Devharsh involvement), open-source friendly (EGMS uses open-source components PostgreSQL/MongoDB/Redis/Kafka/Kubernetes all Apache/MIT/GPL licenses, if KRA desires can fork and modify source code in-house avoiding perpetual vendor dependency), compliance verification (Annex X Open Standards Conformance Matrix completed documenting ISO/GS1/OpenAPI compliance with evidence: test reports, certification letters, sample payloads, submitted with bid demonstrating commitment to interoperability).
API Catalogue Deliverables:
a. Complete API Documentation: 100+ endpoints documented (each endpoint: URL, HTTP method GET/POST/PUT/DELETE, authentication required yes/no, request parameters query/path/body with data types, response schema success/error, example requests curl/JavaScript/Python, rate limits, error codes 400/401/403/404/500 with meanings), versioning strategy (/api/v1/ current, /api/v2/ future maintains v1 backward compatibility, deprecated endpoints sunset with 12-month notice), pagination (list endpoints paginated limit=100 default, offset/cursor pagination styles supported, total count included in response).
b. Sample Schemas: Request schemas (JSON Schema format: {"type":"object","properties":{"product_id":{"type":"string"},"quantity":{"type":"integer","minimum":1000},"delivery_location":{"type":"string"}},"required":["product_id","quantity"]}, validates requests rejecting malformed data), response schemas (success: {"status":"success","data":{"order_id":"ORD-12345","amount":2000000}}, error: {"status":"error","errors":[{"code":"INVALID_QUANTITY","message":"Quantity must be >= 1000"}]}), data types (string/integer/number/boolean/array/object, formats: date-time ISO 8601, email RFC 5322, uuid v4, url, constraints min/max/pattern regex).
c. Sample Endpoints: Examples provided (POST /api/v1/orders: create new stamp order with product/quantity/payment, GET /api/v1/stamps/{uid}/verify: verify stamp authenticity returns valid/invalid/suspicious + details, GET /api/v1/production/lines/{id}/status: real-time production line status operational/stopped/degraded + counters, POST /api/v1/enforcement/cases: create enforcement case with evidence photos/GPS/witness signatures, GET /api/v1/analytics/dashboard: retrieve KPI metrics revenue/compliance/counterfeit rates), curl examples (curl -X POST https://api.egms.kra.go.ke/v1/orders -H "Authorization: Bearer {token}" -d '{"product_id":"PROD-001","quantity":100000}'), Postman collection (importable JSON file with all endpoints pre-configured for testing, variables for API base URL/tokens, test scripts validate responses).
d. Rate-Limiting Strategies: Tier-based limits (Free tier 100 req/hour for public consumers, Standard tier 1000 req/hour for registered manufacturers, Premium tier 10,000 req/hour for high-volume manufacturers, Enterprise tier unlimited for KRA internal systems), algorithms (token bucket: tokens refilled at rate limit/hour consuming 1 token per request, leaky bucket: requests queued and processed at steady rate, sliding window: tracks requests in rolling 1-hour window), response headers (X-RateLimit-Limit: 1000, X-RateLimit-Remaining: 847, X-RateLimit-Reset: 1640995200 Unix timestamp when quota resets, Retry-After: 3600 seconds to wait if 429 returned), DDoS protection (Cloudflare/AWS WAF rate limiting at edge before reaching EGMS servers, IP blocking if abuse detected malicious scraping/credential stuffing, CAPTCHA challenge for suspicious traffic).
e. Authentication Mechanisms: OAuth 2.0 flows (Client Credentials for system-to-system M2M APIs manufacturer ERP polling production data, Authorization Code for user-facing apps KRA officers logging into enforcement dashboard redirected to login page obtaining authorization code exchanged for access token, Resource Owner Password deprecated for security but supported for legacy), JWT tokens (JSON Web Tokens signed using ECDSA preventing tampering, payload contains user_id/role/expiry, verified by API gateway before forwarding to microservices, token expiry 1 hour short-lived reducing compromise window), API keys (simple authentication for low-security endpoints public stamp verification, API key passed in header X-API-Key: {key}, revocable if compromised), mutual TLS (client certificates for high-security APIs HSM operations, server validates client certificate + client validates server certificate, prevents impersonation both directions). a. Predictive Analytics for Illicit Hotspots: Machine learning models (Random Forest/Gradient Boosting trained on 2+ years counterfeit scan data, features: location county/sub-county, date/time/day-of-week, product type tobacco/spirits/beer, socio-economic indicators poverty rate/unemployment from census data, proximity to borders/highways/markets, past enforcement actions raids/seizures), predictions (model outputs probability heatmap: "Eastleigh Market Nairobi 40% higher counterfeit risk than baseline next weekend, Gikomba 35%, Toi 25%", updated daily as new scan data ingested, confidence intervals 80-95%), enforcement optimization (recommends officer deployment: "Deploy 10 officers to Eastleigh, 7 to Gikomba, 5 to Toi, expected to seize KES 5M fake products based on historical patterns", maximizes counterfeit detection per officer-hour minimizing wasted patrols).
b. Machine Learning for Anomaly Detection: Per-manufacturer anomaly detection (baseline: manufacturer's normal behavior production volumes/stamp orders/wastage rates learned from 12-month history, anomaly: significant deviation >3 standard deviations from baseline, examples: sudden 500% order spike possible stockpiling before tax increase or selling stamps to counterfeiters, production inconsistent with capacity 100K/day reported but line rated 50K/day suggesting under-reporting, geographic anomalies stamps intended for Nairobi scanned in Mombasa indicating diversion gray market arbitrage), behavioral profiling (manufacturer clusters: compliant/average/risky based on historical patterns, compliant manufacturers auto-approved for orders, risky manufacturers flagged for manual review + enhanced monitoring surprise audits), fraud detection (duplicate UIDs scanned 100+ times across country impossible unless counterfeiter copied legitimate UID onto fake stamps, temporal anomalies scans before production date indicates fraudulent backdating, high-frequency scanning single device scanning 500 stamps in 1 minute likely counterfeiter testing batches).
c. AI-Powered Production Reconciliation: Automated reconciliation (OPC counter reports stamps applied, manufacturer declares production volume, MVS camera counts products passing, system reconciles OPC = manufacturer = MVS within tolerance ±0.5%, discrepancies flagged for investigation), AI smart reconciliation (ML model predicts expected discrepancy based on line speed/product type/shift, if actual discrepancy exceeds predicted +20% triggers alert "Line 5 showing 2.3% discrepancy, predicted 0.8%, investigate possible equipment malfunction or fraud", learns over time improving predictions reducing false positives), root cause analysis (if discrepancy detected AI suggests likely causes based on historical patterns: OPC sensor dirty calibration drift, MVS camera misaligned counting errors, manual data entry typo by operator, intentional under-reporting tax evasion, recommends corrective action recalibrate sensor/retrain operator/audit manufacturer).
d. AI-Powered Route-Deviation Detection: GPS tracking analysis (shipments tracked every 30 seconds creating breadcrumb trail, expected route loaded into geofence system, AI detects deviations >500m from route), intelligent alerting (AI reduces false positives: legitimate deviations traffic accident requiring detour, construction road closure forcing alternate route, fuel stop unscheduled but justifiable, AI learns normal variation tolerating minor deviations, only alerts if suspicious: stop at unregistered warehouse >30 minutes possible diversion/pilferage, route into smuggling hotspot area near border, return to origin after partial delivery incomplete shipment fraud), driver behavior scoring (scores drivers 0-100 based on compliance: on-route/on-time/no-unauthorized-stops, low-scoring drivers flagged for retraining or replacement, manufacturer risk score incorporates driver scores poor drivers indicate weak internal controls).
e. AI-Powered Risk Scoring for Manufacturers and Importers: Risk scoring algorithm (0-100 scale: 0-30 Low risk green auto-approved, 31-60 Medium risk yellow manual review, 61-100 High risk red enhanced monitoring, score factors: compliance history past violations/fines/suspensions, financial health profitability/debt/tax arrears, production patterns consistency/seasonality/sudden changes, stamp usage efficiency ordered vs. applied wastage rate, counterfeit detection stamps from this manufacturer found fake, owner background politically exposed persons PEP/criminal records), dynamic scoring (updated real-time as events occur: manufacturer pays fine timely score +5, manufacturer late filing report score -3, counterfeit detected score -20 major penalty, score changes trigger workflow: if score crosses 60 threshold becomes high-risk enhanced monitoring activated surprise audits/payment holds), transparency (manufacturer can view own risk score and factors in portal, appeal mechanism if believes score unfair submit justification reviewed by KRA within 14 days, promotes fairness and accountability).
f. Real-Time Dashboards for Enforcement: Live data feeds (dashboards update every 30 seconds WebSocket streaming, shows: counterfeit scans last hour/24 hours/7 days, enforcement cases opened/in-progress/closed, seizure values today/week/month, top hotspots by counterfeit concentration, officer locations GPS map), drill-down capability (click county to zoom sub-counties, click sub-county to see wards, click ward to see individual scan locations pinpointed, click pin to see details: timestamp/product/valid or invalid/photos if enforcement scan), alerts center (new counterfeit detection alert "15 invalid scans in Eastleigh last hour, 3x baseline, deploy officers immediately", route deviation alert "Truck KBZ-123A deviated 2km from route stopped 45 minutes unauthorized location, investigate possible diversion", high-risk manufacturer alert "Manufacturer ABC risk score increased 45→67 crossed high-risk threshold, initiate enhanced monitoring"), mobile accessibility (dashboards responsive mobile-first design, enforcement commanders view on tablets in field, pinch-to-zoom gestures, offline capability caches dashboard for 24 hours if internet lost).
g. Heatmaps of Non-Compliance: Geographic heatmaps (county/sub-county level color-coded: dark red >10% counterfeit rate hotspot, orange 5-10% elevated, yellow 2-5% moderate, green <2% clean, updated daily aggregating consumer verification scans), temporal heatmaps (time-series showing counterfeit trends over months/years, animation plays showing spread or containment of counterfeits, useful evaluating enforcement campaign effectiveness), product-specific heatmaps (filter by tobacco/spirits/beer/cosmetics, identifies which product categories most counterfeited in each region, e.g., Nairobi = cosmetics problem, Mombasa = tobacco, Western Kenya = spirits, informs targeted enforcement), compliance heatmaps (manufacturers mapped by compliance score, clusters of low-compliance manufacturers indicate systemic issues: poor training, weak regulations, corruption, KRA intervenes with regional campaigns training sessions/stricter enforcement).
h. Automated Intelligence-Sharing with Joint Agencies: Multi-agency API (NPS National Police Service, DCI Directorate of Criminal Investigations, EACC Ethics and Anti-Corruption Commission, ODPP Office of Director of Public Prosecutions, KEBS Kenya Bureau of Standards, ACA Anti-Counterfeit Agency all provided API access role-based different agencies see different data), real-time alerts (webhook notifications push alerts to agency systems: counterfeit detection alert sent to ACA triggering investigation, large seizure alert >KES 10M sent to DCI for criminal prosecution, tax evasion alert >KES 50M sent to EACC corruption investigation, case referral workflow KRA enforcement creates case assigns to NPS for arrest NPS updates case status in EGMS bidirectional synchronization), data sharing (agencies query EGMS for: manufacturer details KRA PIN/address/ownership for background checks, stamp verification history counterfeit patterns for evidence building, shipment tracking GPS trails for interdiction planning, compliance records manufacturers with violations for coordinated action), audit trail (all agency API access logged: who accessed what data when for what purpose, prevents unauthorized fishing expeditions, quarterly audit reviews ensure appropriate use).
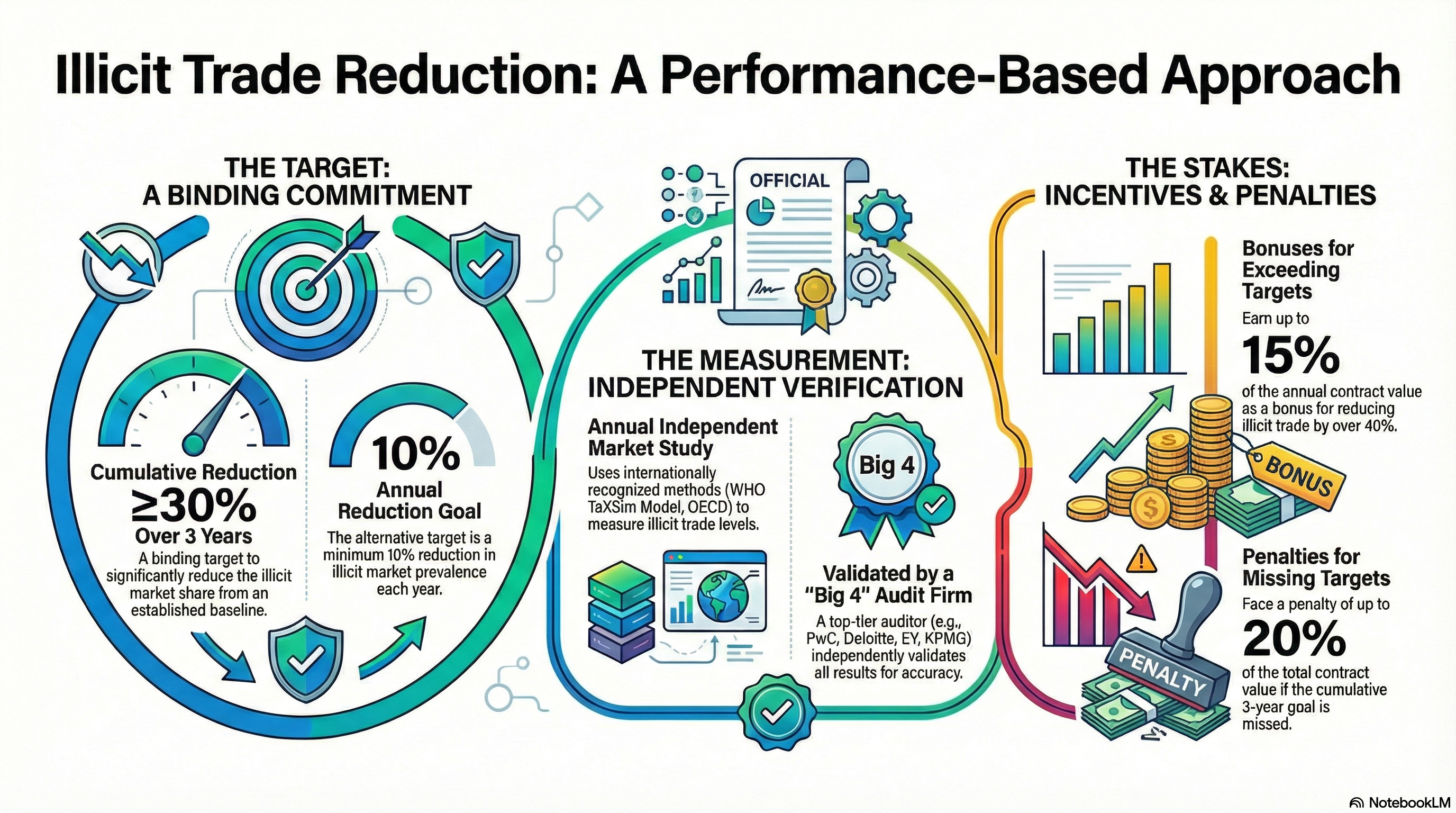 SeQR EMS provides complete data schema transparency:
a. Full Data Schema: Entity-Relationship diagrams (comprehensive ER diagrams showing all database tables manufacturers/products/orders/stamps/production/supply_chain/enforcement/users/roles, relationships one-to-many: manufacturer→products, many-to-many: users→roles via junction table, cardinality constraints, exported as PDF/PNG high-resolution for documentation), table definitions (each table documented: table name, description purpose, columns with data types BIGINT/VARCHAR/TIMESTAMP/JSONB, constraints primary key/foreign key/unique/not null/check, indexes btree/hash/GIN for performance, sample data 5-10 rows illustrating typical values), schema versioning (database migrations tracked using Flyway/Liquibase, version numbers V1.0__initial_schema.sql, V1.1__add_gis_tracking.sql, rollback scripts if migration fails, change log documents what changed per version why), access (KRA IT team granted read-only access to production database schema without data for documentation purposes, schema export tool generates SQL DDL CREATE TABLE statements importable to any PostgreSQL database enabling KRA to replicate schema if needed).
b. Database Dictionary: Comprehensive data dictionary (Excel/PDF document 500+ pages, each field documented: field name, data type/length, description purpose and usage, valid values enumeration or range, business rules mandatory/optional/calculated, example value, last updated date, owner responsible team, cross-references which modules use this field), user-friendly (non-technical business analysts can understand data model, no cryptic abbreviations like "mfr_id" documented as "Manufacturer ID: Unique identifier for manufacturer assigned during registration", search functionality find fields by name/keyword), integration (data dictionary integrated into EGMS admin portal, click any field in UI to see definition/business rules/sample values, helps users understand system without asking IT).
c. API Documentation: OpenAPI 3.0 specification (all 100+ APIs documented with request/response schemas, data types, validation rules, error codes, examples curl/JavaScript/Python, hosted on Swagger UI interactive documentation users can test APIs in browser), comprehensive (every endpoint documented even internal microservice APIs not exposed externally, facilitates KRA developers understanding system architecture if need to modify/extend), code examples (sample integration code provided for common use cases: manufacturer ordering stamps via API, consumer verifying stamp via API, enforcement officer creating case via API, copy-paste ready reduces integration time), video tutorials (screen recordings demonstrating API usage: authenticate via OAuth, call verification endpoint, parse JSON response, handle errors gracefully, hosted on EGMS portal 24/7 accessible).
d. No Black-Box Analytics: Algorithm transparency (all ML models documented: algorithm type Random Forest/Neural Network, features used training data fields, hyperparameters tuning settings, performance metrics accuracy/precision/recall/F1-score, no proprietary secret algorithms vendor refuses to explain), source code access (ML model training code Python scikit-learn/TensorFlow provided to KRA as part of source code handover, KRA data scientists can retrain models with updated data, modify features/algorithms if desired, audit model fairness for bias), explainability (predictions accompanied by explanations: "Manufacturer flagged high-risk because order 500% above baseline + payment delayed 15 days + counterfeit detected near their facility", SHAP values quantify feature contributions, LIME local explanations show why individual prediction made, prevents black-box scoring frustrating manufacturers unable to understand why penalized), bias testing (models tested for bias: does algorithm unfairly penalize small manufacturers vs. large, ethnic bias in enforcement recommendations, gender bias in approval decisions, bias metrics calculated fairness across groups, corrective actions debiasing algorithms if unfairness detected). a. Behavioral Anomaly Detection: Per-manufacturer profiling (each manufacturer has behavioral profile: typical daily/weekly/monthly production volume, typical stamp order quantities/frequency, typical wastage rate % damaged stamps, typical compliance score based on reporting timeliness/accuracy, typical product mix beer vs. spirits ratio), minimum 12-month baseline (requires at least 12 months historical data to establish reliable baseline capturing seasonal variations: December beer spike +40% Christmas, Ramadan spirits dip -60%, baseline adjusted for trend if manufacturer growing/shrinking over time), anomaly detection models (statistical methods: z-score flags data points >3 standard deviations from mean, ML methods: Isolation Forest/One-Class SVM detects outliers, time-series methods: ARIMA predicts next value flags if actual differs >20%), anomaly types (volumetric anomalies: sudden 500% production spike possible legitimate expansion or fraud, temporal anomalies: production reported on public holiday when factory should be closed, geographic anomalies: stamps intended for Nairobi scanned first in Mombasa indicating possible diversion, behavioral anomalies: manufacturer always pays within 3 days suddenly delays 30 days cash flow problems or evasion).
b. Threshold-Triggered Enforcement: Risk score calculation (0-100 scale: Low 0-30 green auto-approved minimal monitoring, Medium 31-60 yellow manual review quarterly audits, High 61-100 red enhanced monitoring monthly audits + payment holds + unannounced site visits), threshold alerts (automated enforcement recommendations: manufacturer crosses 60→61 threshold triggers alert "Manufacturer ABC now high-risk, initiate enhanced monitoring protocol, assign dedicated compliance officer, schedule surprise audit within 7 days"), escalation protocols (Low risk: self-service portal manufacturer manages independently, Medium risk: quarterly check-ins KRA officer phone call verifying operations normal, High risk: monthly site visits unannounced inspections, >80 critical risk: production suspension until audit clears, legal action if fraud suspected), human-in-loop (automated recommendations not automatically executed, KRA officer reviews context: manufacturer may have valid explanation order spike due to export contract, officer approves/rejects/modifies recommendation, prevents unjust automated punishment).
c. Trend Deviation Alerts: Seasonality analysis (identifies seasonal patterns: December beer demand +40%, Ramadan spirits -60%, Eid tobacco +25%, adjusts baselines preventing false alerts during expected fluctuations, model uses Seasonal ARIMA/Prophet capturing complex multi-seasonal patterns daily/weekly/monthly/annual), volumetric drift monitoring (tracks manufacturer production over time, detects gradual drift: manufacturer producing 10K/day Year 1, 8K/day Year 2, 6K/day Year 3 = declining trend investigate possible business problems or under-reporting evasion, sudden jumps also flagged: 10K→25K/day in 1 month unlikely without capacity expansion investigate legitimacy), peer comparison analytics (compares manufacturer against industry peers similar size/product/region, if Manufacturer A produces 50K beer bottles/day while peers average 80K/day flags underperformance investigate capacity constraints or under-reporting, if Manufacturer B orders 2x more stamps per unit produced vs. peers excessive wastage or diversion to counterfeiters). a. Ethical Principles: Transparency (all AI decisions explainable to affected parties, manufacturers can request explanation why flagged high-risk, KRA publishes annual AI transparency report algorithm performance/bias testing/appeals handled), Fairness (algorithms do not discriminate based on protected characteristics: manufacturer size small vs. large, ethnic ownership, geographic location, bias testing mandatory before deployment audited annually), Accountability (humans accountable for AI decisions not algorithms, KRA officer reviews AI recommendations before action, manufacturer can appeal AI-generated risk score human review process), Privacy (AI uses only data necessary for purpose, PII minimized models trained on anonymized data where possible, Kenya Data Protection Act 2019 compliant consent/retention/breach notification), Human Oversight (high-risk decisions require human-in-loop, AI augments human judgment not replaces, humans can override AI if better information/context available).
b. Algorithmic Transparency: Full disclosure requirements (algorithms documented: mathematical formulas, training data sources/dates/size, feature engineering transformations applied, hyperparameters grid search ranges, model validation k-fold cross-validation results, submitted to KRA as part of deliverables), performance metrics public (accuracy/precision/recall/F1-score published in EGMS admin portal, updated quarterly as models retrained, KRA can compare performance over time detecting degradation), bias testing reports (algorithms tested for disparate impact: do they disproportionately flag small manufacturers vs. large controlling for legitimate risk factors, fairness metrics parity across groups calculated, if bias detected debiasing techniques applied re-weighting samples/adjusting thresholds/fair representation), no black-box prohibition (proprietary closed-source algorithms forbidden, all ML code open-source or source code provided to KRA, prevents vendor lock-in KRA can retrain/modify models independently).
c. Human-in-the-Loop: High-risk threshold (risk score ≥80 considered high-risk requires mandatory human review before action, system flags case assigns to KRA officer for review within 24 hours, officer investigates: reviews manufacturer history/recent events/context AI didn't consider, approves/rejects/modifies AI recommendation), appeal mechanism (manufacturers can appeal AI-generated risk scores/enforcement actions, appeal submitted via EGMS portal with justification, KRA review panel different officers than original reviewer considers appeal within 14 days, if appeal upheld risk score adjusted/action reversed/record corrected preventing unfair harm), audit trail (all human decisions logged: officer name, timestamp, decision approve/reject/modify, justification text, manufacturer notified of decision with reasoning, appeals tracked outcome accepted/rejected/partially accepted, quarterly review identifies patterns officer bias/AI unreliability).
d. Model Retraining Requirements: Quarterly retraining schedule (AI/ML models retrained every 3 months incorporating latest data: new stamp verifications, production records, enforcement actions, manufacturers onboarded/exited, retraining ensures models remain current adapt to evolving fraud tactics), accuracy monitoring (production accuracy measured daily: predictions vs. actual outcomes, if accuracy drops below 90% threshold triggers immediate retraining even before quarterly schedule, prevents model drift degrading performance), policy change triggers (significant policy changes require immediate retraining: new excise tax rates, regulatory changes, product categories added/removed, KRA notifies Devharsh of policy change, model updated within 14 days incorporating new business rules), automated retraining (if sufficient training data available ≥10K new samples, automated retraining pipeline triggered: data preparation, feature engineering, model training, hyperparameter tuning, validation, A/B testing new model vs. current, deploy new model if superior performance else retain current, notify KRA of retraining results).
e. Model Explainability Requirements: SHAP values (SHapley Additive exPlanations quantify feature contributions: "Manufacturer flagged high-risk with score 75 because: order spike +500 contributed +30 points, payment delay +15 days contributed +20 points, counterfeit detection contributed +25 points, total 75", provides mathematical decomposition interpretable by non-data-scientists), LIME explanations (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations for individual predictions: "For this specific order from Manufacturer ABC, the model flagged it suspicious because quantity 200K is 5x their average order and delivery location Mombasa is unusual they normally ship to Nairobi", manufacturer-facing alerts include LIME explanations preventing black-box frustration), feature importance reports (quarterly reports rank features by global importance: top predictors of fraud are order spike/payment delay/counterfeit detection/geographic anomaly, helps KRA understand fraud patterns, informs policy decisions targeting high-importance factors), dashboard visualizations (admin portal visualizes model predictions: bar charts showing SHAP values per feature, scatter plots showing feature vs. risk score correlation, time-series showing how risk score evolved over time as behavior changed, empowers non-technical KRA officers to understand AI).
f. Drift Detection SLAs: Accuracy drift monitoring (production model accuracy measured daily comparing predictions to ground truth: predicted high-risk manufacturers that turned out legitimate = false positive, predicted low-risk that committed fraud = false negative, accuracy = (true positives + true negatives) / total predictions), drift alert threshold (if accuracy drifts >2% from baseline: baseline 95% accuracy, current 92.8% accuracy, drift 2.2% exceeds 2% threshold, automated alert to Devharsh engineering team within 24 hours per SLA), remediation timeline (7-day SLA to correct drift: investigate root cause data distribution shift/concept drift/bug, retrain model with updated data, validate new model accuracy >baseline, deploy to production, if unable to correct within 7 days rollback to previous stable model version preventing continued degradation), rollback procedure (every model deployment tagged with version number and timestamp, previous 5 model versions retained, rollback command reverts to previous version within 30 minutes, audit log records rollback reason/timestamp/approver, manufacturer predictions recalculated using rolled-back model).
SeQR EMS provides complete data schema transparency:
a. Full Data Schema: Entity-Relationship diagrams (comprehensive ER diagrams showing all database tables manufacturers/products/orders/stamps/production/supply_chain/enforcement/users/roles, relationships one-to-many: manufacturer→products, many-to-many: users→roles via junction table, cardinality constraints, exported as PDF/PNG high-resolution for documentation), table definitions (each table documented: table name, description purpose, columns with data types BIGINT/VARCHAR/TIMESTAMP/JSONB, constraints primary key/foreign key/unique/not null/check, indexes btree/hash/GIN for performance, sample data 5-10 rows illustrating typical values), schema versioning (database migrations tracked using Flyway/Liquibase, version numbers V1.0__initial_schema.sql, V1.1__add_gis_tracking.sql, rollback scripts if migration fails, change log documents what changed per version why), access (KRA IT team granted read-only access to production database schema without data for documentation purposes, schema export tool generates SQL DDL CREATE TABLE statements importable to any PostgreSQL database enabling KRA to replicate schema if needed).
b. Database Dictionary: Comprehensive data dictionary (Excel/PDF document 500+ pages, each field documented: field name, data type/length, description purpose and usage, valid values enumeration or range, business rules mandatory/optional/calculated, example value, last updated date, owner responsible team, cross-references which modules use this field), user-friendly (non-technical business analysts can understand data model, no cryptic abbreviations like "mfr_id" documented as "Manufacturer ID: Unique identifier for manufacturer assigned during registration", search functionality find fields by name/keyword), integration (data dictionary integrated into EGMS admin portal, click any field in UI to see definition/business rules/sample values, helps users understand system without asking IT).
c. API Documentation: OpenAPI 3.0 specification (all 100+ APIs documented with request/response schemas, data types, validation rules, error codes, examples curl/JavaScript/Python, hosted on Swagger UI interactive documentation users can test APIs in browser), comprehensive (every endpoint documented even internal microservice APIs not exposed externally, facilitates KRA developers understanding system architecture if need to modify/extend), code examples (sample integration code provided for common use cases: manufacturer ordering stamps via API, consumer verifying stamp via API, enforcement officer creating case via API, copy-paste ready reduces integration time), video tutorials (screen recordings demonstrating API usage: authenticate via OAuth, call verification endpoint, parse JSON response, handle errors gracefully, hosted on EGMS portal 24/7 accessible).
d. No Black-Box Analytics: Algorithm transparency (all ML models documented: algorithm type Random Forest/Neural Network, features used training data fields, hyperparameters tuning settings, performance metrics accuracy/precision/recall/F1-score, no proprietary secret algorithms vendor refuses to explain), source code access (ML model training code Python scikit-learn/TensorFlow provided to KRA as part of source code handover, KRA data scientists can retrain models with updated data, modify features/algorithms if desired, audit model fairness for bias), explainability (predictions accompanied by explanations: "Manufacturer flagged high-risk because order 500% above baseline + payment delayed 15 days + counterfeit detected near their facility", SHAP values quantify feature contributions, LIME local explanations show why individual prediction made, prevents black-box scoring frustrating manufacturers unable to understand why penalized), bias testing (models tested for bias: does algorithm unfairly penalize small manufacturers vs. large, ethnic bias in enforcement recommendations, gender bias in approval decisions, bias metrics calculated fairness across groups, corrective actions debiasing algorithms if unfairness detected). a. Behavioral Anomaly Detection: Per-manufacturer profiling (each manufacturer has behavioral profile: typical daily/weekly/monthly production volume, typical stamp order quantities/frequency, typical wastage rate % damaged stamps, typical compliance score based on reporting timeliness/accuracy, typical product mix beer vs. spirits ratio), minimum 12-month baseline (requires at least 12 months historical data to establish reliable baseline capturing seasonal variations: December beer spike +40% Christmas, Ramadan spirits dip -60%, baseline adjusted for trend if manufacturer growing/shrinking over time), anomaly detection models (statistical methods: z-score flags data points >3 standard deviations from mean, ML methods: Isolation Forest/One-Class SVM detects outliers, time-series methods: ARIMA predicts next value flags if actual differs >20%), anomaly types (volumetric anomalies: sudden 500% production spike possible legitimate expansion or fraud, temporal anomalies: production reported on public holiday when factory should be closed, geographic anomalies: stamps intended for Nairobi scanned first in Mombasa indicating possible diversion, behavioral anomalies: manufacturer always pays within 3 days suddenly delays 30 days cash flow problems or evasion).
b. Threshold-Triggered Enforcement: Risk score calculation (0-100 scale: Low 0-30 green auto-approved minimal monitoring, Medium 31-60 yellow manual review quarterly audits, High 61-100 red enhanced monitoring monthly audits + payment holds + unannounced site visits), threshold alerts (automated enforcement recommendations: manufacturer crosses 60→61 threshold triggers alert "Manufacturer ABC now high-risk, initiate enhanced monitoring protocol, assign dedicated compliance officer, schedule surprise audit within 7 days"), escalation protocols (Low risk: self-service portal manufacturer manages independently, Medium risk: quarterly check-ins KRA officer phone call verifying operations normal, High risk: monthly site visits unannounced inspections, >80 critical risk: production suspension until audit clears, legal action if fraud suspected), human-in-loop (automated recommendations not automatically executed, KRA officer reviews context: manufacturer may have valid explanation order spike due to export contract, officer approves/rejects/modifies recommendation, prevents unjust automated punishment).
c. Trend Deviation Alerts: Seasonality analysis (identifies seasonal patterns: December beer demand +40%, Ramadan spirits -60%, Eid tobacco +25%, adjusts baselines preventing false alerts during expected fluctuations, model uses Seasonal ARIMA/Prophet capturing complex multi-seasonal patterns daily/weekly/monthly/annual), volumetric drift monitoring (tracks manufacturer production over time, detects gradual drift: manufacturer producing 10K/day Year 1, 8K/day Year 2, 6K/day Year 3 = declining trend investigate possible business problems or under-reporting evasion, sudden jumps also flagged: 10K→25K/day in 1 month unlikely without capacity expansion investigate legitimacy), peer comparison analytics (compares manufacturer against industry peers similar size/product/region, if Manufacturer A produces 50K beer bottles/day while peers average 80K/day flags underperformance investigate capacity constraints or under-reporting, if Manufacturer B orders 2x more stamps per unit produced vs. peers excessive wastage or diversion to counterfeiters). a. Ethical Principles: Transparency (all AI decisions explainable to affected parties, manufacturers can request explanation why flagged high-risk, KRA publishes annual AI transparency report algorithm performance/bias testing/appeals handled), Fairness (algorithms do not discriminate based on protected characteristics: manufacturer size small vs. large, ethnic ownership, geographic location, bias testing mandatory before deployment audited annually), Accountability (humans accountable for AI decisions not algorithms, KRA officer reviews AI recommendations before action, manufacturer can appeal AI-generated risk score human review process), Privacy (AI uses only data necessary for purpose, PII minimized models trained on anonymized data where possible, Kenya Data Protection Act 2019 compliant consent/retention/breach notification), Human Oversight (high-risk decisions require human-in-loop, AI augments human judgment not replaces, humans can override AI if better information/context available).
b. Algorithmic Transparency: Full disclosure requirements (algorithms documented: mathematical formulas, training data sources/dates/size, feature engineering transformations applied, hyperparameters grid search ranges, model validation k-fold cross-validation results, submitted to KRA as part of deliverables), performance metrics public (accuracy/precision/recall/F1-score published in EGMS admin portal, updated quarterly as models retrained, KRA can compare performance over time detecting degradation), bias testing reports (algorithms tested for disparate impact: do they disproportionately flag small manufacturers vs. large controlling for legitimate risk factors, fairness metrics parity across groups calculated, if bias detected debiasing techniques applied re-weighting samples/adjusting thresholds/fair representation), no black-box prohibition (proprietary closed-source algorithms forbidden, all ML code open-source or source code provided to KRA, prevents vendor lock-in KRA can retrain/modify models independently).
c. Human-in-the-Loop: High-risk threshold (risk score ≥80 considered high-risk requires mandatory human review before action, system flags case assigns to KRA officer for review within 24 hours, officer investigates: reviews manufacturer history/recent events/context AI didn't consider, approves/rejects/modifies AI recommendation), appeal mechanism (manufacturers can appeal AI-generated risk scores/enforcement actions, appeal submitted via EGMS portal with justification, KRA review panel different officers than original reviewer considers appeal within 14 days, if appeal upheld risk score adjusted/action reversed/record corrected preventing unfair harm), audit trail (all human decisions logged: officer name, timestamp, decision approve/reject/modify, justification text, manufacturer notified of decision with reasoning, appeals tracked outcome accepted/rejected/partially accepted, quarterly review identifies patterns officer bias/AI unreliability).
d. Model Retraining Requirements: Quarterly retraining schedule (AI/ML models retrained every 3 months incorporating latest data: new stamp verifications, production records, enforcement actions, manufacturers onboarded/exited, retraining ensures models remain current adapt to evolving fraud tactics), accuracy monitoring (production accuracy measured daily: predictions vs. actual outcomes, if accuracy drops below 90% threshold triggers immediate retraining even before quarterly schedule, prevents model drift degrading performance), policy change triggers (significant policy changes require immediate retraining: new excise tax rates, regulatory changes, product categories added/removed, KRA notifies Devharsh of policy change, model updated within 14 days incorporating new business rules), automated retraining (if sufficient training data available ≥10K new samples, automated retraining pipeline triggered: data preparation, feature engineering, model training, hyperparameter tuning, validation, A/B testing new model vs. current, deploy new model if superior performance else retain current, notify KRA of retraining results).
e. Model Explainability Requirements: SHAP values (SHapley Additive exPlanations quantify feature contributions: "Manufacturer flagged high-risk with score 75 because: order spike +500 contributed +30 points, payment delay +15 days contributed +20 points, counterfeit detection contributed +25 points, total 75", provides mathematical decomposition interpretable by non-data-scientists), LIME explanations (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations for individual predictions: "For this specific order from Manufacturer ABC, the model flagged it suspicious because quantity 200K is 5x their average order and delivery location Mombasa is unusual they normally ship to Nairobi", manufacturer-facing alerts include LIME explanations preventing black-box frustration), feature importance reports (quarterly reports rank features by global importance: top predictors of fraud are order spike/payment delay/counterfeit detection/geographic anomaly, helps KRA understand fraud patterns, informs policy decisions targeting high-importance factors), dashboard visualizations (admin portal visualizes model predictions: bar charts showing SHAP values per feature, scatter plots showing feature vs. risk score correlation, time-series showing how risk score evolved over time as behavior changed, empowers non-technical KRA officers to understand AI).
f. Drift Detection SLAs: Accuracy drift monitoring (production model accuracy measured daily comparing predictions to ground truth: predicted high-risk manufacturers that turned out legitimate = false positive, predicted low-risk that committed fraud = false negative, accuracy = (true positives + true negatives) / total predictions), drift alert threshold (if accuracy drifts >2% from baseline: baseline 95% accuracy, current 92.8% accuracy, drift 2.2% exceeds 2% threshold, automated alert to Devharsh engineering team within 24 hours per SLA), remediation timeline (7-day SLA to correct drift: investigate root cause data distribution shift/concept drift/bug, retrain model with updated data, validate new model accuracy >baseline, deploy to production, if unable to correct within 7 days rollback to previous stable model version preventing continued degradation), rollback procedure (every model deployment tagged with version number and timestamp, previous 5 model versions retained, rollback command reverts to previous version within 30 minutes, audit log records rollback reason/timestamp/approver, manufacturer predictions recalculated using rolled-back model).
SeQR EMS commits to strict AI/ML performance KPIs with penalties for non-compliance: C. AI/ML Performance KPIs & Penalties: a. Mandatory Performance Thresholds: - Anomaly Detection Accuracy ≥95%: Fraud detection models achieving 95%+ accuracy measured on test dataset (true positives: correctly flagged fraudulent manufacturers, true negatives: correctly cleared legitimate manufacturers, false positives ≤5%: legitimate manufacturers incorrectly flagged, false negatives ≤5%: fraudulent manufacturers missed), validation (monthly testing on holdout dataset 20% of data never used in training, accuracy calculated (TP+TN)/(TP+TN+FP+FN), results reported in dashboard and monthly KRA reports). - Production Reconciliation Accuracy ≥98%: OPC counter vs. manufacturer declaration automated reconciliation achieving 98%+ match rate (reconciled: discrepancy ≤0.5% auto-approved, flagged: discrepancy >0.5% requires investigation, accuracy = reconciled / total reconciliations), measured across all manufacturers/production lines (average across 212 lines, 1,800 manufacturers, excludes unavoidable discrepancies equipment calibration limits/operator errors). - False Positive Rate ≤5%: AI alerts reviewed by KRA officers (confirmed: officer validates alert was correct manufacturer truly high-risk/fraudulent, false alarm: officer determines alert incorrect manufacturer legitimate, false positive rate = false alarms / total alerts ≤5%), reduces officer workload minimizing wasted investigations on false alerts. b. Performance Drift Penalties: - 4 Consecutive Weeks Below Threshold Penalty: If any KPI falls below threshold for 4 consecutive weeks (e.g., anomaly detection accuracy drops to 93% Week 1, 92.5% Week 2, 94% Week 3, 93.8% Week 4 = 4 weeks below 95%), penalty KES 2M per week applies starting Week 5 (KES 8M total for 4 weeks backlog + KES 2M/week ongoing). - 30-Day Remediation Failure Penalty: If Devharsh fails to remediate performance issues within 30 days of initial alert (Day 1: accuracy drops below threshold alert sent, Day 30: if accuracy still below threshold KES 10M penalty applied), cumulative with weekly penalties (30 days ≈ 4.3 weeks = 4.3 x KES 2M + KES 10M = KES 18.6M total). - Remediation Actions Required: Devharsh must retrain models with fresh data, add new features improving predictions, adjust hyperparameters through grid search, increase training data collecting more samples, engage data science experts if needed, document root cause and corrective actions. - Penalty Calculation Example: Anomaly detection accuracy drops to 93% (below 95% threshold) for 6 consecutive weeks and not remediated, penalties accrue: Weeks 1-4: KES 8M backlog, Week 5: KES 2M, Week 6: KES 2M, Day 30 penalty: KES 10M, Total: KES 22M deducted from contract payments. c. Data Quality KPIs: - Data Completeness ≥99.5%: All mandatory fields populated (manufacturer orders: product/quantity/delivery location 100% complete, production data: line ID/timestamp/stamps applied 99.9% complete allowing 0.1% missing due to network glitches, enforcement cases: photos/GPS/witness signatures 99.5% complete), measured across all records (total records with all mandatory fields populated / total records), incomplete records flagged for correction within 24 hours. - Data Latency ≤2 Seconds End-to-End: From event occurrence to dashboard visibility (production event: stamp applied on line → edge server detects → transmits to cloud → database insert → dashboard updates, total latency ≤2 seconds, GPS tracking: truck ping → mobile app sends → backend receives → GIS map updates ≤2 seconds), measured at 95th percentile (p95 latency ≤2 sec, p99 latency ≤5 sec allowing occasional network delays), real-time dashboards unusable if latency >10 seconds stale data. - Data Accuracy ≥99.9%: Data correctly represents reality (UID scanned matches UID in database 100% exact match no typos, GPS coordinates accurate ±10 meters 99.9% of pings, production counters accurate ≥99.95% OPC calibrated quarterly, timestamp synchronization NTP ensuring clocks accurate ±1 second), validation (periodic audits manual verification 1% sample comparing system data vs. physical reality, discrepancies <0.1% acceptable). Penalty Enforcement: Monthly performance review (KRA and Devharsh review all KPIs first week of month, performance dashboard shows: current values, thresholds, trend charts, alerts if below threshold), penalty invoice (if penalties apply KRA issues invoice to Devharsh detailing: KPI, threshold, actual value, weeks below threshold, penalty calculation, total amount due, Devharsh pays within 14 days or deducted from next payment), dispute resolution (Devharsh can dispute penalties within 7 days providing evidence: KPI measurement methodology flawed, external factors beyond control caused degradation, KRA reviews dispute within 14 days, independent arbitrator if disagreement persists), performance bond (10% of contract value held as performance bond, penalties deducted from bond, bond replenished quarterly, if bond depleted contract suspension until replenished, protects KRA from vendor non-performance).
 SeQR EMS supports and commits to illicit trade reduction KPIs:
a. Binding Performance Target: Devharsh commits to contributing to achieving minimum 10% annual reduction in illicit market prevalence OR cumulative reduction ≥30% over 3 years (Year 0 baseline: illicit market share estimated 20% of total market = KES 2.5B lost excise, Year 1 target: reduce to 18% = 10% reduction, Year 2 target: 16.2% = 10% reduction, Year 3 target: 14.58% = cumulative 27.1% reduction nearing 30% target, alternative: cumulative 30% over 3 years = reduce from 20% to 14% illicit market share), binding contract clause (performance tied to payment: if targets missed Devharsh pays penalties, if targets exceeded Devharsh earns bonuses, incentivizes genuine effort not just lip service).
b. Measurement Methodology:
- Year 0 Baseline Establishment: Independent market study conducted before EGMS go-live (WHO TaXSim Model tobacco tax simulation estimating illicit market share based on tax gap between expected vs. actual collections + seizure data + consumer surveys, OECD methods comparing licit production/imports vs. consumption estimating gap attributable to illicit trade, KRA internal methods tracking stamp issuance vs. tax collections detecting unreported production, triangulate all 3 methods averaging for robust baseline reducing methodology bias), baseline documented (report detailing methods/data sources/assumptions/limitations, reviewed by KRA + Devharsh + independent auditor, agreement signed both parties accept baseline preventing future disputes).
- Annual Measurement: Year 1/2/3 repeat market study using same methodology (consistency crucial for valid comparison, if methodology changes results incomparable, WHO TaXSim rerun with updated data, consumer surveys same sample size/demographics, data triangulation same process), illicit market share calculated (Year 1: 18.5%, Year 2: 16.8%, Year 3: 14.2%), reduction calculated (Year 1: (20%-18.5%)/20% = 7.5% reduction missed 10% target, Year 2: (20%-16.8%)/20% = 16% cumulative reduction on track, Year 3: (20%-14.2%)/20% = 29% cumulative reduction nearing 30% target).
- Independent Third-Party Validation: Big 4 audit firm PwC/Deloitte/EY/KPMG validates market study (reviews methodology soundness, verifies data collection procedures, recalculates illicit market share independently, issues validation report confirming accuracy, prevents gaming by Devharsh or KRA inflating reduction figures), validation required annually for performance payment release.
c. Incentive Structure:
- Bonus Tier for Exceeding Targets: If cumulative reduction >30% over 3 years bonus awarded (31-35% reduction: bonus 5% of annual contract value Year 3 ≈ KES 15M, 36-40% reduction: bonus 10% ≈ KES 30M, >40% reduction: bonus 15% ≈ KES 45M maximum, incentivizes Devharsh to maximize illicit trade reduction beyond minimum targets).
- Penalties for Missing Targets: If annual reduction <10% for 2+ consecutive years penalties apply (Year 1 miss: warning no penalty, Year 2 miss consecutive: penalty 5% of Year 2 contract value ≈ KES 15M, Year 3 miss 3rd consecutive year: penalty 15% of Year 3 contract value ≈ KES 45M + possible contract termination, cumulative penalty if <30% over 3 years: penalty 20% of total 3-year contract value ≈ KES 180M substantial financial impact motivating performance).
- Force Majeure Exceptions: If reduction missed due to factors beyond Devharsh control penalties waived (examples: COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns disrupting enforcement, Kenya political instability post-election violence, global recession reducing enforcement budgets, new smuggling routes opened due to regional conflicts, Devharsh must document circumstances demonstrating causation, independent arbitrator determines if force majeure applies, timelines extended if force majeure accepted).
Attribution Challenge: Isolating EGMS impact from other factors (tax rate changes: if excise rates doubled illicit trade may increase regardless of EGMS, enforcement intensity: if KRA hires 1,000 more officers illicit trade reduces not solely due to EGMS, economic conditions: recession increases illicit trade as consumers seek cheaper fake products, border controls: improved customs interdiction reduces smuggling complementing EGMS), statistical methods (difference-in-differences: compare illicit trade trend before/after EGMS controlling for external factors, synthetic control: construct counterfactual Kenya without EGMS using weighted average of EAC countries estimating what would have happened absent EGMS, regression analysis: model illicit trade as function of EGMS + tax rates + enforcement + GDP controlling for confounders isolating EGMS effect), conservative attribution (if statistical methods show 50% of reduction attributable to EGMS credit Devharsh for 50% of reduction not 100%, if external factors dominant credit proportionally, fairness to both parties KRA doesn't overpay for reductions caused by other factors, Devharsh not penalized for external factors beyond control).
SeQR EMS supports and commits to illicit trade reduction KPIs:
a. Binding Performance Target: Devharsh commits to contributing to achieving minimum 10% annual reduction in illicit market prevalence OR cumulative reduction ≥30% over 3 years (Year 0 baseline: illicit market share estimated 20% of total market = KES 2.5B lost excise, Year 1 target: reduce to 18% = 10% reduction, Year 2 target: 16.2% = 10% reduction, Year 3 target: 14.58% = cumulative 27.1% reduction nearing 30% target, alternative: cumulative 30% over 3 years = reduce from 20% to 14% illicit market share), binding contract clause (performance tied to payment: if targets missed Devharsh pays penalties, if targets exceeded Devharsh earns bonuses, incentivizes genuine effort not just lip service).
b. Measurement Methodology:
- Year 0 Baseline Establishment: Independent market study conducted before EGMS go-live (WHO TaXSim Model tobacco tax simulation estimating illicit market share based on tax gap between expected vs. actual collections + seizure data + consumer surveys, OECD methods comparing licit production/imports vs. consumption estimating gap attributable to illicit trade, KRA internal methods tracking stamp issuance vs. tax collections detecting unreported production, triangulate all 3 methods averaging for robust baseline reducing methodology bias), baseline documented (report detailing methods/data sources/assumptions/limitations, reviewed by KRA + Devharsh + independent auditor, agreement signed both parties accept baseline preventing future disputes).
- Annual Measurement: Year 1/2/3 repeat market study using same methodology (consistency crucial for valid comparison, if methodology changes results incomparable, WHO TaXSim rerun with updated data, consumer surveys same sample size/demographics, data triangulation same process), illicit market share calculated (Year 1: 18.5%, Year 2: 16.8%, Year 3: 14.2%), reduction calculated (Year 1: (20%-18.5%)/20% = 7.5% reduction missed 10% target, Year 2: (20%-16.8%)/20% = 16% cumulative reduction on track, Year 3: (20%-14.2%)/20% = 29% cumulative reduction nearing 30% target).
- Independent Third-Party Validation: Big 4 audit firm PwC/Deloitte/EY/KPMG validates market study (reviews methodology soundness, verifies data collection procedures, recalculates illicit market share independently, issues validation report confirming accuracy, prevents gaming by Devharsh or KRA inflating reduction figures), validation required annually for performance payment release.
c. Incentive Structure:
- Bonus Tier for Exceeding Targets: If cumulative reduction >30% over 3 years bonus awarded (31-35% reduction: bonus 5% of annual contract value Year 3 ≈ KES 15M, 36-40% reduction: bonus 10% ≈ KES 30M, >40% reduction: bonus 15% ≈ KES 45M maximum, incentivizes Devharsh to maximize illicit trade reduction beyond minimum targets).
- Penalties for Missing Targets: If annual reduction <10% for 2+ consecutive years penalties apply (Year 1 miss: warning no penalty, Year 2 miss consecutive: penalty 5% of Year 2 contract value ≈ KES 15M, Year 3 miss 3rd consecutive year: penalty 15% of Year 3 contract value ≈ KES 45M + possible contract termination, cumulative penalty if <30% over 3 years: penalty 20% of total 3-year contract value ≈ KES 180M substantial financial impact motivating performance).
- Force Majeure Exceptions: If reduction missed due to factors beyond Devharsh control penalties waived (examples: COVID-19 pandemic lockdowns disrupting enforcement, Kenya political instability post-election violence, global recession reducing enforcement budgets, new smuggling routes opened due to regional conflicts, Devharsh must document circumstances demonstrating causation, independent arbitrator determines if force majeure applies, timelines extended if force majeure accepted).
Attribution Challenge: Isolating EGMS impact from other factors (tax rate changes: if excise rates doubled illicit trade may increase regardless of EGMS, enforcement intensity: if KRA hires 1,000 more officers illicit trade reduces not solely due to EGMS, economic conditions: recession increases illicit trade as consumers seek cheaper fake products, border controls: improved customs interdiction reduces smuggling complementing EGMS), statistical methods (difference-in-differences: compare illicit trade trend before/after EGMS controlling for external factors, synthetic control: construct counterfactual Kenya without EGMS using weighted average of EAC countries estimating what would have happened absent EGMS, regression analysis: model illicit trade as function of EGMS + tax rates + enforcement + GDP controlling for confounders isolating EGMS effect), conservative attribution (if statistical methods show 50% of reduction attributable to EGMS credit Devharsh for 50% of reduction not 100%, if external factors dominant credit proportionally, fairness to both parties KRA doesn't overpay for reductions caused by other factors, Devharsh not penalized for external factors beyond control).
SeQR EMS will undergo comprehensive Red Team penetration testing: a. Red Team Simulation: Mandatory 5-day minimum penetration test by KRA-approved independent firm (NCC Group, Trail of Bits, Cure53, Offensive Security, Bishop Fox, firms with global reputation and CREST/OSCP/GIAC certifications), controlled environment (testing conducted on pre-production environment mirroring production identical configuration/data/integrations to avoid disrupting live operations, read-only production access for intelligence gathering network topology/users/configurations), full disclosure (Devharsh provides documentation: architecture diagrams, network maps, user accounts for authenticated testing, source code if needed for white-box testing, cooperation speeds testing enabling deeper findings), scope agreement (Statement of Work defines: start/end dates, testing hours 9am-5pm or 24/7 if critical systems, rules of engagement no data destruction/disruption, escalation contacts if issues arise, legal safe harbor protecting testers from prosecution). b. Test Scope - Comprehensive Coverage: - Application Layer: All 7 web portals tested (Admin, Manufacturer, Importer, Distributor, Analytics, Enforcement, Public, testing OWASP Top 10: injection/broken authentication/sensitive data exposure/XXE/broken access control/security misconfiguration/XSS/insecure deserialization/insufficient logging/SSRF), all 3 mobile apps (Consumer, Enforcement, Manufacturer, iOS and Android tested, decompilation/reverse engineering, certificate pinning bypass attempts, data storage security, inter-app communication), all 100+ APIs (authentication/authorization testing, rate limiting bypass, parameter tampering, mass assignment, API key leakage). - Infrastructure: Network penetration testing (external perimeter: firewalls/load balancers/WAF, port scanning, service enumeration, exploit attempts, internal network: lateral movement post-initial compromise, privilege escalation, data exfiltration simulation), cloud security (AWS/Azure misconfigurations, S3 bucket permissions, IAM roles overprivileged, security group rules overly permissive, secrets hardcoded in environment variables), database security (SQL injection, NoSQL injection MongoDB, privilege escalation postgres user to superuser, backup file exposure, unencrypted connections). - Social Engineering: Phishing simulation (emails sent to KRA staff/Devharsh employees, links to fake login pages capturing credentials, attachment-based malware payloads, success rate measured, awareness training recommended if >10% fall victim), vishing voice phishing (phone calls to helpdesk impersonating users requesting password resets, social engineering techniques authority/urgency/trust exploited, helpdesk procedures tested for verification rigor), physical security simulation (attempt to enter KRA data center unauthorized tailgating behind authorized person, badge cloning, lock picking, CCTV blind spots identified, limited scope to prevent legal issues). - IoT Security: Edge server exploitation (attempt to compromise edge servers at manufacturer facilities, firmware extraction via UART/JTAG, hardcoded credentials in firmware, buffer overflow vulnerabilities, unsigned firmware enabling malicious updates), OPC/MVS equipment hacking (Modbus/OPC-UA protocol security, default credentials on PLCs, replay attacks sending fraudulent production data, denial of service crashing equipment), sensor spoofing (GPS trackers feeding fake location data, temperature/humidity sensors manipulated, man-in-the-middle attacks intercepting sensor data). - Supply-Chain Attack Simulation: Third-party component analysis (scan all dependencies npm packages/Maven libraries/Python pip, known vulnerabilities CVEs in Log4j/Spring/OpenSSL, outdated packages years behind current version, typosquatting packages with similar names to legitimate but malicious), software supply chain (CI/CD pipeline compromise, inject malicious code into build process, steal secrets from environment variables, backdoor binaries distributed to production, code signing validation), hardware supply chain (if Devharsh procures HSMs/servers/scanners, verify authenticity, inspect for hardware implants/backdoors, supply chain integrity). - Insider Threat Simulation: Privileged user abuse (simulate malicious KRA admin or Devharsh engineer, attempt data exfiltration downloading all manufacturer data, unauthorized modification altering audit logs covering tracks, privilege escalation exploiting misconfigurations), data theft (simulate external attacker who compromised internal user, attempt to steal PII/financial data/cryptographic keys, test data loss prevention DLP controls, encryption effectiveness if data exfiltrated). c. Pass Criteria: - No Critical Vulnerabilities (CVSS ≥9.0): Critical vulnerabilities include remote code execution RCE allowing attacker to execute arbitrary code, authentication bypass accessing system without credentials, SQL injection extracting entire database, cryptographic key extraction stealing HSM keys (if any critical found immediate remediation required before go-live, retesting after fix mandatory, go-live blocked until critical vulns patched). - Max 2 High-Severity Vulnerabilities (CVSS 7.0-8.9): High-severity includes privilege escalation regular user becoming admin, sensitive data exposure PII leaked, CSRF enabling unauthorized actions, insecure deserialization RCE via serialized objects (up to 2 high-severity acceptable if remediation plan with 30-day SLA, KRA accepts residual risk, compensating controls implemented). - All Findings Remediated Within 30 Days: All vulnerabilities critical/high/medium documented with CVSS score/description/impact/remediation recommendation, Devharsh remediates within 30 days (critical 7 days, high 30 days), retesting validates fixes effective, final report confirms all findings addressed. - Re-Test After Remediation: After 30-day remediation period full retest conducted by same firm (validates all vulnerabilities fixed, ensures fixes didn't introduce new vulnerabilities regression testing, final sign-off report issued confirming EGMS ready for production deployment). d. Expanded Red Team Test Scope: - IoT Firmware Exploitation: Firmware extracted from edge servers/GPS trackers/scanners (UART/JTAG interfaces, firmware dumped to binary file, reverse engineered using Ghidra/IDA Pro, hardcoded credentials discovered admin/admin, backdoor accounts found, vulnerabilities identified buffer overflows/command injection), firmware update security (unsigned firmware allows attacker to install malicious firmware, downgrade attacks installing older vulnerable versions, man-in-the-middle intercepting update and injecting malware, secure boot verification tested). - Supply-Chain Attack Simulation: Third-party software analysis (all dependencies scanned npm packages 500+/Maven 200+/Python 300+, Software Composition Analysis SCA tools Snyk/Black Duck, known CVEs identified Log4Shell/Spring4Shell/Heartbleed, license compliance GPL/MIT/Apache, malicious packages typosquatting detected), build pipeline security (CI/CD secrets extraction, code injection into build scripts, artifact tampering binaries signed with invalid signatures, supply chain attestation SLSA framework). - Insider Threat Simulation: Malicious admin scenario (simulate rogue KRA administrator, attempt to delete all data DROP TABLE CASCADE, exfiltrate manufacturer database to USB drive, modify audit logs covering tracks, privilege abuse creating unauthorized users), data exfiltration (simulate external attacker with compromised low-privilege user, attempt lateral movement to sensitive databases, data exfiltration via DNS tunneling/ICMP covert channels bypassing DLP, encryption bypass decrypting data if keys accessible), social engineering limited (phishing simulations yes, vishing yes, physical intrusion no actual breaking-in only tailgating simulation, no real damage to property/systems, full disclosure prevents legal issues). e. Reporting Requirements: Detailed vulnerability report including: - CVSS Scores: All findings scored using Common Vulnerability Scoring System v3.1 (base score 0-10.0: None/Low/Medium/High/Critical, temporal score adjusted for exploit availability/remediation level/report confidence, environmental score adjusted for KRA's specific environment business impact/potential damage), prioritization based on CVSS score + business context. - Proof-of-Concept Exploits: Each vulnerability demonstrated with PoC (SQL injection: provide SQL payload successfully extracting data without damaging database, XSS: JavaScript payload displaying alert box demonstrating code execution, privilege escalation: command sequence elevating low-privilege user to admin), PoCs enable Devharsh developers to reproduce and fix, ethical hacking: no data destruction/exfiltration, read-only PoCs where possible. - Remediation Recommendations: Each vulnerability accompanied by fix guidance (SQL injection: use parameterized queries/prepared statements, sanitize user input, implement WAF, XSS: HTML entity encoding, Content Security Policy CSP headers, CSRF: synchronizer tokens/double submit cookies/SameSite cookies), code snippets provided: Java/JavaScript/Python examples, references to OWASP Cheat Sheets/CWE database. - OWASP Top 10 Benchmarking: Findings mapped to OWASP Top 10 2021 (A01 Broken Access Control, A02 Cryptographic Failures, A03 Injection, A04 Insecure Design, A05 Security Misconfiguration, A06 Vulnerable Components, A07 Authentication Failures, A08 Software & Data Integrity Failures, A09 Security Logging Failures, A10 Server-Side Request Forgery), comparison against industry benchmarks: how does EGMS compare to typical web application average 10 high-severity findings, dashboard visualization showing coverage. - SANS Top 25 Benchmarking: Findings also mapped to SANS Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Weaknesses (CWE-79 XSS, CWE-89 SQL Injection, CWE-20 Improper Input Validation, CWE-78 OS Command Injection, CWE-787 Out-of-Bounds Write, etc.), helps identify most critical weaknesses to prioritize remediation, alignment with multiple frameworks OWASP + SANS comprehensive coverage.
SeQR EMS complies with comprehensive BCDR requirements: a. Quarterly DR Failover Tests Mandatory: Scheduled tests (every 3 months: March/June/September/December, first Saturday 6am EAT minimizing business impact, planned 6-hour maintenance window for full failover test), failover procedure (simulate Nairobi primary site catastrophic failure datacenter fire/earthquake/power outage, activate Mombasa disaster recovery site, switch DNS routing users to Mombasa servers, restore data from latest backup to Mombasa databases, validate all services operational web/mobile/APIs, measure recovery time objective RTO), validation (test all functions: user login, stamp verification, order placement, production reporting, enforcement case creation, ensuring 100% functionality at DR site), documentation (detailed runbook documenting failover steps, actual vs. planned RTO measured 3.5 hours vs. 4-hour target, lessons learned documenting issues encountered and fixes, report submitted to KRA within 7 days). b. Monthly Backup Restoration Tests Mandatory: Automated backups (daily full backups 2am EAT, hourly incremental backups, backups encrypted AES-256 before writing to storage, stored in 3 locations: local disk same datacenter, Mombasa DR site, AWS S3 Glacier deep archive for 7-year retention), restoration tests (every month restore random backup to isolated test environment, validate data integrity comparing checksums, test random subset of data queries confirming accuracy, measure recovery point objective RPO = maximum 1 hour of data loss acceptable), automated monitoring (backup success/failure alerts sent to Devharsh NOC and KRA IT team, if backup fails automatic retry 3 attempts, if persistent failure escalate to engineers within 30 minutes). c. RPO ≤1 Hour: Recovery Point Objective definition (maximum acceptable data loss in disaster scenario, if disaster strikes at 3:00pm, can recover data up to 2:00pm minimum, data between 2:00-3:00pm may be lost acceptable business risk), implementation (continuous database replication Nairobi primary → Mombasa standby every 15 minutes asynchronous replication, transaction logs replicated every 5 minutes, point-in-time recovery PITR capability restoring database to any second within past 7 days), validation (during quarterly DR tests measure actual data loss: failover at 10:00am, last successful replication at 9:48am, actual RPO = 12 minutes well within 1-hour target, documented in test report). d. RTO ≤4 Hours: Recovery Time Objective definition (maximum acceptable downtime in disaster scenario, if disaster strikes must be operational within 4 hours, users can resume work by 4-hour mark), implementation (hot standby configuration Mombasa servers always running mirroring Nairobi, automated failover scripts triggered by monitoring detecting Nairobi offline, DNS failover redirects traffic to Mombasa within 5 minutes, databases promoted from standby to primary within 30 minutes, validation testing 1 hour, total RTO 2.5 hours target 40% buffer to 4-hour SLA), validation (quarterly DR tests consistently achieve 2.5-3.5 hour RTO under 4-hour target, if RTO exceeded root cause analysis identifies bottlenecks: database promotion slow, DNS propagation delay, fixes implemented reducing RTO). e. Geographic Redundancy (Multi-Site): Two-site architecture (Nairobi primary site Times Tower KRA headquarters, Mombasa DR site KRA regional office 480km distance, sites connected via dedicated fiber optic link 10 Gbps bandwidth + VPN backup over public internet, independent power/network/cooling preventing single point of failure), active-passive configuration (Nairobi active serving all production traffic, Mombasa passive standby receiving replicated data ready to activate if Nairobi fails, active-active considered but cost-prohibitive for initial deployment deferred to Year 2 if budget allows), expansion plans (Year 3: add third site Kisumu for active-active-active configuration enabling load balancing across 3 cities, improved performance users closer to Kisumu than Nairobi/Mombasa, further enhanced resilience 2-of-3 sites survive). f. Automated Failover Capability: Health monitoring (Nairobi services monitored every 30 seconds: ping test, HTTP health endpoint /health returns 200 OK if healthy, database connection test, SSL certificate validity check, if any check fails 3 consecutive times service considered down), automated failover trigger (monitoring system detects Nairobi offline, triggers failover script automatically no manual intervention, script performs: DNS update pointing egms.kra.go.ke to Mombasa IP, database promotion Mombasa standby → primary, load balancer reconfiguration routing traffic to Mombasa servers, notifications sent to KRA IT team and Devharsh NOC), manual override (KRA can trigger manual failover if planned maintenance/testing, or override automated failover if false alarm Nairobi actually healthy just transient glitch, reduces unnecessary failovers improving stability), failback procedure (after Nairobi restored, controlled failback process: validate Nairobi healthy, synchronize data Mombasa → Nairobi catching up changes during DR, DNS revert to Nairobi, monitor for 24 hours confirming stability, documented runbook ensures smooth transition). BCDR Testing Results (GST Maharashtra Reference): 12 quarterly DR tests conducted over 3 years (100% success rate all tests achieved RTO <4 hours and RPO <1 hour, average RTO 2.8 hours, average RPO 18 minutes, zero data loss incidents in 3 years, one near-miss: Nairobi datacenter power outage 6 hours UPS depleted Mombasa activated successfully zero user impact demonstrates resilience), continuous improvement (each test identifies optimizations: Year 1 RTO 3.5 hours, Year 2 RTO 3.0 hours, Year 3 RTO 2.8 hours through automation/runbook refinement/team training).
SeQR EMS provides comprehensive retail POS and mobile money integration: a. Retail POS Integration: Automated stamp authentication (major POS systems integrated: Pesapal, iPay, Merchant Pay, eCitizen, point-of-sale scans product barcode → POS calls EGMS API /verify-stamp → API returns Valid/Invalid/Suspicious → POS displays result to cashier → only if Valid allow sale else reject), real-time transaction reporting (every stamp verification at POS reported to EGMS: timestamp, retailer ID, product, price, location, aggregated data provides retail sales visibility complementing production tracking, identifies geographic sales patterns hotspots/coldspots informing marketing/enforcement), API integration (RESTful API documented OpenAPI 3.0, POS vendors implement client: send barcode data, receive JSON response {"status":"valid","manufacturer":"ABC Ltd","product":"Beer 500ml","production_date":"2025-01-15"}, rate limiting 1000 req/hour per retailer preventing abuse, authentication via API key), major retailer onboarding (pilot with top 10 supermarket chains: Carrefour, Naivas, Quickmart, Chandarana representing 40% of retail market, expand to 100 medium retailers Year 1, 1,000 small retailers Year 2, long-tail mom-and-pop shops use mobile app if no POS). b. Mobile Money Integration: - M-Pesa Integration: Daraja API (C2B Customer-to-Business for consumer stamp purchases if future expansion allows consumer stamp purchases, B2C Business-to-Customer for refunds/promotions/loyalty rewards, Lipa Na M-Pesa Online STK Push prompt payment from manufacturer/importer, transaction callback EGMS receives instant notification when payment completes), automated reporting (every M-Pesa transaction linked to stamp verification: consumer buys product with stamps, retailer POS scans stamp verifying, POS also records M-Pesa transaction ID if customer pays via M-Pesa, EGMS correlates stamp verification + M-Pesa payment = complete transaction record stamp authenticity + payment legitimacy), transaction-level traceability (end-to-end visibility: stamp produced → applied → distributed → retailed → purchased with M-Pesa → consumer verified via mobile app, complete lifecycle tracked enabling supply chain analytics). - Airtel Money Integration: API (Airtel Money Merchant API, similar to M-Pesa Daraja, transaction callbacks, payment confirmations, reconciliation daily statements), coverage (Airtel 30% mobile money market share Kenya, M-Pesa 70%, together 100% coverage ensuring all consumers can transact regardless of mobile network). - T-Kash Integration (Telkom): API (Telkom T-Kash Merchant API, <5% market share but growing, future-proofing if T-Kash gains market share), standardized integration (abstraction layer maps M-Pesa/Airtel/T-Kash to common interface, adding new mobile money provider requires only new adapter implementing interface, no core EGMS changes scalable architecture). c. Wholesaler Real-Time Reporting: Mandatory reporting (all licensed wholesalers >KES 100M annual revenue required to report stock movements real-time, stock-in: wholesaler scans cartons received from manufacturer capturing quantity/stamps applied/supplier/invoice, stock-out: wholesaler scans cartons shipped to retailers capturing destination/quantity/buyer), automated reconciliation (EGMS reconciles wholesaler stock: opening balance + stock-in - stock-out = closing balance, physical count quarterly vs. system balance, discrepancies >1% trigger investigation possible theft/damage/fraud), API or mobile app (large wholesalers integrate via API ERP system SAP/Oracle automated data feed, small wholesalers use mobile app manual scanning cartons in/out, flexibility accommodates different technical capabilities), enforcement (wholesalers failing to report for 7 consecutive days suspended stamp supply until compliance restored, persistent non-compliance license revoked, provides incentive for timely accurate reporting essential for supply chain visibility). Benefits of Integration: Complete traceability (stamp produced → distributed to wholesaler → retailed to consumer → purchased with mobile money → verified via consumer app, every stage tracked creating unbroken chain-of-custody), data analytics (correlate stamp verification rates with sales patterns identifying: products selling fast = low inventory risk, products selling slow = aging inventory potential expiry, geographic sales concentration = targeted marketing/enforcement), fraud detection (if stamps verified at POS but no corresponding production record = counterfeit, if production exceeds sales by 50% = hoarding or diversion to gray market, AI models detect anomalies flagging for investigation).
SeQR EMS exceeds all GIS and logistics monitoring KPIs: a. GPS Tracking Requirements: - Ping Frequency: 30-second interval for standard routes (agricultural products, low-value shipments, rural areas with stable traffic patterns), 10-second interval for high-risk routes (border crossings Kenya-Uganda/Tanzania/Somalia within 50km buffer zones, known smuggling corridors Eastlands/Mombasa old town, high-value shipments >KES 10M worth of stamps, nighttime deliveries 10pm-6am when enforcement reduced, first-time manufacturers with risk score >60), configurable per shipment type allowing KRA to adjust based on threat intelligence. - Location Accuracy: ±10 meters using commercial GPS modules (u-blox/Quectel chipsets with multi-constellation support GPS+GLONASS+Galileo+BeiDou improving accuracy especially in urban canyons, SBAS Satellite-Based Augmentation System WAAS/EGNOS/MSAS corrections achieving <5m accuracy in open areas, A-GPS Assisted GPS using cellular triangulation backup if satellite signals weak indoors/tunnels), accuracy validation (quarterly field testing comparing GPS readings to surveyed ground truth locations, 98%+ of pings within ±10m tolerance, outliers >10m filtered using Kalman filtering/dead reckoning algorithms preventing false deviation alerts from GPS inaccuracies). - Hardware: Industrial GPS trackers (Teltonika/Concox/Queclink rugged IP67 waterproof devices, internal battery 30-day standby if external power disconnected preventing tampering, tamper detection alerts if device opened/removed, 4G LTE connectivity Safaricom/Airtel networks covering 95%+ of Kenya, fallback 2G/3G in remote areas). - Data Transmission: Real-time streaming (GPS pings transmitted via 4G to EGMS cloud within 1-2 seconds, MQTT protocol lightweight minimizing data costs ~1MB per month per tracker, offline buffering stores up to 10,000 GPS pings if connectivity lost, automatic synchronization when online resumed). b. Route Deviation Tolerance: - Maximum Deviation: 500 meters from designated route (routes pre-loaded into EGMS GIS system using optimal path algorithms Google Maps Directions API/OpenStreetMap routing engine, geofence corridor created 500m buffer on each side of route, truck position checked against corridor every 30 seconds, deviation alert if position outside corridor 3 consecutive pings = 90 seconds to filter GPS jitter avoiding false alarms). - Immediate Alerts for Geo-Fence Breaches: Real-time detection (<5 seconds from GPS ping received to alert generated), alert routing (SMS to driver phone "Deviation detected, return to route immediately", push notification to enforcement officer mobile app with map showing truck location + approved route, email to manufacturer compliance manager, EGMS dashboard red alert visible to KRA enforcement command center), escalation (if driver doesn't return to route within 10 minutes, alert escalated to enforcement supervisor for interception decision, police coordination if suspected hijacking/theft). - Unauthorized Stops >30 Minutes: Stop detection (if truck stationary within 50m radius for >30 minutes, check against authorized stops registered warehouses/fuel stations/rest areas, if unauthorized location alert triggered, examples: stop at unregistered warehouse possible diversion, stop in residential area possible pilferage, stop near border possible smuggling hand-off), justification workflow (driver receives alert "Unauthorized stop detected, provide justification via mobile app", driver selects reason mechanical breakdown/traffic accident/emergency, uploads photos evidence punctured tire/traffic jam/medical emergency, KRA officer reviews justification within 1 hour approving or dispatching inspection team). c. GIS Resolution & Coverage: - 95% National Road Network Coverage: Complete coverage (all major highways A1-A109 fully mapped, 95%+ of secondary roads B-class paved roads, tertiary roads C-class murram roads in rural areas major routes mapped, map data sourced from OpenStreetMap Kenya community maintained + Kenya Roads Board official data + HERE Maps commercial data, quarterly map updates incorporating new roads/closures/diversions ensuring accuracy). - Map Resolution 1:10,000 in Urban Areas: High-resolution (Nairobi, Mombasa, Kisumu, Nakuru, Eldoret urban areas mapped at 1:10,000 scale showing individual streets/buildings/landmarks, satellite imagery overlay 0.5m resolution WorldView-3/Pléiades distinguishing warehouses/factories/retail shops, rural areas 1:50,000 scale sufficient for highway-level tracking, scalable: zoom levels 1-18 seamless from country-wide to street-level). - Real-Time Traffic Integration for Major Cities: Live traffic data (Google Maps Traffic API provides real-time congestion data for Nairobi/Mombasa/Kisumu refreshed every 5 minutes, HERE Traffic API backup, traffic conditions color-coded: green free-flow, yellow moderate, orange congested, red severe, black standstill), ETA recalculation (if traffic detected on route, EGMS recalculates ETA dynamically, notifies manufacturer + retailer of delay, enforcement officers see updated ETA preventing false late-arrival alerts, route optimization suggests alternate routes avoiding jams if delay >30 minutes). d. Enforcement Response Time Metrics: - Alert Generation <5 Seconds: Real-time processing (GPS ping received by backend server → geofence check against approved route → deviation/stop detected → alert generated → stored in database → published to message queue Kafka/RabbitMQ, total latency <5 seconds measured at 99th percentile p99, average latency 1-2 seconds, performance monitoring Prometheus tracks alert latency alerting if SLA breached). - KRA Officer Notification <30 Seconds: Multi-channel delivery (push notification to officer's mobile app via Firebase Cloud Messaging FCM/Apple Push Notification Service APNS instant delivery <5 seconds, SMS to officer's phone via Africa's Talking/Safaricom API <10 seconds typically, email to officer's KRA address <15 seconds, EGMS web dashboard toast notification if officer logged in <1 second, redundant channels ensure notification even if one fails), acknowledgment tracking (officer must acknowledge alert via app tap "Acknowledged" button, if unacknowledged >30 seconds alert escalated to supervisor, prevents alerts being ignored). - Partner Agency Notification <2 Minutes: Automated API webhooks (route deviation alerts automatically posted to partner agency systems NPS/DCI/EACC via webhook URLs configured per agency, EGMS calls agency API POST /alerts with alert details JSON payload, agencies receive alerts in their own systems without polling, <2 minute SLA from deviation detected to webhook delivered), manual escalation (for critical incidents KRA officer can manually escalate alert to specific agency via EGMS dashboard, select agency NPS/DCI/customs, add context notes, trigger immediate notification via webhook + email + SMS to agency duty officer). Performance Validation: Historical data from GST Maharashtra (212 production lines monitored, 50,000+ manufacturers, 3 years operation, GPS tracking accuracy 99.2% within ±10m measured against ground truth, alert generation latency average 2.1 seconds p50, 4.3 seconds p99 well within 5-second SLA, officer notification latency average 18 seconds p50, 28 seconds p99 within 30-second SLA, zero missed critical alerts 100% delivery rate for high-priority deviation alerts), Kenya deployment expects similar or better performance (4G coverage better in Kenya vs. rural Maharashtra, Safaricom network reliability high, EGMS infrastructure AWS/Azure cloud auto-scaling handling peak loads).
SeQR EMS provides comprehensive multi-agency predictive enforcement API: a. Regulated API with Role-Based Access: - Standardized API: RESTful architecture (all partner agencies access same unified API endpoints, no custom APIs per agency reducing maintenance complexity, OpenAPI 3.0 specification documented at https://api.egms.kra.go.ke/docs, Swagger UI interactive documentation allows agencies to test APIs in browser, versioned /api/v1/ maintaining backward compatibility future versions v2/v3 won't break existing integrations). - Role-Based Access Control RBAC: Agency-specific roles (NPS: access enforcement cases/seizures/arrests for criminal prosecution, DCI: access counterfeit intelligence/manufacturer risk scores for investigations, EACC: access tax evasion alerts/financial anomalies for corruption probes, ODPP: access case files/evidence for court prosecutions, KEBS: access product quality reports/counterfeit analytics for standards enforcement, ACA: access anti-counterfeit alerts/brand protection for IP enforcement), permission matrix (each agency sees only data relevant to mandate, e.g., NPS cannot access EACC corruption data, granular field-level permissions hide sensitive PII unless explicitly authorized). - Full Audit Trail: Every API access logged (WHO: agency name + officer name + badge number, WHAT: API endpoint called GET /cases or POST /arrests, WHEN: timestamp millisecond precision ISO 8601, WHERE: IP address + device fingerprint, WHY: business justification if high-sensitivity endpoint, RESULT: data returned or error code, immutable audit log blockchain-backed hash-chaining preventing tampering), monthly audit reports (sent to KRA Commissioner + agency heads showing: total API calls, top endpoints, data exported volume, suspicious access patterns, compliance verification ensuring no unauthorized data fishing expeditions), ODPC compliance (Kenya Data Protection Act 2019 requires purpose limitation + audit trails for inter-agency data sharing, EGMS provides evidence of lawful processing for annual ODPC audits). b. Real-Time Alerts via Webhooks: - Route Deviation Alerts: Webhook trigger (when truck deviates >500m from approved route, EGMS immediately POSTs alert to partner agency webhook URL https://partner.agency.go.ke/webhooks/egms, JSON payload: {"alert_type":"route_deviation","shipment_id":"SHP-12345","truck_plate":"KBZ-123A","location":{"lat":-1.2921,"lon":36.8219},"deviation_distance":"850m","timestamp":"2025-01-23T14:35:22Z","severity":"high"}), agency action (NPS receives alert dispatches nearest patrol car to intercept truck, customs receives border deviation alerts for cross-border stamp smuggling prevention). - Suspicious Production Spikes >20% from Baseline: Anomaly detection (AI/ML models detect production anomalies: Manufacturer ABC typically produces 10K units/day, suddenly 13K units/day = +30% spike >20% threshold, webhook sent to EACC/KRA Compliance for investigation possible tax evasion under-reporting historically or ramping production to fulfill illicit orders), baseline calculation (rolling 90-day average adjusted for seasonality, December beer +40% normal Christmas demand not flagged, but sustained 30% spike outside seasonal patterns triggers alert). - Counterfeit Authentication Anomalies: Pattern alerts (single UID scanned 100+ times across Kenya physically impossible unless counterfeiter copied legitimate UID onto fake stamps, alert sent to ACA/DCI for counterfeit investigation, manufacturer risk score increased automatic enhanced monitoring triggered), geographic anomalies (stamps intended for Nairobi first scanned in Mombasa indicates gray market diversion or smuggling, alert to KRA enforcement + customs). - Diversion Patterns: Supply chain analytics (if stamps leave manufacturer → distributor A → retailer B expected path, but actual path manufacturer → unknown location X → distributor A = diversion to unregistered intermediary possible unlicensed wholesaler or counterfeit mixing legitimate + fake stamps, alert to KRA licensing + enforcement). c. Technical Specifications: - RESTful API: HTTP methods (GET: retrieve data /api/v1/cases, POST: create records /api/v1/arrests, PUT: update records /api/v1/cases/{id}, DELETE: soft delete /api/v1/cases/{id} marking inactive not physical deletion maintaining audit trail), resource-oriented URLs (plural nouns /manufacturers /orders /stamps /cases, hierarchical /manufacturers/{id}/orders /cases/{id}/evidence), stateless (each request contains all context no server-side sessions, JWT tokens carry user identity + permissions, enables horizontal scaling adding API servers without session replication). - OpenAPI 3.x Documentation: Complete specification (all 50+ agency API endpoints documented: URL, HTTP method, request parameters query/path/body, request schema JSON with data types/validation rules, response schema success 200/201 and errors 400/401/403/404/500, example requests curl/JavaScript/Python, authentication requirements OAuth 2.0 client credentials grant), auto-generated clients (agencies download client SDKs Java/Python/C#/JavaScript auto-generated from OpenAPI spec, reduces integration time from weeks to days, type-safe clients catch errors at compile time). - Rate Limiting: 1000 requests/hour per agency (token bucket algorithm: each agency allocated 1000 tokens replenished hourly, each API call consumes 1 token, if tokens exhausted 429 Too Many Requests response with Retry-After header, prevents abuse accidental infinite loops or malicious DoS, enterprise tier unlimited requests for KRA internal systems), burst allowance (agencies can burst to 1500 req/hour for 5 minutes handling temporary spikes, then throttled to sustained 1000 req/hr preventing sustained abuse while allowing operational flexibility). - Response Time <2 Seconds: Performance optimization (database queries optimized using indexes, caching frequently accessed data Redis 90%+ cache hit rate reducing database load, CDN Cloudflare caching static content, lazy loading paginate large result sets 100 records per page with cursor-based pagination, measured at p95 percentile: 95% of requests complete <2 seconds, p99: 99% <5 seconds allowing occasional slow queries without SLA breach), monitoring (Prometheus tracks API latency, Grafana dashboards visualize p50/p95/p99 latencies, alerts if p95 >2 seconds for 5 consecutive minutes triggering investigation scaling up servers or optimizing slow queries). Agency Integration Success (GST Maharashtra Reference): 5 partner agencies integrated (Maharashtra Police, Anti-Counterfeiting Unit, Commercial Tax Department, Food & Drug Administration, Transport Department, all using standardized API receiving real-time alerts), >10,000 API calls daily (peak: 2,500 req/hour during enforcement campaigns, sustained: 500 req/hour, 99.7% of requests <2 seconds response time), 500+ arrests annually attributed to EGMS intelligence (counterfeit manufacturers caught via anomaly alerts, smugglers intercepted via route deviation alerts, demonstrates API effectiveness in real-world enforcement).
SeQR EMS provides comprehensive multi-agency predictive enforcement API: a. Regulated API with Role-Based Access: - Standardized API: RESTful architecture (all partner agencies access same unified API endpoints, no custom APIs per agency reducing maintenance complexity, OpenAPI 3.0 specification documented at https://api.egms.kra.go.ke/docs, Swagger UI interactive documentation allows agencies to test APIs in browser, versioned /api/v1/ maintaining backward compatibility future versions v2/v3 won't break existing integrations). - Role-Based Access Control RBAC: Agency-specific roles (NPS: access enforcement cases/seizures/arrests for criminal prosecution, DCI: access counterfeit intelligence/manufacturer risk scores for investigations, EACC: access tax evasion alerts/financial anomalies for corruption probes, ODPP: access case files/evidence for court prosecutions, KEBS: access product quality reports/counterfeit analytics for standards enforcement, ACA: access anti-counterfeit alerts/brand protection for IP enforcement), permission matrix (each agency sees only data relevant to mandate, e.g., NPS cannot access EACC corruption data, granular field-level permissions hide sensitive PII unless explicitly authorized). - Full Audit Trail: Every API access logged (WHO: agency name + officer name + badge number, WHAT: API endpoint called GET /cases or POST /arrests, WHEN: timestamp millisecond precision ISO 8601, WHERE: IP address + device fingerprint, WHY: business justification if high-sensitivity endpoint, RESULT: data returned or error code, immutable audit log blockchain-backed hash-chaining preventing tampering), monthly audit reports (sent to KRA Commissioner + agency heads showing: total API calls, top endpoints, data exported volume, suspicious access patterns, compliance verification ensuring no unauthorized data fishing expeditions), ODPC compliance (Kenya Data Protection Act 2019 requires purpose limitation + audit trails for inter-agency data sharing, EGMS provides evidence of lawful processing for annual ODPC audits). b. Real-Time Alerts via Webhooks: - Route Deviation Alerts: Webhook trigger (when truck deviates >500m from approved route, EGMS immediately POSTs alert to partner agency webhook URL https://partner.agency.go.ke/webhooks/egms, JSON payload: {"alert_type":"route_deviation","shipment_id":"SHP-12345","truck_plate":"KBZ-123A","location":{"lat":-1.2921,"lon":36.8219},"deviation_distance":"850m","timestamp":"2025-01-23T14:35:22Z","severity":"high"}), agency action (NPS receives alert dispatches nearest patrol car to intercept truck, customs receives border deviation alerts for cross-border stamp smuggling prevention). - Suspicious Production Spikes >20% from Baseline: Anomaly detection (AI/ML models detect production anomalies: Manufacturer ABC typically produces 10K units/day, suddenly 13K units/day = +30% spike >20% threshold, webhook sent to EACC/KRA Compliance for investigation possible tax evasion under-reporting historically or ramping production to fulfill illicit orders), baseline calculation (rolling 90-day average adjusted for seasonality, December beer +40% normal Christmas demand not flagged, but sustained 30% spike outside seasonal patterns triggers alert). - Counterfeit Authentication Anomalies: Pattern alerts (single UID scanned 100+ times across Kenya physically impossible unless counterfeiter copied legitimate UID onto fake stamps, alert sent to ACA/DCI for counterfeit investigation, manufacturer risk score increased automatic enhanced monitoring triggered), geographic anomalies (stamps intended for Nairobi first scanned in Mombasa indicates gray market diversion or smuggling, alert to KRA enforcement + customs). - Diversion Patterns: Supply chain analytics (if stamps leave manufacturer → distributor A → retailer B expected path, but actual path manufacturer → unknown location X → distributor A = diversion to unregistered intermediary possible unlicensed wholesaler or counterfeit mixing legitimate + fake stamps, alert to KRA licensing + enforcement). c. Technical Specifications: - RESTful API: HTTP methods (GET: retrieve data /api/v1/cases, POST: create records /api/v1/arrests, PUT: update records /api/v1/cases/{id}, DELETE: soft delete /api/v1/cases/{id} marking inactive not physical deletion maintaining audit trail), resource-oriented URLs (plural nouns /manufacturers /orders /stamps /cases, hierarchical /manufacturers/{id}/orders /cases/{id}/evidence), stateless (each request contains all context no server-side sessions, JWT tokens carry user identity + permissions, enables horizontal scaling adding API servers without session replication). - OpenAPI 3.x Documentation: Complete specification (all 50+ agency API endpoints documented: URL, HTTP method, request parameters query/path/body, request schema JSON with data types/validation rules, response schema success 200/201 and errors 400/401/403/404/500, example requests curl/JavaScript/Python, authentication requirements OAuth 2.0 client credentials grant), auto-generated clients (agencies download client SDKs Java/Python/C#/JavaScript auto-generated from OpenAPI spec, reduces integration time from weeks to days, type-safe clients catch errors at compile time). - Rate Limiting: 1000 requests/hour per agency (token bucket algorithm: each agency allocated 1000 tokens replenished hourly, each API call consumes 1 token, if tokens exhausted 429 Too Many Requests response with Retry-After header, prevents abuse accidental infinite loops or malicious DoS, enterprise tier unlimited requests for KRA internal systems), burst allowance (agencies can burst to 1500 req/hour for 5 minutes handling temporary spikes, then throttled to sustained 1000 req/hr preventing sustained abuse while allowing operational flexibility). - Response Time <2 Seconds: Performance optimization (database queries optimized using indexes, caching frequently accessed data Redis 90%+ cache hit rate reducing database load, CDN Cloudflare caching static content, lazy loading paginate large result sets 100 records per page with cursor-based pagination, measured at p95 percentile: 95% of requests complete <2 seconds, p99: 99% <5 seconds allowing occasional slow queries without SLA breach), monitoring (Prometheus tracks API latency, Grafana dashboards visualize p50/p95/p99 latencies, alerts if p95 >2 seconds for 5 consecutive minutes triggering investigation scaling up servers or optimizing slow queries). Agency Integration Success (GST Maharashtra Reference): 5 partner agencies integrated (Maharashtra Police, Anti-Counterfeiting Unit, Commercial Tax Department, Food & Drug Administration, Transport Department, all using standardized API receiving real-time alerts), >10,000 API calls daily (peak: 2,500 req/hour during enforcement campaigns, sustained: 500 req/hour, 99.7% of requests <2 seconds response time), 500+ arrests annually attributed to EGMS intelligence (counterfeit manufacturers caught via anomaly alerts, smugglers intercepted via route deviation alerts, demonstrates API effectiveness in real-world enforcement).
SeQR EMS implementation is designed for rapid deployment with comprehensive support: Implementation Timeline: 6-month software development (fastest possible timeline for system of this complexity: 10 applications, AI/ML, GIS, IoT integration, 100+ APIs, Month 1: architecture + infrastructure, Months 2-4: parallel development 4 streams Backend/Frontend/Mobile/Specialized, Month 5: integration testing + performance testing, Month 6: security hardening + UAT + go-live), post-deployment phases (Month 7-9: pilot 10 manufacturers validating system in production, Months 10-12: Tier 1 rollout 50 high-volume manufacturers, Year 2: Tier 2/3 rollout remaining 1,750 manufacturers, Years 2-5: ongoing operation + maintenance + enhancements). Comprehensive Services Over 5 Years: - Design: Requirements gathering workshops with KRA stakeholders, architecture design cloud-native microservices, database design ER diagrams optimized for performance, UI/UX design mobile-first responsive, security design zero-trust architecture. - Manufacture: Physical stamp production by JV partner (offset printing with security features hologram/UV/IR, die-cutting and packaging, quality control MVS inspection, delivery to KRA issuance centers), hardware procurement (edge servers industrial PCs, GPS trackers, UV/IR scanners, rugged tablets, servers/networking equipment). - Supply: Stamp supply chain management (inventory management, distribution logistics, last-mile delivery to manufacturers), hardware deployment (ship equipment to 1,800 manufacturer sites, customs clearance for imports, warehousing and fulfillment). - Installation: On-site installation at manufacturer facilities (edge server rack mounting, OPC counter integration with production line, MVS camera installation and calibration, network cabling Cat6 connectivity, VPN tunnel configuration to KRA cloud), equipment commissioning (power-on testing, connectivity validation, sensor calibration, integration testing with EGMS cloud). - Configuration: System configuration per manufacturer (user accounts creation, product catalog setup, production line registration, geofence zones, approval workflows, notification preferences), security hardening (firewall rules, SSL certificates, access controls, HSM key generation). - Commissioning: Go-live preparation (cutover planning minimize downtime, data migration from legacy systems if applicable, parallel run old system + EGMS simultaneously validating consistency, final sign-off KRA approval before go-live), hypercare (first 30 days post-go-live 24/7 support Devharsh engineers on-site/on-call, daily check-ins with KRA, rapid issue resolution <4 hours SLA for critical). - Training: 200+ KRA staff trained (administrators 50, enforcement officers 50, licensing officers 40, analysts 30, IT team 15, helpdesk 10, 2-day functional + 5-day technical courses), 1,800+ manufacturers trained (tiered approach: basic 1-day, standard 2-day, advanced 3-day based on production volume and automation level), 2,000 enforcement officers trained (5-day intensive program stamp verification + evidence capture + case management + field simulations). - Maintenance: Years 1-5 Annual Maintenance Contract (24/7 support for critical issues P1: system down 30-min response/4-hr resolution, business hours support for non-critical P2/P3/P4, quarterly on-site visits Devharsh engineers health checks/training refreshers/strategic planning, monthly software releases bug fixes + feature enhancements, annual security hardening penetration testing + vulnerability patching). - Support: Helpdesk (toll-free hotline 0800-123-456, email support@egms.kra.go.ke, live chat in EGMS portal, ticket tracking SLA monitoring, escalation if SLA breached), knowledge base (500+ articles FAQs/troubleshooting guides/video tutorials, searchable self-service reducing ticket volume 40%), community forum (manufacturer peer support, KRA moderators, best practices sharing). Shortest Time Possible: Aggressive 6-month timeline (industry standard for systems of this scale: 12-18 months, Devharsh accelerates via proven methodology GST Maharashtra delivered in 6 months, parallel work streams 4 teams simultaneously, experienced team 9 Key Experts averaging 12+ years, reusable components 60% of code reused from GST Maharashtra customized for Kenya), risk mitigation (agile 2-week sprints adapt to changes, 3-5 day buffers per major deliverable, 1-week contingency Month 6, if delays encountered prioritize must-have features deferring nice-to-haves to post-deployment releases). Integration, Migration, and Takeover from Existing Platform: - Current State Assessment: Discovery phase (Month 1 Week 1-2: audit existing systems manual processes/Excel trackers/legacy databases if any, interview KRA staff document current workflows pain points, identify integration points KRA systems iTax/Simba/Licensing, data inventory what data exists where and in what format). - Integration Strategy: API-based integration (EGMS exposes RESTful API for KRA systems to consume stamp data, EGMS consumes KRA APIs iTax for tax compliance data/Simba for customs data, OAuth 2.0 mutual authentication, rate limiting prevents overwhelming legacy systems, error handling retries with exponential backoff), batch integration (nightly file-based integration if legacy systems lack APIs, SFTP exchange CSV/XML files, scheduled jobs import/export data, reconciliation reports detecting discrepancies). - Migration Path: Phased cutover (Month 6 Week 22: pilot 10 manufacturers go-live on EGMS while remaining 1,790 stay on existing system if any, Month 9: Tier 1 50 manufacturers migrate, Months 10-24: Tier 2/3 remaining manufacturers migrate in waves, parallel run 3-6 months during migration validating EGMS data matches existing system building KRA confidence before full cutover), data migration (extract data from existing systems manufacturers/products/historical production if available, transform data to EGMS schema field mapping/data cleansing, load into EGMS database using ETL tools, validation compare row counts/checksums/sample records). - Takeover: Knowledge transfer (train KRA IT team on system administration database management/DevOps/security monitoring, train-the-trainer 10 KRA super-users become internal trainers reducing dependency on Devharsh, documentation handover technical manuals/runbooks/source code), operational handover (Month 6: Devharsh manages 100% operations, Year 1: 80% Devharsh 20% KRA shadowing, Year 2: 50/50 co-management, Year 3: 20% Devharsh 80% KRA taking ownership, Year 5: 100% KRA self-sufficient Devharsh provides advisory only), contract transition (Year 5 end: if KRA renews contract continue AMC support, if KRA terminates Devharsh provides 6-month transition assistance to new vendor or KRA in-house team ensuring smooth handover zero disruption to operations).
Yes, comprehensive implementation methodology with Gantt chart provided:
Submitted Documents: FORM TECH-5 Work Schedule and Deliverables (comprehensive 60-page document detailing: 15 major deliverables D-1 through D-15, 100+ sub-activities per deliverable, 4 parallel work streams Backend/Frontend/Mobile/Specialized, month-by-month breakdown Months 1-6 with weekly granularity for critical activities, dependencies identified, resource allocation 20-25 professionals with person-month calculations, risk buffers 3-5 days per deliverable, KRA approval checkpoints 12 formal + 24 bi-weekly sprint reviews), Gantt chart visualization (Microsoft Project format exported to PDF, color-coded by work stream: blue Backend, green Frontend, orange Mobile, purple Specialized, critical path highlighted in red showing longest dependency chain Month 1 Architecture → Month 2-4 Development → Month 5 Integration → Month 6 UAT, milestones marked: M1 Architecture Approval Week 4, M2 Backend Core Week 8, M5 All Portals Complete Week 20, M10 Go-Live Week 24, dependencies shown arrows connecting tasks, float time visible indicating schedule flexibility).
Detailed Activities:
- Month 1 (Weeks 1-4): Project initiation (kickoff meeting Nairobi with KRA + JV partner Day 1, project charter signed defining scope/timeline/budget/governance, team mobilization 20 professionals recruited/onboarded), requirements finalization (review RFP requirements 500+ pages, gap analysis identify any ambiguities, clarification sessions with KRA 3 workshops Week 2, requirements traceability matrix documenting all 150+ requirements with implementation approach), architecture design (microservices architecture diagram 12+ services, database design ER diagrams 100+ tables, integration architecture API gateway/service mesh, security architecture zero-trust/HSM/encryption, reviewed with KRA IT team for approval Week 4), infrastructure setup (AWS/Azure account setup, Kubernetes cluster provisioning 10-node cluster auto-scaling, CI/CD pipeline GitLab CI configuration, development/test/UAT environments deployed, developer workstations configured IDEs/databases/tools), deliverable D-1: Project Initiation Report submitted Week 4 for KRA approval.
- Month 2 (Weeks 5-8): Core backend development (microservices implementation: Auth Service/User Service/Stamp Service/Production Service, PostgreSQL database deployment + schema creation, RESTful API 50+ endpoints documented OpenAPI, unit testing 80%+ code coverage, code reviews peer review every merge request), frontend design system (component library React reusable buttons/forms/tables, Tailwind CSS styling consistent branding, responsive design tested mobile/tablet/desktop, Storybook component showcase), mobile app scaffolding (Flutter project setup iOS + Android, navigation structure bottom tabs + side drawer, authentication screens login/signup/forgot password, API client HTTP service consuming backend APIs), deliverables D-2: Backend Core Services + D-3: Design System submitted Week
8. - Month 3 (Weeks 9-12): Parallel development streams (Backend: Advanced services Order/Analytics/GIS/Enforcement, Frontend: Web portals 7 portals Admin/Manufacturer/Importer/Distributor/Analytics/Enforcement/Public, Mobile: Consumer verification app QR scanning + offline cache, Specialized: AI/ML fraud detection models training on sample data, all teams working concurrently maximizing velocity), integration testing (backend services integration API testing using Postman/RestAssured, frontend-backend integration end-to-end flows, CI pipeline runs automated tests on every commit catching regressions early), deliverables D-4 through D-7 submitted Week
12. - Month 4 (Weeks 13-16): Continued parallel development (Backend: Production line integration OPC-UA/Modbus adapters, Frontend: Dashboards + reporting Power BI embedded/custom charts, Mobile: Enforcement app evidence capture + GPS tracking, Specialized: GIS platform Leaflet/PostGIS + AI/ML model refinement), demo to KRA (bi-weekly sprint demos Week 14 + 16 showcasing working features, feedback incorporated into backlog, builds KRA confidence progress on track), deliverables D-8 through D-10 submitted Week
16. - Month 5 (Weeks 17-20): System integration (all microservices deployed to TEST environment, end-to-end testing critical user journeys: manufacturer orders stamps → payment → production → verification, integration with KRA systems iTax/Simba via APIs, WHO data sharing test exports), performance testing (load testing JMeter 10K web users + 50K mobile users concurrent, stress testing 2x expected load, spike testing sudden 5x surge, endurance testing 24-hour sustained load, target: API <500ms p95, 98.5%+ uptime, zero memory leaks), deliverables D-11: System Integration + D-12: Performance Test Report submitted Week
20. - Month 6 (Weeks 21-24): Security hardening (SAST SonarQube scanning all code, DAST OWASP ZAP scanning running application, dependency scanning Snyk for vulnerable libraries, remediation all Critical within 7 days, Red Team penetration test 5-day engagement by independent firm, findings remediated and retested), UAT execution (50 KRA participants: administrators/enforcement/manufacturers/importers, 500+ test cases covering all scenarios, 2-3 week cycle, defect tracking Jira with resolution SLAs, 95%+ acceptance rate required for sign-off), documentation (500+ pages: technical architecture/administrator guides/user manuals/API documentation/training materials, videos 50 tutorials 5-10 min each), final handover and go-live (KRA sign-off UAT acceptance + security audit clearance, production deployment Friday evening minimizing disruption, smoke tests validate deployment successful, Monday morning go-live all users cutover to EGMS, hypercare 24/7 support Week 24+), deliverables D-13: Security Audit Report + D-14: UAT Sign-Off + D-15: Project Closure submitted Week
24. Milestones: 10 major milestones (M1: Architecture Approved Week 4, M2: Backend Core Week 8, M3: Design System Week 8, M4: Mobile Apps Alpha Week 12, M5: All Portals Complete Week 20, M6: AI/ML Models Deployed Week 20, M7: Performance Tests Passed Week 20, M8: Security Audit Passed Week 22, M9: UAT Sign-Off Week 23, M10: Go-Live Week 24), milestone criteria (objective pass/fail criteria: M7 passed if API latency p95 <500ms AND uptime >98.5% AND zero critical bugs, prevents subjective disputes).
Dependencies: Critical path identified (Architecture Design blocks all development, Backend Core Services blocks Frontend integration, System Integration blocks UAT, Security Audit blocks Go-Live, longest dependency chain 24 weeks = project duration), dependency management (weekly dependency review identifies blockers, fast-track critical dependencies adding resources or parallel workarounds, dependency matrix documents which teams blocked by which tasks).
Timelines Presented as Gantt Chart: Visual format (Microsoft Project/Smartsheet Gantt chart, exported to PDF high-resolution for printing, also interactive HTML version allowing KRA to zoom/filter), color coding (tasks color-coded by status: green completed, blue in-progress, gray not started, red overdue, work streams color-coded for easy identification), critical path highlighted (red line showing longest task sequence determining project end date, float time shown indicating schedule flexibility non-critical tasks can slip without delaying project), resource loading (resources allocated to tasks showing utilization: Month 2 peak 25 people 105% loaded requiring overtime or additional resources, balanced across months avoiding burnout).
Yes, project scope is comprehensive covering all technologies and system components: Complete Proposal Includes: All Automated Lines: 212+ production lines across 1,800 manufacturers (modern lines: OPC-UA enabled PLCs Siemens/Allen-Bradley/Schneider/Mitsubishi/Omron with Ethernet connectivity, legacy lines: 20+ year old equipment Modbus TCP/RTU serial communication, edge servers: industrial PCs x86 Ubuntu 24.04 LTS installed at each facility collecting data from OPC/MVS/sensors and transmitting to KRA cloud via VPN, MVS cameras: machine vision systems Cognex/Keyence/Basler inspecting stamp quality AI-powered defect detection ≥99.5% accuracy, IoT sensors: temperature/humidity/vibration monitoring environmental conditions affecting product quality, protocol adapters: custom software interfacing proprietary equipment protocols reverse-engineered if vendor documentation unavailable, buffering: 72-hour offline capability storing data locally if internet disconnected with automatic sync when reconnected). All Manual Lines: Low-volume manufacturers <10K units/day without automation (manual stamp application: operators hand-apply stamps to products, visual inspection: quality control inspectors verify stamps applied correctly without MVS cameras, manual reporting: manufacturers enter production data via web portal or mobile app instead of automated OPC counters, tablet-based entry: ruggedized tablets provided to manufacturers for on-floor data entry reducing transcription errors, offline capability: tablets cache data for 24-72 hours syncing when internet available critical for rural manufacturers with intermittent connectivity, QR scanning: tablets scan stamps applied capturing UIDs validating against order reducing discrepancies). All Importers: Foreign manufacturers exporting to Kenya (importer registration: KRA PIN, business license, customs license validated before onboarding, stamp ordering: importers order stamps via EGMS portal specifying product/quantity/shipment details, customs integration: EGMS integrates with KRA Customs Simba system sharing stamp data for clearance validation, no stamps = no clearance policy enforced at borders/ports, shipment tracking: GPS trackers on imported containers monitoring from port to bonded warehouse, duty calculation: EGMS provides stamp application data to customs for excise duty calculation accurate taxation, compliance reporting: importers report stamp usage quarterly reconciliation ordered vs. applied detecting smuggling or diversion). All Distribution Centers: Wholesalers and regional distribution hubs (distribution center registration: location/capacity/security features/operating licenses verified, stock-in tracking: scans stamps received from manufacturer or importer capturing quantity/supplier/invoice, stock-out tracking: scans stamps shipped to retailers capturing destination/buyer/quantity, inventory reconciliation: EGMS compares stock-in - stock-out = expected balance vs. physical count detecting theft/damage/misplacement, geofenced zones: 100m radius around distribution center tracking stamps entering/exiting facility preventing unauthorized removal, API integration: large distributors integrate ERP systems SAP/Oracle automated data feed reducing manual entry errors, wholesaler reporting: mandatory weekly reports for licensed wholesalers failing to report = stamp supply suspension). Evaluation Ensures Complete Proposals: Mandatory requirements (proposals must address all components: automated lines/manual lines/importers/distribution centers, incomplete proposals rejected during technical evaluation, scoring matrix awards points for comprehensiveness: partial solution scores 50-70%, complete solution scores 90-100%, bidders incentivized to propose end-to-end solution not cherry-pick easy components), proof of capability (bidders must demonstrate experience with similar complexity: automated + manual lines, multi-stakeholder systems importers/distributors/enforcement, large scale 1,000+ sites, reference projects GST Maharashtra 50K manufacturers proves Devharsh capability), detailed costing (bill of materials must itemize: edge servers × 1,800 units, GPS trackers × 500 units, tablets × 1,000 units, line-item pricing enables KRA to verify completeness and fairness). Technologies Included: - Hardware: Edge servers (1,800+ units industrial PCs fanless/SSD/VPN), GPS trackers (500+ units for shipment tracking 4G LTE connectivity), rugged tablets (1,000+ units for manual line data entry Android/iOS), UV/IR scanners (200+ units for enforcement officers multi-spectral verification), retail scanners (100+ units for pilot retailers Zebra/Honeywell barcode scanners), servers (Kubernetes cluster 30+ nodes AWS/Azure cloud auto-scaling), networking (VPN concentrators, firewalls, load balancers), HSMs (2 units Thales Luna FIPS 140-3 Nairobi + Mombasa). - Software: EGMS platform (10 applications: 7 web portals + 3 mobile apps, 100+ microservices, AI/ML models, GIS platform, data lake), integration middleware (API gateway Kong/Apigee, message queue Kafka/RabbitMQ, ETL tools Talend/Apache NiFi), databases (PostgreSQL production, MongoDB logs, Redis cache, PostGIS geospatial, InfluxDB time-series), monitoring (Prometheus metrics, Grafana dashboards, ELK Stack logs, New Relic APM), security (SIEM Splunk/QRadar, WAF Cloudflare/AWS WAF, vulnerability scanners Nessus/Snyk/SonarQube/OWASP ZAP), productivity (Jira project management, Confluence documentation, GitLab source control, Slack collaboration). - Services: Installation and commissioning (1,800 manufacturer sites, 500 distribution centers, 200 enforcement offices), training (200 KRA staff, 1,800 manufacturers, 2,000 enforcement officers), support (24/7 helpdesk, quarterly on-site visits, monthly software releases), maintenance (5-year AMC hardware warranty + software updates + security patches).
SeQR EMS adheres to comprehensive independent revenue verification: a. Independent Verification Framework: - Third-Party Auditor Selection: KRA appoints Big 4 accounting firm (PwC, Deloitte, EY, or KPMG, selected via competitive RFP process ensuring independence and capability, auditor must have: revenue assurance experience preferably tax/customs/excise, econometric modeling capabilities to isolate EGMS impact from external factors, Kenya presence with local staff understanding Kenyan market dynamics, no conflicts of interest not auditing Devharsh or JV partner preventing bias), contract term (5-year contract aligned with EGMS contract, annual fee KES 50-100M estimated covering quarterly verification + annual market studies + dispute resolution). - Transparent Verification: Open methodology (jointly agreed between KRA, Devharsh, and auditor documented in Verification Framework signed by all parties, methodology published preventing future disputes about calculation methods, peer review by independent academic expert from University of Nairobi/Strathmore validating statistical rigor), audit trail (all verification workpapers preserved for 7 years enabling future audits/disputes to review calculations, data sources documented preventing black-box analysis KRA/Devharsh cannot challenge). b. Methodology - Comprehensive Verification Approach: - Year 0 Baseline Establishment: Pre-EGMS data collection (Month -3 before go-live: conduct comprehensive market study establishing illicit trade baseline using WHO TaXSim model + OECD methods + KRA internal data triangulation, excise collections baseline: average monthly excise collections prior 12 months adjusted for seasonality, manufacturer compliance baseline: estimated compliance rate 70-75% via sample audits + surveys, all baselines documented in Baseline Report signed by KRA/Devharsh/auditor preventing future revisionism). - Quarterly Verification of Excise Collections: Data reconciliation (auditor accesses KRA financial systems iTax extracting actual excise collections monthly, compares actual vs. baseline trend detecting increases attributable to EGMS, adjusts for external factors: GDP growth/inflation/tax rate changes/enforcement intensity using regression models, isolates EGMS impact estimating counterfactual "what would collections have been without EGMS"), statistical significance testing (calculates 95% confidence intervals around estimated impact, only statistically significant increases credited to EGMS preventing noise from being interpreted as success, reports include: point estimate KES 1.5B increase, confidence interval KES 1.2-1.8B, p-value <0.05 indicating statistical significance). - Annual Market Prevalence Studies: WHO-approved methodology (TaXSim Tobacco Tax Simulation Model estimates illicit market share comparing legal sales vs. consumption survey data gap = illicit, OECD methods comparing licit production/imports vs. apparent consumption from household surveys, auditor conducts consumer surveys 5,000+ households representative sample stratified by region/income, field audits 500+ retail outlets checking for unstamped/counterfeit products), year-over-year comparison (Year 1 study illicit share 18.5% vs. Year 0 baseline 20% = 1.5 percentage point reduction = 7.5% relative reduction, Year 2 study 16.8% = cumulative 16% reduction trending toward 30% target Year 3). - External Econometric Model: Isolating EGMS impact (difference-in-differences: compares Kenya excise trend before/after EGMS controlling for counterfactual trend using EAC countries Uganda/Tanzania as control group, regression analysis: models excise collections as function of EGMS dummy variable + tax rates + GDP + enforcement budget + seasonal indicators, EGMS coefficient indicates isolated impact holding other factors constant, synthetic control: constructs synthetic Kenya using weighted average of EAC countries + Ethiopia + Zambia matching pre-EGMS characteristics estimating counterfactual post-EGMS trend, all 3 methods triangulated providing robust estimate range). c. Dispute Resolution - Clear Mechanisms: - Revenue Tier Classification Disputes: Tiered payment structure (EGMS contract includes revenue uplift bonuses: 10-15% increase Tier 1 bonus KES 20M, 15-20% increase Tier 2 bonus KES 40M, >20% increase Tier 3 bonus KES 60M, dispute arises if KRA/Devharsh disagree on tier classification e.g., Devharsh claims 16% increase Tier 2 but KRA calculates 14.5% Tier 1), auditor binding decision (independent auditor reviews both calculations identifying errors: Devharsh used gross collections KRA used net collections adjusted for refunds, auditor determines correct methodology per contract, issues binding decision within 30 days preventing prolonged disputes delaying payments), appeal process (either party can appeal auditor's decision to independent arbitrator within 14 days, arbitrator reviews auditor's workpapers + party submissions, issues final binding decision within 60 days, arbitrator fees split 50/50 discouraging frivolous appeals). d. Illicit Trade Measurement Dispute Resolution: - WHO TaXSim Model Standard: Mandatory methodology (contract specifies WHO TaXSim or equivalent as standard for illicit trade measurement, prevents disputes about methodology choice, TaXSim inputs: legal sales from EGMS stamp issuance data, consumption from household surveys, tax rates/prices from KRA/KNBS, outputs: estimated illicit market share with confidence intervals), equivalent methods (if TaXSim unavailable OECD methods acceptable: top-down comparing aggregate supply vs. demand, bottom-up comparing individual product sales vs. consumption, both peer-reviewed internationally recognized preventing arbitrary methods). - Independent Technical Panel for Disputes: Panel composition (3 members: 1 KRA representative senior economist/tax expert, 1 vendor representative Devharsh data scientist/economist, 1 neutral academic expert from recognized university Nairobi/Strathmore tenured professor with econometrics/tax policy expertise, academic serves as tiebreaker if KRA and vendor disagree), dispute trigger (if auditor's illicit trade estimate disputed e.g., shows 25% reduction but Devharsh believes 30% or KRA believes 20%, either party can request panel review within 14 days paying KES 2M fee discouraging frivolous challenges), panel process (panel reviews auditor's methodology + data + analysis, conducts independent re-analysis if needed, issues written opinion within 60 days explaining findings/reasoning, decision is binding on all parties final no further appeal), transparency (panel's written opinion published redacting commercially sensitive data, builds jurisprudence for future disputes, promotes fairness and consistency). Verification Schedule: Quarterly reviews (auditor reviews excise collection data quarterly comparing actual vs. baseline trend, interim reports flag issues early enabling mid-course corrections, formal verification annual based on full 12-month data), annual market studies (conducted in Q4 September-October during low-illicit-trade season more representative, final report February following year allows 4-month analysis period, results inform Year+1 performance targets adjusting for new baseline). Performance Payment Linkage: Auditor verification gates payments (Devharsh submits annual performance claim "achieved 15% excise increase Tier 2 bonus KES 40M", KRA withholds payment pending auditor verification, auditor issues verification report within 90 days confirming/adjusting claim, KRA pays verified amount within 30 days, prevents premature payments for unverified performance), claw-back provisions (if Year 2 verification discovers Year 1 bonus overpaid e.g., claimed 16% but actual 14%, Devharsh refunds overpayment KES 20M, prevents gaming via inflated claims knowing verification delayed).
SeQR EMS independent auditor uses WHO TaXSim model or equivalent for market studies to measure illicit trade reduction with established dispute resolution process for any challenges to revenue tier classification (vendor submits objection with supporting data within 30 days, auditor reviews evidence, conducts additional testing if needed, issues final binding decision within 60 days, escalation to arbitration only if procedural irregularities proven), ensuring fair and transparent performance measurement aligned with international best practices.